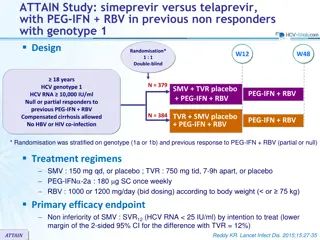
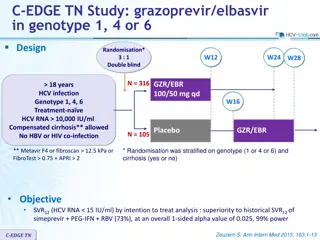
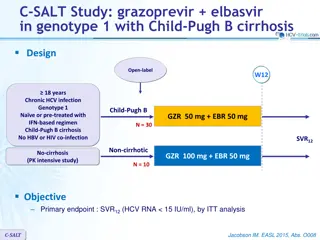
Comparison of SOF+RBV vs PEG-IFN-2a+RBV for HCV Genotype 2 and 3 Treatment
FISSION Study compared the efficacy of SOF+RBV and PEG-IFN-2a+RBV for HCV genotypes 2 and 3 in treatment-naive patients with chronic HCV infection. The study included 256 participants in the SOF+RBV group and 243 in the PEG-IFN-2a+RBV group. The primary objective was to determine the non-inferiority of SOF+RBV in achieving SVR12. Results showed higher SVR rates in the SOF+RBV group, with fewer virologic breakthroughs during treatment. Factors associated with SVR12 included genotype, cirrhosis status, baseline HCV RNA levels, and RBV exposure. Resistance testing showed no mutations associated with decreased SOF susceptibility. Overall, SOF+RBV demonstrated better efficacy and tolerability compared to PEG-IFN-2a+RBV.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
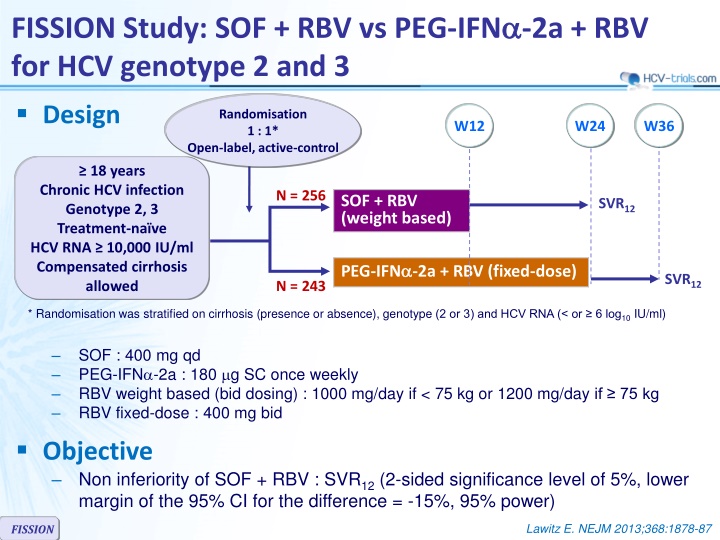
FISSION Study: SOF + RBV vs PEG-IFN -2a + RBV for HCV genotype 2 and 3 Design Randomisation 1 : 1* Open-label, active-control W12 W24 W36 18 years Chronic HCV infection Genotype 2, 3 Treatment-na ve HCV RNA 10,000 IU/ml Compensated cirrhosis allowed N = 256 SOF + RBV (weight based) SVR12 PEG-IFN -2a + RBV (fixed-dose) SVR12 N = 243 * Randomisation was stratified on cirrhosis (presence or absence), genotype (2 or 3) and HCV RNA (< or 6 log10 IU/ml) SOF : 400 mg qd PEG-IFN -2a : 180 g SC once weekly RBV weight based (bid dosing) : 1000 mg/day if < 75 kg or 1200 mg/day if 75 kg RBV fixed-dose : 400 mg bid Objective Non inferiority of SOF + RBV : SVR12 (2-sided significance level of 5%, lower margin of the 95% CI for the difference = -15%, 95% power) Lawitz E. NEJM 2013;368:1878-87 FISSION
FISSION Study: SOF + RBV vs PEG-IFN -2a + RBV for HCV genotype 2 and 3 Baseline characteristics and patient disposition SOF + RBV 12 W N = 256 48 33% 87% / 5% 28 1%* / 27% / 71% 42% 6.0 0.8 57% 20% 11 3 / 1 / 2 246 239 PEG-IFN + RBV 24W N = 243 48 36% 87% / 2% 28 28% / 72% 44% 6.0 0.8 65% 21% 54 26 / 17 / 5 233 225 Mean age, years Female Race : white/black Body mass index, mean HCV genotype 1 / 2 / 3 IL28B CC genotype HCV RNA log10IU/ml, mean (SD) HCV RNA 800,000 IU/ml Cirrhosis Discontinued treatment, N For AE / for virologic failure / lost to follow-up Returned for post-treatment W4 visit Returned for post-treatment W12 visit * Excluded from efficacy analysis Lawitz E. NEJM 2013;368:1878-87 FISSION
