Proposal for Random Access Efficiency Enhancement in IEEE 802.11be Networks
This document presents a proposal for enhancing random access efficiency in IEEE 802.11be networks through a Random-Access NFRP (RA-NFRP) principle. The proposal addresses the challenges of low efficiency in the current UORA procedure and introduces modifications based on the 802.11ax standard to im
6 views • 16 slides
Bluetooth Low Energy Addresses in IEEE 802.11-21/1535r0
The document explores the features of resolvable addresses in Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) within the IEEE 802.11-21/1535r0 standard. It discusses the two types of addresses in BLE, Public and Random, and their usage. The emphasis is on Random addresses due to their popularity and privacy features. Th
2 views • 11 slides
Random Forests: A Comprehensive Overview
Random Forests, a popular ensemble learning technique, utilize the wisdom of the crowd and diversification to improve prediction accuracy. This method involves building multiple decision trees in randomly selected subspaces of the feature space. By combining the predictions of these trees through a
1 views • 21 slides
Plane Failures in Rock Slopes
Plane failures in rock slopes are rare but significant, indicating sensitivity to changes in shear strength and groundwater conditions. Geometrical conditions must be met for such failures to occur, including specific alignments and interactions between the sliding plane and slope face. Analysis inv
0 views • 22 slides
Evolution of Hill Slopes: Penck's Slope Replacement Theory
Penck's slope replacement theory proposes that the angle of a hill slope decreases as gentler slopes replace steeper ones, leading to the concavity of the slope profile. The model explains how vertical erosion by streams and denudation shape hillslopes, causing them to retreat in a parallel manner.
0 views • 9 slides
Simplifying Random Assignment with The Cambridge Randomizer
The Cambridge Randomizer offers a cost-effective and efficient solution for random assignment in research studies, enabling treatment providers to conduct the process securely. This innovative online portal streamlines the assessment of participant eligibility, provides instant baseline data, and en
2 views • 8 slides
High-Throughput True Random Number Generation Using QUAC-TRNG
DRAM-based QUAC-TRNG provides high-throughput and low-latency true random number generation by utilizing commodity DRAM devices. By employing Quadruple Row Activation (QUAC), this method outperforms existing TRNGs, achieving a 15.08x improvement in throughput and passing all 15 NIST randomness tests
1 views • 10 slides
Circular Failure in Rock Slopes: Causes and Design Considerations
Circular failure in rock slopes, such as those containing discontinuities or weak materials like highly weathered or fractured rock, occurs along circular surfaces. This type of failure is common when geological features are not clearly defined. Factors influencing circular failure, conditions under
0 views • 21 slides
Slope Development Theories in Applied Geomorphology
Slopes are formed through different processes as described by Wood's slope development theories, such as the Four Unit Slope Model and the 9-Unit Slope Model. These models illustrate various manifestations of slope profiles based on factors like rock composition and water movement. Different slope t
0 views • 10 slides
Random Variables and Their Applications in Various Fields
Random variables play a crucial role in statistics, engineering, and business applications. They can be discrete or continuous, depending on the nature of the outcomes. Discrete random variables have countable values, while continuous random variables can take on any real number. This article explor
1 views • 6 slides
Random Variables and Probability Distributions
Random variables are variables whose values are unknown and can be discrete or continuous. Probability distributions provide the likelihood of outcomes in a random experiment. Learn how random variables are used in quantifying outcomes and differentiating from algebraic variables. Explore types of r
2 views • 13 slides
Advanced Imputation Methods for Missing Prices in PPI Survey
Explore the innovative techniques for handling missing prices in the Producer Price Index (PPI) survey conducted by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The article delves into different imputation methods such as Cell Mean Imputation, Random Forest, Amelia, MICE Predictive Mean Matching, MI Predict
0 views • 22 slides
Measurement of Flow Velocity on Frozen and Non-Frozen Slopes of Black Soil Using Leading Edge Method
This study presented a detailed methodology for measuring flow velocity on frozen and non-frozen slopes of black soil, focusing on the Leading Edge method. The significance of shallow water flow velocity in soil erosion processes was emphasized. Various methods for measuring flow velocity were compa
0 views • 23 slides
Random Class in Java Programming
The Random class in Java is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. By utilizing methods such as nextInt and nextDouble, you can generate random integers and real numbers within specified ranges. This chapter explores common usage scenarios, such as generating random numbers between specific ranges
