Understanding Motor Proteins and Cytoskeletal Dynamics in Cell Biology
Motor proteins, such as myosin, kinesin, and dynein, utilize chemical energy to move along cellular tracks, influencing processes like muscle contraction, organelle movements, and cellular migration. With the ability to translocate using ATP hydrolysis, these proteins play crucial roles in various c
5 views • 14 slides
Understanding Syrups: Types, Formulations, and Storage Considerations
Syrups are sweet, viscous liquids used in pharmaceutical preparations. They can be non-medicated for flavoring or medicated for therapeutic purposes. There are sugar-based and sugar-free syrups, with sucrose preferred for its purity and handling ease. Preservatives like benzoate and sorbic acid are
4 views • 16 slides
Assessment and Control of Sugar Production Losses in Pakistan
Maximizing sucrose recovery in sugar production is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and profitability. This study focuses on identifying and managing operational losses within the sugar production process in Pakistan, categorizing losses as determined (easily measurable) and undetermine
2 views • 16 slides
Understanding Digestion and Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract are crucial processes for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller compounds that can be absorbed by the body. Carbohydrates undergo hydrolysis to convert into monosaccharides, fats are broken down from triglycerides, and pro
1 views • 22 slides
Understanding Carbohydrates in Living Organisms
Carbohydrates, along with proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, are essential macromolecules in living organisms. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Carbohydrates provide the main energy source for living things, with examples including glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
0 views • 58 slides
Understanding Movement of Substances Through Cell Membrane
Substances enter and leave cells through diffusion and osmosis processes, driven by concentration gradients. The cell membrane plays a crucial role in selectively allowing substances to pass, ensuring cell survival. Osmosis can be demonstrated using Visking tubing, showing water molecules moving whi
0 views • 15 slides
Isolation of AM Fungi by Wet Sieving and Sucrose Gradient Methods
Wet sieving is a popular technique to isolate different sizes of spores from soil samples. Developed by Gerdemann and Nicolson in 1963, this method involves passing an aqueous suspension through different sieves to collect spores of varying sizes. The process includes agitating the soil-water mixtur
0 views • 14 slides
The Chemistry of Soaps and Emulsions: An Overview
Explore the fascinating world of soap-making and emulsions' chemistry. Discover how soaps are formed through alkaline hydrolysis, the structure of soap molecules, and how they clean oily stains effectively. Learn about emulsions, emulsifiers, and the science behind soap production.
1 views • 24 slides
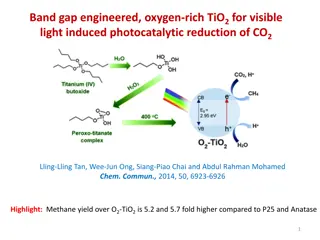
Band Gap Engineered Oxygen-Rich TiO2 for Visible Light-Induced Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2
Band gap engineering and oxygen-rich modifications in TiO2 have been explored for visible light-induced photocatalytic reduction of CO2. The engineered O2-TiO2 photocatalyst exhibited significantly higher methane yield compared to conventional TiO2 types. The preparation involves hydrolysis of titan
1 views • 17 slides
Dried Ice Cream Mix in Dairy Technology: Advancements and Manufacturing Process
Ice cream manufacturing faces challenges during lean seasons due to milk shortages. Dried ice cream mix powder offers a solution with benefits like reduced storage space, ease of packaging, and lower transportation costs. The composition includes milk fat, protein, sucrose, stabilizers, and emulsifi
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Metabolic Pathways in Microbes
Metabolism in living organisms involves anabolism and catabolism, where anabolism generates essential biomolecules for growth using energy, while catabolism breaks down nutrients for energy release. Anabolic processes include synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and other gro
7 views • 24 slides
Sugar Processing Control Formulas and Parameters
Explore the key concepts of crystal content, exhaustion, and the SJM formula in sugar processing control. Learn how to calculate crystal content, manage viscosity limitations, maximize sucrose recovery, and apply the SJM formula for sucrose recovery percentage. Understand the factors affecting exhau
1 views • 8 slides
Overview of Ammonium Chloride: Properties, Preparation, and Uses
Ammonium Chloride, with the formula NH4Cl, is a compound containing not less than 99.5% NH4Cl. It is prepared commercially by neutralizing ammonia with hydrochloric acid or treating ammoniacal gas liquors with lime. The compound is essential for maintaining acid-base equilibrium, acts as an expector
2 views • 4 slides
Understanding the Integration of Carbohydrate, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism
The integration of metabolism involving carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins can be divided into three stages: hydrolysis to simpler units, preparatory stage, and oxidative stage. In the hydrolysis stage, complex polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are broken down to simpler forms. The preparatory
3 views • 13 slides
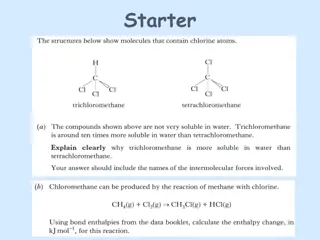
Qualitative Analysis Experiments and Bond Enthalpy
Qualitative tests are conducted on an unknown compound to identify it, followed by an experiment analyzing the rate of hydrolysis in different haloalkanes. Experiments involving silver nitrate and haloalkanes provide insights into the bond enthalpies of carbon-halogen bonds. Suggestions on modifying
0 views • 7 slides
Synthesis of Salicylic Acid: Theory, Derivatives, and Applications
Salicylic acid is synthesized from methyl salicylate through ester hydrolysis with aqueous alkali. It is a versatile compound used in organic synthesis, as a plant hormone, and derived from salicin metabolism. The derivatives of salicylic acid can minimize gastric disturbances and enhance therapeuti
4 views • 12 slides
Understanding Translocation in the Phloem
This lecture explores the process of translocation in the phloem, supported by evidence from studies such as aphid experiments, ringing experiments, and the use of radioactive isotopes. It delves into the materials translocated in phloem sap, including water, sucrose, non-reducing sugars, nitrogen c
5 views • 18 slides
Organic Chemistry Concepts and Reactions
Learn about reactions involving silver bromide, nucleophilic substitution to prepare ethers, steam and acid catalyst reactions, reaction mechanisms using curly arrows, allyl bromide reaction with sodium hydroxide, alcohol synthesis, alkaline hydrolysis, and bromine water identification. Understand m
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Sucrose Hydrolysis and Reducing Sugars in Carbohydrate Chemistry
This content delves into the mechanisms of sucrose hydrolysis through non-enzymatic and enzymatic processes, highlighting disaccharides like sucrose, lactose, and maltose. It explores the significance of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrate structures and discusses the reducing capacity of sugars such a
7 views • 16 slides
Understanding Nonelectrolytes in Solutions
Physical properties of substances are classified into colligative, additive, and constitutive properties. Colligative properties depend on the number of particles in a solution and are similar for different nonelectrolytes. Additive properties are based on the total contribution of atoms, while cons
1 views • 14 slides
Experimenting with Supersaturated Solutions: Rock Candy Creation
Exploring the phenomenon of supersaturated solutions through an experiment creating rock candy. The solubility of sucrose in water is observed at different temperatures, showcasing how more sugar can dissolve in a hot solution than in a cold one. The process of supersaturation and crystallization is
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Proteins: Functions, Structure, and Breakdown
Explore the world of proteins, from their essential functions in living organisms to the chemistry of amino acids that form them. Learn how proteins are structured, the significance of amide links, and how they are broken down through hydrolysis. Delve into the importance of essential amino acids an
0 views • 17 slides
Determination of Ester Hydrolysis Constant Rate by Conductivity Measurement
This study focuses on determining the ester hydrolysis constant rate through conductivity measurement, presenting a second-order reaction example. Conductivity meter is utilized for accurate monitoring. The procedure involves utilizing equal concentrations of ester and sodium hydroxide, measuring co
0 views • 6 slides
Amino Acid Absorption Mechanisms in Small Intestine
Amino acid absorption in the small intestine is an active process requiring energy derived from ATP hydrolysis. It involves two main mechanisms: carrier proteins transport system and glutathione transport system. The carrier proteins transport system uses ATP energy for absorption, while glutathione
0 views • 18 slides
Colorimetric Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide Using Magnetic Rod-Based Metal-Organic Framework Composites
Nanomaterials, particularly magnetic rod-based metal-organic frameworks composites, are gaining attention for their exceptional properties and various applications in different fields. This study by Benjamin Edem Meteku focuses on using these composites for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxid
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Evaporation Principles in Sugar Processing
Evaporation plays a crucial role in sugar processing by removing water from solutions to concentrate sucrose. This process involves boiling liquor, vaporizing water through heat, and crystallizing sucrose. Learn about the boundary between evaporation and sugar boiling, quantity of water to be evapor
5 views • 38 slides
Understanding Carbohydrates: Composition, Structure, and Function