FISSION Study: SOF + RBV vs PEG-IFN -2a + RBV for HCV genotype 2 and 3 HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml SOF + RBV PEG-IFN + RBV SVR12by genotype and cirrhosis 99 98 97 100 89 78 74 74 74 72 75 67 67 67 63 56 47 50 38 25 0 250 236 253 243 253 243 253 243 70 67 183 176 204 193 49 50 W4 W12 W4 W12 Genotype 2 Genotype 3 No cirrhosis Cirrhosis During treatment Post treatment (SVR) Lawitz E. NEJM 2013;368:1878-87 FISSION
FISSION Study: SOF + RBV vs PEG-IFN -2a + RBV for HCV genotype 2 and 3 Virologic breakthrough during treatment 1 in SOF + RBV group vs 18 (7%) in PEG-IFN + RBV group Relapse in patients with HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml at end of completed treatment 74/249 (30%) in SOF + RBV group vs 46/217 (21%) in PEG-IFN + RBV group Multivariate analysis of factors associated with SVR12 in SOF + RBV group OR (95% CI) p Genotype 2 (vs 3) 42.49 (9.54 189.2) < 0.0001 Cirrhosis (no vs yes) 2.94 (1.38 6.26) 0.005 Baseline HCV RNA < vs 6 log10 IU/ml RBV exposure, mg/kg/day 2.33 (1.24 4.37) 0.009 1.26 (1.09 1.46) 0.002 Resistance testing (sequencing) in SOF + RBV group 74 relapses : No SOF-associated mutation (S282T) No change in susceptibility to SOF in patients with NS5B substitutions Lawitz E. NEJM 2013;368:1878-87 FISSION
FISSION Study: SOF + RBV vs PEG-IFN -2a + RBV for HCV genotype 2 and 3 Adverse events, n (%) PEG-IFN -2a + RBV 24W N = 243 SOF + RBV 12W N = 256 AE leading to treatment discontinuation 3 (1%) 26 (11%) Serious adverse event 7 (3%) 3 (1%) AE occurring in > 15% in either group Fatigue Headache Nausea Insomnia Decreased appetite Influenza-like illness Chills Rash Diarrhea Pruritus Myalgia Irritability 36% 25% 18% 12% 7% 3% 3% 9% 9% 7% 8% 10% 55% 44% 29% 29% 18% 18% 18% 18% 17% 17% 16% 16% Lawitz E. NEJM 2013;368:1878-87 FISSION
FISSION Study: SOF + RBV vs PEG-IFN -2a + RBV for HCV genotype 2 and 3 Summary In this open-label, randomised trial of previously untreated patients with genotype 2 or 3 infection, the rate SVR12 was the same among patients who were assigned 12 weeks of SOF + RBV or 24 weeks of PEG-IFN + RBV (67% in each group) In genotype 2, SVR12 was higher with SOF + RBV (97% vs 78%) In genotype 2, SVR12 was similarly low in both groups (56% vs 63%) SOF + RBV was associated with fewer adverse events than PEG-IFN + RBV Influenza-like constitutional symptoms and neuropsychiatric events were less common among patients receiving SOF + RBV than among those receiving PEG- IFN + RBV. Although the rates of anemia was similar in both groups, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were not observed in the SOF + RBV group No virologic resistance was detected in patients who did not have a sustained virologic response Lawitz E. NEJM 2013;368:1878-87 FISSION