Changes in State of Matter
Explore the concepts of solids, liquids, and gases and how matter changes states through the addition or removal of thermal energy. Discover the properties and behaviors of different states of matter, from solids with fixed shapes to gases with high energy particles. Dive into demonstrations and resources to deepen your understanding of kinetic energy and state changes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
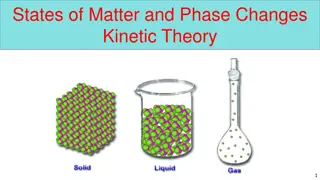
Lets Review! Solids Have a definite shape and a definite volume Particles are packed very close together in a fixed position Particles vibrate in place - low energy Liquids Has a definite volume, but no shape Liquids take the shape of container particles are freely moving, but still packed close together - medium energy Viscosity- a liquids resistance to flowing Gases Gases have no definite volume or shape Particles can spread out or be packed close together Particles bounce around - high energy
Kinetic Energy and Matter All matter is made up of particles that are moving constantly When heat is added, the particles move faster When the particles move faster, more space is added between the atoms As this happens, the state of matter begins to change When heat leaves the substance, the particles slow down and get closer together
Solids expand when they are heated In the picture to the left, some workers are trying to reconnect two rails that have separated due to the extreme cold. To fix the problem, the workers have lit an oil-soaked rope that lies next to the track. The heat of the fire will cause the tracks to expand so that they can be reconnected once again.
Mystery Mud http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/phy03.sci.phy s.matter.mud/mystery-mud-exploring-changes-in-states- of-matter/ What properties did the mud have of a liquid? What properties did the mud have of a solid?
States of matter demo https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/states-of-matter-basics
How does matter change from one state to another? A change in thermal energy, or temperature, change a substance from one state of matter to another by adding or taking away energy from the particles of matter https://www.brainpop.com/science/matterandchemistry/matterchangingstates/ After the video, we will fill out the graphic organizer that goes along with the video and answer the quiz questions
Changes in Matter Melting- the change from a solid to a liquid as the particles gain energy Freezing- the change from a liquid to a solid as the particles lose thermal energy Vaporization-the change from a liquid to a gas Evaporation- vaporization that takes place just at the surface Boiling-when liquid changes to a gas below the surface Condensation- when particles of a gas lose enough energy to become a liquid Sublimation-particles of a solid turn directly into a gas and pass over the liquid state