Section 5.6 — Intermolecular Forces & Properties
Water's exceptional properties, including polarity and hydrogen bonding, make it essential for life and an excellent solvent. The intermolecular forces in water allow it to function as a vital molecule with distinct characteristics that enable it to interact with other substances like soap. By lever
0 views • 23 slides
Ethanol production
Ethanol, produced through fermentation by yeast in oxygen-free conditions, serves as a chemical feedstock, solvent, disinfectant, and fuel additive. The biochemistry involves sugar breakdown to pyruvic acid, then conversion to acetaldehyde and finally ethanol. Yeast growth in rich medium leads to et
0 views • 21 slides
Adhesives which harden without chemical reaction
Adhesives can harden without a chemical reaction, using water-soluble materials, or through the loss of solvents. Environmental pressures are leading to the development of water-based adhesives to replace solvent-based ones. Various adhesives like neoprene adhesives and starch-based pastes offer dif
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Solutions and Precipitation Reactions
Solutions are classified as saturated, unsaturated, or supersaturated based on the concentration of solute in the solvent. Solubility plays a critical role in determining the amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature. Reactions yielding products of limited solubility
6 views • 10 slides
Modern Trends in Adhesives Development
Adhesives industry is evolving to meet environmental and safety regulations by developing water-based systems and reducing the use of solvents. Water-soluble materials are being used in adhesives, as well as adhesives that harden by loss of solvent or water. Different types of adhesives like contact
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Evaporation in the Food Industry
Evaporation, a key process in the food industry, involves removing excess water from raw materials or processed foods to enhance preservation and reduce costs. It requires considerations such as heat transfer, temperature control, and prevention of overheating. Evaporation differs from dehydration a
0 views • 22 slides
Paints & Coatings Market to be Worth $244.6 Billion by 2031
Paints & Coatings Market Size, Share, Forecast, & Trends Analysis by Resin (Acrylic, Epoxy, Polyester, Polyurethane, Silicone), Technology (Water, Solvent, Powder, UV), Application (Commercial, Industrial, Infrastructure, Marine) - Global Forecast to 2031
1 views • 5 slides
Oleoresins Industry Projected to Value $2.49 Billion by 2031
Meticulous Research\u00ae\u2014a leading global market research company, published a research report titled,\n 'Oleoresins Market Size, Share, Forecast, & Trends Analysis by Source (Spices {Paprika, Black\n Pepper, Turmeric}, Capsicum, Marigold, Garlic), Extraction Process (Solvent Extraction),\n Ap
0 views • 3 slides
Chemical Reactions: Vocabulary Practice and Experiments in Chemistry 101
In this additional text for practicing chemical reactions vocabulary, students in Chemistry 101 conduct an experiment by combining a solvent and a solute to observe a simple chemical reaction, focusing on the proper process and product description. The materials, instructions, and objectives are pro
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Solubility of Organic Compounds
A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of a solute dissolved in a solvent. Solubility refers to the ability of one compound to dissolve in another. The solubility of organic compounds can be categorized based on chemical reactions like acid-base interactions. Different methods such as gravity
0 views • 6 slides
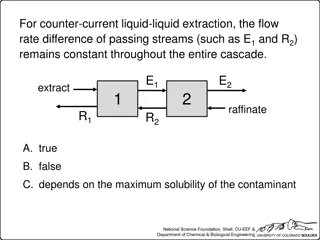
Liquid-Liquid Extraction Techniques and Considerations
Understanding liquid-liquid extraction processes like counter-current and co-current cascades, material balances, and system degrees of freedom. Topics include impact of flow rates, partition coefficients, solvent ratios, and purity on extraction efficiency.
