Understanding Atomic Configurations and Term Symbols
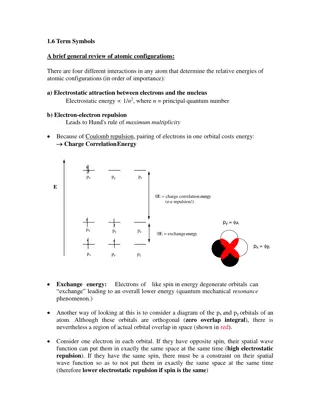
The energy of atomic configurations is determined by electrostatic attraction between electrons and the nucleus, electron-electron repulsion, spin-orbit coupling, and spin-spin interactions. Term symbols in electronic spectroscopy specify atomic states using quantum numbers. Hund's rule and the Paul
8 views • 12 slides
Operating a DC Series Motor from a Single Phase Supply
Connecting a DC series motor to an AC supply results in pulsating torque due to reversed current flow. This setup leads to inefficiencies and challenges such as eddy current losses and poor power factor. To improve performance, modifications like laminating core structures, using compensated winding
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Magnets: Properties, Attraction, and Repulsion
Explore the fascinating world of magnets through a series of True or False questions, visual aids, and practical examples. Learn about magnetic materials, the Earth's magnetic field, and the behavior of magnets when interacting with different objects. Test your knowledge with fun activities and enha
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Magnets and Magnetic Fields
Explore the fascinating world of magnets and magnetic materials. Discover how magnets have two poles, North and South, and how they interact with each other. Learn about magnetic materials like iron, cobalt, and nickel, and understand the concept of magnetizing and demagnetizing. Dive into the magne
0 views • 15 slides
Overview of Semi-Empirical Methods Based on Hartree-Fock
Semi-empirical methods derived from Hartree-Fock theory aim to reduce computational effort by approximating or eliminating electron repulsion integrals. Strategies include introducing adjustable parameters to replace ERI calculations and utilizing zero differential overlap methods like CNDO, INDO, N
1 views • 11 slides
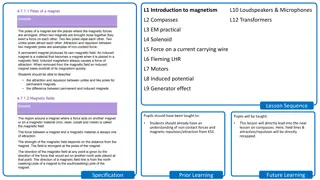
Understanding Magnetism: Introduction to Key Concepts
Delve into the fundamentals of magnetism with a focus on magnets, magnetic fields, and induced vs. permanent magnets. Explore the concepts of attraction, repulsion, magnetic materials, and the behavior of different metals in the presence of magnets. This lesson sets the foundation for a deeper under
0 views • 19 slides
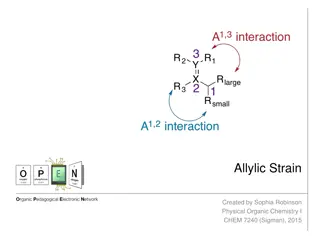
Understanding Allylic Strain in Organic Chemistry
Allylic strain refers to the unfavorable nonbonding repulsion caused by certain substituents in the allylic position of a molecule. This strain can impact reaction outcomes and diastereoselectivity, as seen in examples like Diels-Alder and hydroboration oxidation reactions. Proper understanding and
1 views • 9 slides
Week 7 Vocabulary Words - English 8
Explore the vocabulary words for Week 7 in English 8, including definitions and contextual sentences. Enhance your understanding of words like "repulsion," "mien," "disconsolate," "abject," "traverse," "explicit," "doggedly," "amply," "amiss," and "lamentation" through visual aids and examples.
0 views • 11 slides
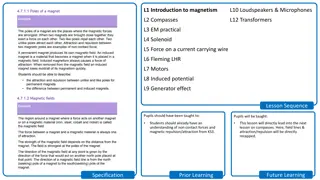
Understanding Magnetism: Introduction and Key Concepts
Delve into the fascinating world of magnetism in this lesson, covering topics such as compasses, solenoids, motors, and generators. Explore the basics of magnetic fields, attraction and repulsion, and the difference between permanent and induced magnets. Strengthen your understanding of magnetism th
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Magnets and Electromagnets in 3rd Grade Science
Explore the unique properties of magnets and electromagnets in this 3rd Grade Science lesson. Learn about polarity, attraction, repulsion, and strength. Discover how magnets work, the importance of poles, and the behavior of like and unlike poles. Dive into the world of magnets to develop models and
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Electricity and Charges: A Teaching Resource
Explore the fascinating world of electricity, charges, electrons, voltage, current, series, parallel circuits, and resistance through engaging slides designed to complement worksheets. Discover hands-on experiments that illustrate concepts like rubbing plastic to create static charges, observing eff
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Coulomb Interaction in Many-Particle Hamiltonian
Explore the treatment of Coulomb interaction in a many-particle Hamiltonian, where careful integration is crucial due to divergence issues. Learn about solving the Coulomb Hamiltonian with Slater integrals and expanding the operator on spherical harmonics for analytical solutions. Discover the signi
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Coulomb Repulsion and Slater Integrals
Dive into the intricate world of Coulomb repulsion and Slater integrals, essential concepts in quantum physics. Explore the challenges posed by the diverging Coulomb integral and the complex calculations required to evaluate these interactions. Discover how Slater integrals play a crucial role in cr
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Electrostatic Properties of Polyelectrolyte Solutions for DNA Molecules
Double-stranded DNA molecules exhibit repulsion due to their linear charge distribution, which can be mitigated by positively charged counter-ions. The Bjerrum length and Manning structural parameter play crucial roles in defining charge density. Electrostatic repulsion terms and calculations involv
0 views • 27 slides
Exploring the World of Magnets: Designs, Properties, and Applications
Delve into the fascinating realm of magnets, learning about their composition, attraction and repulsion properties, as well as their diverse applications in various products. Discover how magnets are used in innovative designs and get inspired to create your own magnetic products.
0 views • 7 slides
Exploring Magnetism: Concepts and Applications
Understanding magnetism involves learning about magnetic fields, poles, attraction, repulsion, and electromagnetism. Explore how magnets work, magnetic fields interact, and electromagnets are created. Dive into the properties of permanent and induced magnets while uncovering the magic of compasses a
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Static Electricity and Electrostatics
Static electricity is a result of electric charge buildup on insulating materials due to friction, causing electrons to transfer and create a charge difference. This can lead to phenomena like a balloon sticking to a wall. The origin of static charge lies in the electrons and protons within atoms, w
0 views • 9 slides