Analog and Digital Communications Concepts
Exploring the differences between analogue and digital signals, this content presents a comprehensive overview. It covers the definitions of analog, the prevalence of analog signals in our surroundings, and the advantages of digital communication such as error correction, encryption, and data processing. The content highlights the reasons why digital communication is preferred over analog and explains the benefits in terms of speed, reliability, cost, and efficiency.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
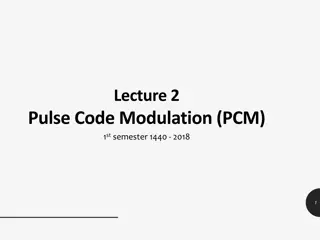
Digital Communications Concepts Presented by Dr. Julius Butime Head Engineering Training AFRALTI AFRALTI 1
Outline Analogue and Digital: what do we really mean? Why digital AFRALTI 2
Analogue and Digital: what do we really mean? Full Definition of ANALOG a : of, relating to, or being a mechanism in which data is represented by continuously variable physical quantities b : of or relating to an analog computer c : being a timepiece having hour and minute hands AFRALTI 3
Analogue and Digital: what do we really mean? AFRALTI 4
The world around us is mostly composed of analog signals. Analog refers to something that is continuous in itself. TIME Music is a good example of an analogue signal. AFRALTI 5
Analogue AFRALTI 6
Analogue and Digital: what do we really mean? Digital comes from the Latin word digit or digitus meaning finger of, relating to, or being data in the form of especially binary digits <digital images> <adigit al readout>; especially : of, relating to, or employing digital communications signals <adigital broadcast> compare ANALOG 2 AFRALTI 7
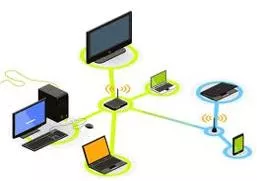
Communication Block AFRALTI 8
Why digital Speed Error correction/detection Better encryption algorithms: Can not be done in analog communication More reliable data processing Easily reproducible designs Reduced cost Easier data multiplexing Facilitate data compression AFRALTI 9
Why digital Messages storage is much longer Distance is not an issue Low cost Reduces paper Translation of content is a lot easier AFRALTI 10
Why digital Technology enabler - Email - Sms - MPESA - Social media - Video streaming - E commerce - Video conferencing AFRALTI 11
Cons Social media Data security Environmental issues Power requirement Sociability AFRALTI 12
Questions AFRALTI 13

 undefined
undefined