0 views • 14 slides
Polymeric Controlled Drug Delivery Systems
Polymeric controlled drug delivery systems play a crucial role in regulating drug release through diffusion, solvent penetration, and chemical mechanisms. These systems include diffusion-controlled, solvent-controlled, and chemically-controlled devices, each operating based on specific principles. S
0 views • 33 slides
Recrystallization for Solid Organic Compound Purification
Recrystallization is a laboratory technique used to purify solids based on their different solubilities. It involves dissolving an impure solid in a suitable solvent, cooling the solution to allow pure crystals to form, filtering to isolate the purified solid, and drying it. Finding a good recrystal
1 views • 11 slides
Understanding Column Chromatography: Methodology, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications
Column chromatography, a type of adsorption chromatography, involves separating components based on their affinity to an adsorbent. The methodology includes passing a solvent through a column to improve separation, obtaining a chromatogram, and eluting components for analysis. The principle relies o
2 views • 24 slides
Understanding Pharmaceutical Solutions: Types, Classifications, and Preparation Procedures
Exploring the world of pharmaceutical solutions, this content covers the different types of solutions, classifications based on preparation methods, and dosage forms. It discusses the importance of standard solutions and provides insights into the general procedures for preparing simple solutions. A
2 views • 17 slides
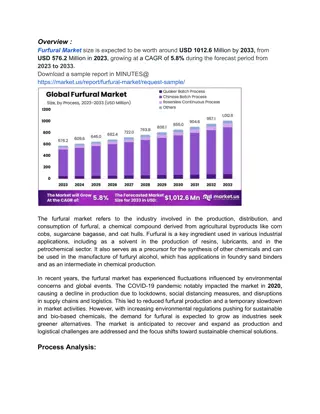
Furfural Market Boom: Key Drivers and Opportunities for 2024 and Beyond
Furfural Market By Process (Chinese Batch Process, Quaker Batch Process, and Rosenlew Continuous Process), By Raw Material (Sugarcane bagasse, Corn cob, Rice husk, and Sunflower hull), By Application(Furfuryl Alcohol, Solvent, Intermediate, Others),
0 views • 4 slides
An Overview of High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful analytical technique used for separating and identifying compounds in a mixture. It involves a mobile phase and a stationary phase to achieve separation based on different physicochemical properties. The mobile phase plays a crucial role in
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful analytical technique used to separate, identify, and quantify components dissolved in a liquid solvent with high resolution. It involves pumping the sample mixture through a column at high pressure, where the components interact with the st
1 views • 34 slides
Understanding Standard Solutions in Chemistry
Definitions of terms like solute, solvent, and saturation are explained. The importance of preparing standard solutions, methods for their preparation, and how results are expressed are discussed. Stock solutions and their benefits are also covered. Images are used for illustration throughout the co
1 views • 65 slides
Understanding Liniments: Alcoholic and Oleaginous Solutions for External Application
Liniments are topical solutions intended for external application to the skin through rubbing. They can be alcoholic or oleaginous, with the choice of vehicle depending on the desired action and solubility of components. Emulsions require thorough shaking before use, and the solvent for oleaginous l
4 views • 5 slides
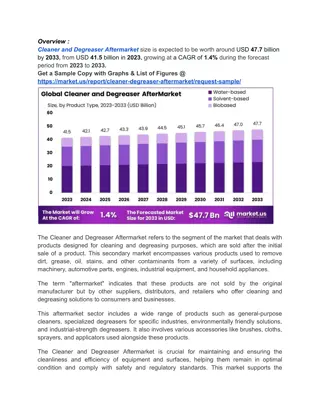
Global Health Crises Drive Demand for Cleaning Solutions in Aftermarket
Cleaner and Degreaser Aftermarket By Part Types(Cleaner Aftermarket, Degreaser Aftermarket), By Product Type(Water-based, Solvent-based, Biobased), By Application( Automotive, Aerospace, Marine, Machinery and Equipment, Building and Construction, Oth
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Body Fluids and Composition in the Human Body
The body composition of an average young adult male includes protein, mineral, fat, and water in varying proportions. Water is the major component, with intracellular and extracellular distribution. Movement of substances between compartments occurs through processes like simple diffusion and solven
0 views • 37 slides
Understanding Evaporation in Chemical and Petroleum Industries
Evaporation is a process of vaporizing a solvent to produce concentrated solutions used in various industries like sugar, salt, and chemical production. This article covers the principles, purposes, and types of evaporators used in the field. It explains single and multiple effect operation methods,
13 views • 11 slides
Understanding the Evaporation Process in Concentrating Solutions
Evaporation is a process used to concentrate solutions by removing a volatile solvent, often water, leaving behind a liquid residue. This method differs from distillation and drying, with considerations for liquid characteristics like concentration, foaming, temperature sensitivity, scale, and mater
1 views • 37 slides
Water as a Compound: Essential Properties and Properties
Water, a vital element covering 70% of the Earth, is composed of hydrogen and oxygen. It has various physical and chemical properties, acts as a universal solvent, and plays crucial roles in nature. From boiling and freezing points to chemical reactions, water's significance is undeniable. Its sourc
0 views • 63 slides
Exploring Freshwater: A Vital Resource on Earth
Water, the universal solvent, exists in various forms and covers 71% of the Earth's surface. Freshwater, crucial for life, is limited with only a small percentage available for organisms. River basins play a vital role in water distribution and quality. Understanding the importance of freshwater res