2 views • 10 slides
Economic Applications of Single-Variable Calculus Derivatives in Economics
In economics, derivatives play a crucial role in analyzing various economic phenomena such as marginal amounts, maximization, minimization, graphing, elasticity, and growth. This involves understanding derivatives of single-variable functions, slopes, instantaneous slopes, and the applications of de
0 views • 75 slides
Linear Equations and Relationships
Explore various questions related to linear equations, slopes, y-intercepts, proportional relationships, and unit rates with step-by-step solutions and explanations. Practice identifying linear functions and graphing equations through real-life scenarios. Enhance your understanding of slope-intercep
1 views • 16 slides
Quantum Key Agreements and Random Oracles
This academic paper explores the impossibility of achieving key agreements using quantum random oracles, discussing the challenges and limitations in quantum communication, cryptographic protocols, quantum computation, and classical communication. The study delves into the implications of quantum ra
1 views • 29 slides
Approximate Inference in Bayes Nets: Random vs. Rejection Sampling
Approximate inference methods in Bayes nets, such as random and rejection sampling, utilize Monte Carlo algorithms for stochastic sampling to estimate complex probabilities. Random sampling involves sampling in topological order, while rejection sampling generates samples from hard-to-sample distrib
0 views • 9 slides
Slope: Graphing Lines and Finding Slope
Learn about the concept of slope, how to identify positive, negative, zero, and undefined slopes in a graph, and methods to calculate slope using rise over run or two points. Get insights into graphical representation of slopes and practical tips to determine slope values accurately.
1 views • 15 slides
Volcanoes: Structure, Caldera Formation, and Characteristics
Volcanoes are geological formations with vents, craters, and slopes. The structure of a volcano includes a vent for lava emission and a crater connected to a magma chamber. Understanding the difference between a caldera and a crater is crucial - calderas are much larger, around 50 km in diameter, fo
1 views • 5 slides
IEEE 802.11-21/1585r10: Identifiable Random MAC Address Presentation Summary
This presentation discusses the concept of Identifiable Random MAC (IRM) addresses in the IEEE 802.11-21/1585r10 standard. It covers the purpose of IRM addresses in preventing third-party tracking while allowing trusted parties to identify specific devices. The presentation outlines the use of Ident
1 views • 24 slides
Linear Equations and Slope Interpretation in Algebra
Understand linear equations, slopes, and intercepts in algebraic models through examples involving calculations, interpretations of slope meaning, y-intercepts, and x-intercepts in various scenarios. Explore how to compare costs, determine points of intersection, and analyze the implications of slop
0 views • 8 slides
Laplace Transforms for Continuous Random Variables
The Laplace transform is introduced as a generating function for common continuous random variables, complementing the z-transform for discrete ones. By using the Laplace transform, complex evaluations become simplified, making it easy to analyze different types of transforms. The transform of a con
0 views • 17 slides
Discrete Random Variables and Variance Relationships
Explore the concepts of independence in random variables, shifting variances, and facts about variance in the context of discrete random variables. Learn about key relationships such as Var(X + Y) = Var(X) + Var(Y) and discover common patterns in the Discrete Random Variable Zoo. Embrace the goal of
1 views • 27 slides
GUC-Secure Commitments via Random Oracles: New Findings
Exploring the feasibility of GUC-secure commitments using global random oracles, this research delves into the differences between local and global random oracles, outlining motivations and future work. It discusses UC frameworks, zero-knowledge proofs, oblivious transfers, and the GUC framework for
1 views • 18 slides
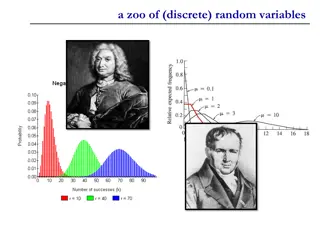
A Zoo of Discrete Random Variables
Discrete random variables play a crucial role in probability theory and statistics. This content explores three key types: Bernoulli random variable, binomial random variable, and error-correcting codes. From understanding the basics of Bernoulli trials to exploring the application of error correcti
0 views • 27 slides
Structural Analysis: Beam Deflection and Slope Calculation
In this structural analysis problem, we are tasked with determining the deflection and slopes at point B of a loaded beam. The calculations involve applying the moment-area method and the conjugate-beam method to create shear, bending moment diagrams, and the deflected curve. Theorems related to slo
0 views • 18 slides
Random Slopes in Data Analysis
Exploring the impact of grand-mean and group-mean centering on intercept interpretation with random slopes, as well as variations in slope/intercept covariance. Differentiating between fixed and random coefficients, and the effects of adding group mean as a Level 2 variable. Delving into within vs.
