Kinetic Theory of Matter and Phases
Explore the fundamental concepts of the Kinetic Theory of Matter, including the three pillars of kinetic energy and forces of attraction, which determine the states of matter like solid, liquid, gas. Learn about temperature, phase changes, and the phases of matter, emphasizing the role of kinetic energy and atomic forces.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
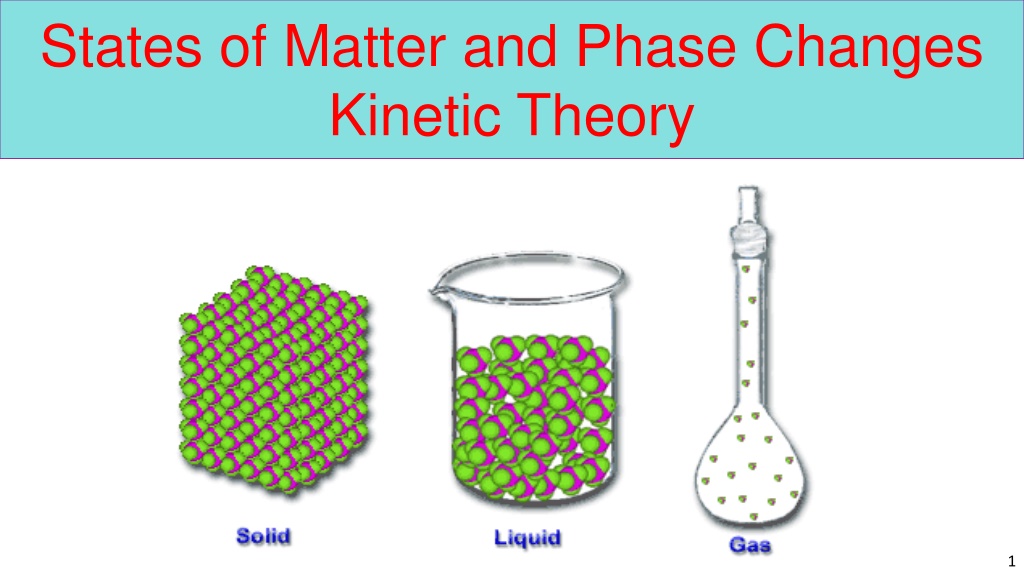
States of Matter and Phase Changes Kinetic Theory 1
Kinetic Theory Forces of Attraction States of Matter Phase Change Solid, Liquid, Gas Temperature Evaporation Condensation Boiling Melting Sublimation Deposition 2
Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory The 3 pillars of KE The 3 pillars of KE 1. All matter is composed of small particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). 2. They are in constant, random motion. 3. These molecules constantly collide with each other and their surroundings. 3
Forces of Attraction Forces of Attraction Kinetic Energy Attraction Forces According to the kinetic theory of matter, the state (phase) of a substance is determined by the interplay of two opposing forces within a substance. Kinetic energy pulls particles apart while forces of attraction hold them together. 4
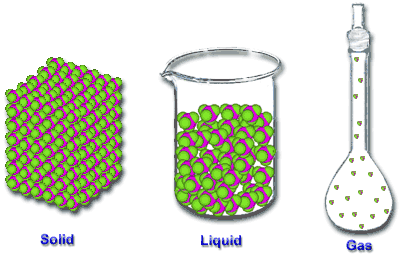
Phases of Matter Phases of Matter The phases or states of matter can exist in four phases; solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Whether a substance is a solid, liquid or gas depends on the kinetic energy and the atomic forces of attraction holding the particles together. 5
Temperature Temperature Definition: is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substances. The specific form of KE concerning Kinetic Theory of Matter is thermal energy. Thermal energy is particle motion at the molecular scale. Temperature is only the measure of this. 6
Temperature cont. Temperature cont. During a phase change, temperature of the matter remains constant. It does not change. However when matter is a particular state say gas the temperature can range dramatically. 7
Phase Change Phase Change Definition: this is the transformation of one state of matter into another. Relative thermal energy is what causes matter to change phases. Temperature is the effect that we measure not what drives the change. 8
Evaporation Evaporation Definition: the change from a liquid to a gas at the surface of a liquid. 9
Condensation Condensation Definition: the phase change of a substance from a gas or vapor to a liquid. Ex: cloud formation / What has to happen ? Relative humidity rises to 100% Saturation of the air occurs Condensing nuclei must be present 10
Boiling Boiling Definition: the action of bringing a liquid to the temperature at which it bubbles and turns to vapor. Liquid to gas. Ex: (for fresh water at sea level) at 212 F (100 C). 12
Melting Melting Definition: the process of becoming liquid or to be liquefied by heat. Solid to liquid. 13
Sublimation Sublimation https://youtu.be/7_p9LOTUIDQ Defined: is the process by which a solid changes phase and turns directly into a gas without passing through the liquid phase. Ex: dry ice, snow high up in the mtns https://youtu.be/6JzQ08AGuhI <= dry ice video 14
Deposition Deposition (precipitation) (precipitation) Defined: is the process by which a gas changes phase and turns directly into a solid without passing through the liquid phase. Ex: hail, frost, snow https://youtu.be/rM04U5BO3Ug <= nitrogen gas to nitrogen solid 15