2 views • 5 slides
Understanding Osmosis and Cell Membrane Transport
Osmosis is the process of water molecules diffusing across a semi-permeable membrane, crucial for maintaining cell function. It involves the movement of water from areas of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. Special proteins called aquaporins facilitate water trans
1 views • 24 slides
Development of Presumption Criteria for Solvent-Induced Hearing Loss
Development of a presumption criteria by the Department of Labor (DOL) for identifying the exposure-disease relationship in cases of solvent-induced hearing loss. The DOL requires a diagnosis of sensorineural hearing loss in both ears, exposure to specific solvents, and a history of working in desig
0 views • 7 slides
Guide to Recrystallization Techniques for Purifying Solid Organic Compounds
Solid organic compounds obtained from organic reactions are often impure and require purification through recrystallization. This process involves choosing a suitable solvent, testing solubility, and using decolorizing charcoal to remove impurities. Proper solvent selection is crucial for successful
0 views • 13 slides
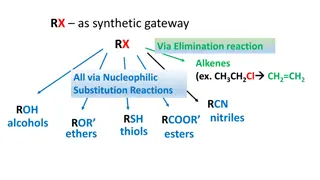
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: Factors Affecting SN2 Reactivity
Understanding the factors influencing SN2 reactions in synthetic gateways involving elimination reactions of alkenes is crucial for predicting reaction rates. This includes analyzing the impact of solvent types on reaction rates in different scenarios. Polar protic solvents and polar aprotic solvent
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry
Different solvents can have varying effects on chemical reactions by influencing solubility, stability, and reaction rates. Solvents can control the pathway towards forming either thermodynamic or kinetic products based on their selection. Solutes dissolve based on intermolecular interactions with s
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Solution Concentration in Chemistry
Solutions in chemistry are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances where each maintains its own chemical identity. They consist of a solute, the substance being dissolved, and a solvent, the substance used to dissolve the solute. Solution concentration can be described qualitatively as concen
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Mixtures: Solutions, Colloidal Dispersions, and Suspensions
Food mixtures can be classified based on particle size distribution, with the dispersed phase scattered throughout a continuous medium. Solutions, a type of mixture, consist of a solute (dispersed phase) and a solvent (continuous phase), forming a homogenous blend. Factors like temperature, particle
0 views • 80 slides
Understanding Freezing Point Depression and Molality for Solutions
Introduction to molality and freezing point depression in solutions. Molality is a way to measure solution concentration, calculated using moles of solute and kilograms of solvent. By calculating the moles of NaCl in a salt solution and the mass of the solvent (ice/water), the molality can be determ
0 views • 9 slides
Role of Solvent in Spectral Properties and Solvatochromism
Solvent plays a crucial role in physical and chemical processes, affecting kinetics, equilibria, and spectral properties such as UV-vis, IR, and NMR. Solvathochromism describes the change in spectral bands caused by solvent interactions. Factors like solvent polarity and hydrogen bonding influence d
0 views • 19 slides
Criteria for Solvent-Related Hearing Loss and Compensation Claims
The Department of Labor (DOL) has specific criteria for accepting claims related to solvent-induced hearing loss in employees. If an employee has sensorineural hearing loss in both ears, was exposed to certain chemical solvents, and worked in particular job categories for a concurrent 10-year period
0 views • 8 slides
Recent Advances in FEVE Fluoropolymer Resin Technology
Recent discoveries in FEVE technology showcase the impressive properties of Fluoroethylene Vinyl Ether (FEVE) resins, such as weatherability, chemical resistance, gloss, solubility, and crosslinking. These resins offer ambient cure for field applications, OH functionality for crosslinking, solvent s
0 views • 25 slides
Different Methods of Textile Scouring Explained
Wool scouring and solvent scouring are two essential processes in textile production. Wool scouring involves removing wool grease before spinning yarn, while solvent scouring uses solvents to clean fabrics like polyester and nylon. Solvent scouring offers benefits like simultaneous desizing and blea
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Concentration and Dilution of Solutions by Dr. Laila Al-Harbi
Dr. Laila Al-Harbi explains the concept of concentration of solutions, focusing on molarity and the calculation involved. The molar concentration of solutions is determined by the amount of solute in a given volume of solvent, expressed as moles of solute per liter of solution. Additionally, the pro
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding the SQUEEZE Tool in PLATON for Solvent Refinement
The SQUEEZE tool in PLATON, developed by Utrecht University, offers an effective method for handling disordered solvent refinement in crystallography. This tool, part of the SHELXL suite, aids in modeling and refining solvent parameters when traditional methods may not suffice. Learn about its histo
0 views • 23 slides