0 views • 21 slides
Differential Calculus II: Applications in Curve Analysis
This content discusses various applications of differential calculus in analyzing curves, including finding slopes, turning points, and maximum heights. Detailed solutions and explanations are provided for revision and exam-style questions related to curve equations. The content covers topics such a
0 views • 30 slides
Differentiation Techniques and Slope Functions Analysis" (Limit: 61 characters)
Alternative methods for finding derivatives and analyze the slope functions of various equations. Examine the behavior of functions and determine slopes at different points. Includes visual representations and practical examples. Discover how to calculate slopes, interpret results, and understand th
0 views • 42 slides
Features of x^3 Graphs and Tangents Analysis
Investigate the key features of x^3 graphs, including the stationary points, slope function characteristics, and tangent behavior. Understand the relationship between the original function f(x) and its derivative dy/dx. Explore where slopes are increasing, decreasing, or stationary, along with the t
0 views • 10 slides
Slope and Line Steepness
Learn about slope, which is a number indicating line steepness. Positive slopes go up to the right, negative slopes go down, and horizontal lines have a slope of 0. Find slope by ratio of vertical and horizontal changes. Explore examples to practice concepts.
0 views • 7 slides
Algebra Unit 4 Review: Graphs & Equations
Explore standards related to identifying coordinates, plotting points, graphing linear functions, determining slopes, and more in Algebra Unit 4 review. Practice graphing linear functions, determining slopes, identifying intercepts, and analyzing real-world applications using linear equations.
0 views • 23 slides
Randomized Algorithms and Independence Concepts
Types of independence in randomized algorithms are explored alongside the concept of random bit complexity and generation. The idea of mutually independent random variables versus pairwise independent random variables is discussed, illustrating how to generate uniformly random and pairwise independe
0 views • 18 slides
Random Number and Variate Generation Overview
Random numbers play a crucial role in modern computing, aiding in cryptography, simulation, and system testing. This overview delves into the properties of random numbers, the generation of pseudo-random numbers, techniques for generating them, and tests for their validity. It explores the significa
0 views • 59 slides
Equations of Lines: Standard Form and Slopes
Understand how to determine the standard form equation of a line passing through given points, identify whether lines are parallel or perpendicular based on their slopes, and solve problems involving parallel and perpendicular lines.
0 views • 10 slides
High Energy Particle Environment: Analysis of Large SEP Events
This content explores the high-energy particle environment during large solar energetic particle (SEP) events, focusing on spectral slopes, fluence measurement intervals, and parameter variability. Spectral slopes are examined below the rollover energy, showcasing significant variability at both low
0 views • 5 slides
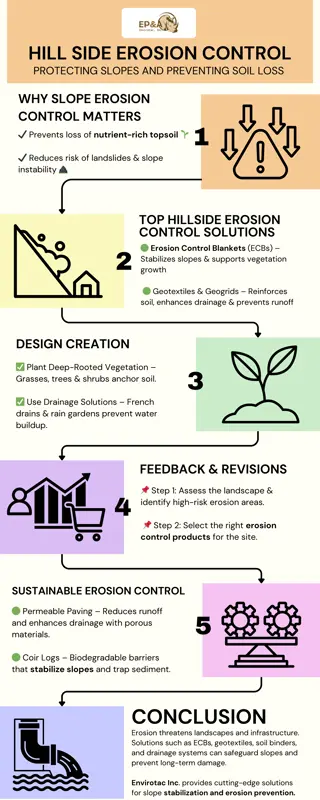
Hillside Erosion Control Products: Protecting Slopes and Preventing Soil Loss.
Hillside erosion control products, like geotextiles, coir mats, and hydroseeding, stabilize slopes, prevent soil loss, and reduce runoff. They reinforce soil structure, promote vegetation growth, and protect against environmental damage, ensuring sus
0 views • 1 slides
Hillside Erosion Control Products: Protecting Slopes and Preventing Soil Loss.
Hillside erosion control products, like geotextiles, coir mats, and hydroseeding, stabilize slopes, prevent soil loss, and reduce runoff. They reinforce soil structure, promote vegetation growth, and protect against environmental damage, ensuring sus
0 views • 9 slides
Discrete Random Variables and Associated Probability Functions
Explore the concept of discrete random variables, their associated probability mass functions, and examples of typical discrete random variables like the Binomial and Poisson random variables. Understand the difference between discrete and continuous random variables with practical examples.
0 views • 19 slides