Overview of Ammonium Chloride: Properties, Preparation, and Uses
Ammonium Chloride, with the formula NH4Cl, is a compound containing not less than 99.5% NH4Cl. It is prepared commercially by neutralizing ammonia with hydrochloric acid or treating ammoniacal gas liquors with lime. The compound is essential for maintaining acid-base equilibrium, acts as an expectorant and diuretic, and undergoes hydrolysis to yield ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen chloride. Various methods for its assay, including precipitation titration and acid-base titration techniques, are highlighted in this document. Additionally, its properties, solubility, and uses in various applications are discussed.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
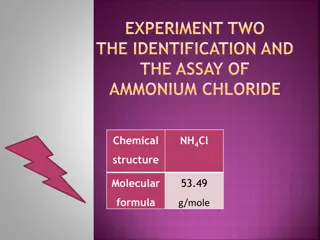
AMMONIUM CHLORIDE Formula- NH4Cl It is having not less than 99.5 % of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) which is calculated with reference to substance dried over silica gel for 4 hrs. Preparation: 1.Commercially, it is prepared by neutralizing ammonia with hydrochloric acid (HCl). The solution is evaporated till crude, vitreous, crystalline mass of ammonium chloride is obtained. NH3 + HCl NH4Cl The crude salt is purified either by crystallization or sublimation. 2.It is also prepared by treating ammoniacal gas liquors with lime and liberated NH3 is passed into HCl solution. The crude ammonium chloride obtained is known commercially as Sal ammoniac and occurs as tough, crystalline masses. 3.Ammonium chloride is also produced by heating ammonium sulphate with sodium chloride.
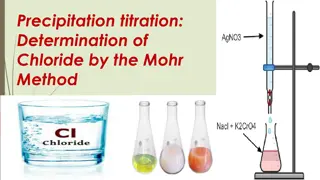
2 NaCl + (NH4)2SO4 2 NH3+ 2 HCl+ Na2SO4 NH3+ HCl NH4Cl Assay: It was previously assayed by precipitation titration by using Volhard s method. This method is as follows: An accurately weighed quantity (0.2g) of Ammonium chloride is dissolved in 40ml of water. Then the solution is acidified with nitric acid(3ml).the solution is shaken vigorously after adding 50ml of N/10 silver nitrate and 5ml of nitrobenzene. The excess of silver nitrate is titrated with N/10 ammonium thiocyanate ,using ferric ammonium sulphate(2ml) as an indicator. NH4Cl+AgNO3 NH4NO3+AgCl Each ml of 0.1N AgNO3 0.005349g of NH4Cl Now it is assayed by acid-base titration technique, which is simpler and cheaper(no silver nitrate required).About 0.1g of NH4Cl sample accurately weighed is kept in a conical flask, about 50ml of water is added to dissolve it followed by 5ml of neutralized formaldehyde solution. Formaldehyde solution may have a small amount of formic acid formed due to atmospheric oxidation. This should be carefully neutralized with dilute sodium hydroxide solution, using phenolphthalein as an indicator. There should be no excess alkali in this reagent. After keeping aside for a couple of minutes, the liberated hydrochloric acid is made to
titrate with standard sodium hydroxide solution,by adding some more of phenolphthalein indicator.Each ml of 0.1N sodium hydroxide consumed is equal to 0.005349g of NH4Cl Ammonium chloride undergoes hydrolysis to yield ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen chloride.This reaction is facilitated by adding formaldehyde,as it fixes ammonia,by forming hexamine(C6H12N4).The acid can now be titrated with alkali without interference.These reactions are represented as follows NH4Cl+H2O NH4OH +HCl 4NH4OH+6CH2O C6H12N4+10H2O HCl+NaOH NaCl+ H2O Now the assay of ammonium chloride is based on formal titration principle.The formaldehyde which is added to the ammonium chloride solution imparts acidic properties to the compound and it can be titrated with standard alkali solution using phenolphthalein as indicator.
Description: It is a white, fine or coarse crystalline powder. It is odourless. It has a cool saline taste. It is slightly hygroscopic and is soluble in 2.6 parts of water, 1.4 parts of boiling water and 100 parts of alcohol. It is freely soluble in glycerin. Uses: It acts in maintaining acid-base equilibrium of body fluids. It acts as a mild expectorant when administered in small doses. It causes local irritation which produces increasing secretion of respiratory tract and makes the mucus less viscous. It also has diuretic effect.[Because of -utilization of ammonium cation in conversion into urea and in the process H+& Cl-ions are formed. The hydrogen ion (H+) reacts with bicarbonate and CO2 and H2O are produced. On continuous use, it causes metabolic acidity by increasing acidity of urine.]