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio. Monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, and galactose are carbohydrate monomers, while polysaccharides like lactose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, and glycogen are carbohydrate polymers. The chemical formula for glucose
0 views • 8 slides
Assay of Aspirin by Indirect Acid-Base Titration
Indirect titration, also known as residual titration, is an analytical technique used to determine the weight of an unknown sample by employing excess standard solution. In the case of aspirin, which is a weak acid undergoing slow hydrolysis, back titration with NaOH and HCl is utilized to overcome
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Active Transport of Molecules: Driven by ATP Hydrolysis
Active transport, fueled by ATP hydrolysis, facilitates the movement of molecules against their concentration gradients, essential for processes like ion pumping across membranes. The Na+-K+ pump, a prime example, utilizes ATP to transport Na+ and K+ ions across cellular membranes, maintaining impor
0 views • 23 slides
pH Effects on Bacterial Growth: The Influence of Environment
This study explores the impact of pH levels on bacterial growth, highlighting the minimum, optimum, and maximum pH requirements for different categories of microbes - acidophiles, neutrophiles, and alkaliphiles. It delves into the consequences of pH variations on cellular processes like DNA stabilit
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Salt Hydrolysis in Chemistry
Salt hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a salt reacts with water to produce an acid and a base. This reaction occurs when the cation or anion of the salt interacts with water, resulting in either an acidic or basic solution. The type of hydrolysis depends on the strength of the acid and base
0 views • 6 slides
Enzymatic Digestion of Fat by Pancreatic Lipase
The experiment focuses on studying the enzymatic digestion of fat by pancreatic lipase. It covers the structure of triglycerides, the role of lipase enzyme in hydrolyzing triglycerides to release fatty acids, and the general hydrolysis process. The aim is to investigate the effects of lipase enzyme
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Mole Calculations and Its Applications
Dive into the world of mole calculations with Chapter 5 homework assignments, exploring concepts such as mole weight, the dozen concept, and sweet mole calculations. Discover the significance of moles in chemistry and how they relate to everyday scenarios like calculating the weight of eggs and unde
1 views • 28 slides
Obtention of Cellulose Nanofiber from Almond Shell Using Different Chemical Treatments
This study conducted in Trabzon, Turkey, focused on obtaining cellulose nanofibers from almond shells through various chemical treatments. Different procedures involving alkaline solutions, bleaching, hydrolysis, and acetylation were used to remove lignin content and achieve optimal crystallinity. A
0 views • 7 slides
Essential Nutrients for Plant Tissue Cultures: A Comprehensive Guide
The composition of culture media for plant tissue cultures includes inorganic and organic nutrients, sources of energy like sucrose and amino acids, and essential macro and micronutrients. Providing gas exchange, waste removal, and growth regulators, the medium supports plant growth by offering acce
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Glycosides: A Comprehensive Overview
Glycosides are compounds that undergo hydrolysis to yield sugar and non-sugar parts. The aglycone is also known as the genin, while the sugar part is the glycone. They are soluble in water and alcohols, with different solubility properties for glycone and aglycone parts. Glycosides can be hydrolyzed
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Carbohydrates: Qualitative Tests and Classification
Carbohydrates serve as a crucial energy source and structural element in living organisms. This lab explores the qualitative tests and classification of carbohydrates, including monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Learn about the properties and distinctions of diff
0 views • 13 slides
Qualitative Tests of Lipids and Derived Lipids Overview
Qualitative tests of lipids distinguish between oil, neutral fat, saturated fatty acids, and unsaturated fatty acids using methods like the copper acetate test. Derived lipids include substances like cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins that are either soluble in lipids or derived from lipids throug
0 views • 14 slides
Polymer Reactivity and Modification: Synthesis and Reactions
Reactions of polymers involve the synthesis of new polymers through modification, such as esterification of cellulose, crosslinking of polyisoprene, hydrolysis of poly(vinyl acetate), and chlorination of polyethylene. Polymer reactions utilize chemical processes to create new materials, carriers, or
0 views • 48 slides
In Vitro Culture of Ovule and Ovary for Haploid Plant Production
In vitro culture of unpollinated ovaries and ovules offers an alternative method for haploid plant production. This process involves isolating and culturing ovules in a chemically defined nutrient medium to understand zygote development and embryo maturation stages. Techniques for collecting, prepar
0 views • 34 slides