Understanding Carbohydrates: Composition, Structure, and Function
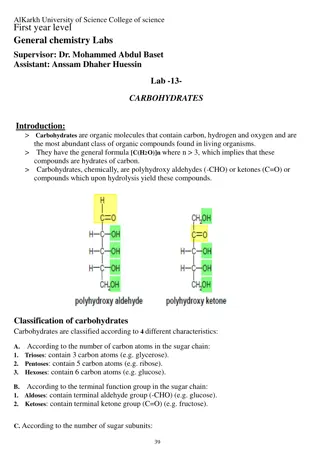
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio. Monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, and galactose are carbohydrate monomers, while polysaccharides like lactose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, and glycogen are carbohydrate polymers. The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6. This essential molecule plays a crucial role in animals. Carbohydrate molecules can be described as having a specific shape and are linked by reactions that produce byproducts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Your carbohydrate notes A sheet of notebook paper Something to write with Highlighter
What elements are carbohydrates composed of? Is there a specific ratio? What do we call a carbohydrate monomer? Monosaccharide 1. Carbon, Hydrogen & Oxygen Carbon 1 : 2 Hydrogen : 1 Oxygen 2. 3. Glucose, Fructose & Galactose A. Can you give an example? What do we call a carbohydrate polymer? Polysaccharide 4. Lactose, Sucrose, Starch, Cellulose & Glycogen A. Can you give an example?
Carbon Atoms Hydrogen Atoms Oxygen Atoms Bond between atoms Green Marshmallow White Marshmallow Pink Marshmallow Toothpicks What is the Chemical formula for glucose? C6H12O6
What is the Chemical formula for glucose? C6H12O6
1. What shape would best describe this molecule? 2. Think of 4 titles this molecule could accurately be called (do not use fructose or galactose). 3. What is the function of this molecule in animals?
Carbon Atoms Hydrogen Atoms Oxygen Atoms Bond between atoms Green Marshmallow Yellow Marshmallow Pink Marshmallow Toothpicks
4. What type of reaction links the monomers? 4. What is produced as a byproduct of the reaction?