Discrete Mathematics
Explore the foundations of logic and proofs in discrete mathematics, focusing on compound propositions, bit operations, and applications of propositional logic. Learn about how computers use bits for information representation and manipulation, and delve into translating English sentences into logic
5 views • 15 slides
Understanding Conditional Probability and Bayes Theorem
Conditional probability relates the likelihood of an event to the occurrence of another event. Theorems such as the Multiplication Theorem and Bayes Theorem provide a framework to calculate probabilities based on prior information. Conditional probability is used to analyze scenarios like the relati
1 views • 5 slides
Understanding the Coase Theorem: Property Rights and Economic Efficiency
The Coase Theorem, developed by economist Ronald Coase, posits that under certain conditions, bargaining related to property rights will lead to an optimal outcome regardless of the initial distribution. It provides a framework for resolving conflicts by emphasizing negotiation and efficient market
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Resolution Theorem Proving in Predicate Logic
Resolution theorem proving is a method used in predicate logic to find contradictions within a database of clauses. By negating statements and applying resolution rule of inference, it aims to show inconsistency to prove the original theorem. The process involves putting premises into clause form, a
0 views • 24 slides
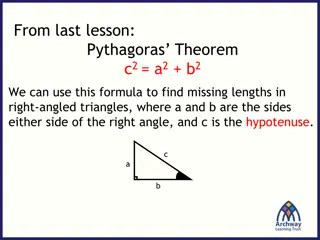
Understanding the Pythagorean Theorem and Right-Angled Triangles
Explore the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a and b). Learn how to identify the hypotenuse, use the theorem to find missing lengths, and visually understand th
1 views • 25 slides
Engineering Mechanics: Lami's Theorem and Cylinder Reactions Problem
This course material covers Lami's Theorem in Engineering Mechanics taught by Ranbir Mukhya. It includes an outline of the theorem, problem scenarios involving cylinders with given weights and diameters, and the determination of reactions at various points. Detailed force diagrams and calculations a
0 views • 8 slides
Insights into the Mean Value Theorem and Its Applications
Delve into the Mean Value Theorem (MVT) with a focus on concepts like Lagrange's MVT, Rolle's Theorem, and the physical and geometrical interpretations. Explore the conditions, statements, and special cases of MVT, along with practical applications and geometric insights. Dr. Arnab Gupta, an Assista
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Resolution in Theorem Proving
Exploring the process of resolution in theorem proving, starting from propositional resolution to the complexities of First-Order Logic. The conversion of FOL sentences to CNF, elimination of implications, variable standardization, Skolemization, and dropping universal quantifiers are all dissected
0 views • 34 slides
Applications and Equivalences in Propositional Logic
This lecture explores applications of propositional logic, including translating sentences, system specifications, logic puzzles, and logic circuits. It also defines tautology, contradiction, and contingency as types of compound propositions, along with logical equivalences. Examples and illustratio
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding the Residue Theorem in Complex Analysis
The Residue Theorem is a powerful tool in complex analysis that allows us to evaluate line integrals around paths enclosing isolated singularities. By expanding the function in a Laurent series, deforming the contour, and summing residues, we can evaluate these integrals efficiently. This theorem ex
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Superposition Theorem in Electrical Circuits
Superposition theorem in electrical circuits states that the effects of multiple voltage and current sources in a network can be analyzed independently and then combined algebraically. This allows for calculating the voltage and current distribution in a network more efficiently. The theorem involve
0 views • 9 slides
RESOLUTION METHOD IN AI
Resolution method in AI is an inference rule used in propositional and first-order predicate logic to prove sentence satisfiability. It employs a proof by refutation technique to achieve contradiction, ultimately concluding the original goal's truth. The process involves converting statements to cla
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Lami's Theorem in Physics
Lami's Theorem is an equation that explains how the magnitudes of forces acting on a point keep an object in equilibrium. This theorem relates the forces with corresponding angles and is derived by understanding the sum of forces acting on a point. By utilizing complementary angles and the sine rule
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Valid Arguments in Propositional Logic
An argument in propositional logic consists of premises leading to a conclusion. Valid arguments are those where the truth of the premises implies the truth of the conclusion. To determine validity, you can construct a truth table to check if the conclusion always holds when all premises are true. T
0 views • 9 slides
Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem and Its Origins
The Pythagorean Theorem, named after the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras, is a fundamental principle in geometry relating to right triangles. While Pythagoras is credited with offering a proof of the theorem, evidence suggests that earlier civilizations like the Babylonians and ancient Chines
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Forward Chaining in Propositional Logic
Forward chaining in propositional logic is a recursive, stack-based version of back-chaining that can be modified to handle variables using unification and negation context. By applying a set of rules and facts, the process aims to prove a given query by iteratively inferring new information. Illust
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic and Logical Operators
Learn about propositional logic, statements, logic operators, compound statements, exclusive-or, logical equivalence, and writing logical formulas for truth tables. Explore how to create compound statements for exclusive-or using different approaches and ensure logical equivalence. Enhance your know
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Normal Forms in Propositional Logic
Explore the concept of normal forms in propositional logic, where each formula has a unique truth-value function. Learn about equivalence of formulas, determining normal forms, and canonic forms like Disjunctive Normal Form (DNF) and Conjunctive Normal Form (CNF). Discover how to find canonic forms
1 views • 22 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic at Kwame Nkrumah University
Dive into the world of symbolic logic and compound statements with a focus on Propositional Logic at Kwame Nkrumah University in Ghana. Explore the concepts of connectives, simple and compound statements, truth values, and more. Enhance your logical reasoning skills through a tutorial on symbolic lo
0 views • 57 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic and Mathematical Logic in Computer Science
Study the development of formal logic in computer science, focusing on propositional logic and mathematical logic. Learn about propositions, logical operators, and ways of combining statements to derive conclusions. Explore examples and understand how to determine the validity of arguments using log
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Predicate Logic: From Propositional to Predicate Logic
Transitioning from propositional to predicate logic allows reasoning about statements with variables without assigning specific values to them. Predicates are logical statements dependent on variables, with truth values based on those variables. Explore domains, truth values, and practical applicati
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Bayes Theorem in NLP: Examples and Applications
Introduction to Bayes Theorem in Natural Language Processing (NLP) with detailed examples and applications. Explains how Bayes Theorem is used to calculate probabilities in diagnostic tests and to analyze various scenarios such as disease prediction and feature identification. Covers the concept of
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic Concepts
Explore different facets of propositional logic, including conditional statements, logic operators, logical equivalence, contrapositives, and proofs. Delve into the intricacies of if-then statements, logical negations, and the nuances of if, only-if conditions. Enhance your understanding of proposit
0 views • 25 slides
Problem Solving with Pythagoras Theorem in Geometry
Explore the application of Pythagoras Theorem in solving problems related to right-angled triangles, diagonals of shapes like rectangles and rhombuses, and the height of triangles. Learn how to use Pythagoras Theorem effectively by drawing diagrams, identifying known lengths, and using the theorem t
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Conceptualization in Machine Learning
Discussion on two types of representations (Propositional, Non-propositional) and the role of similarity in categorizing stimuli. Exploring supervised and unsupervised categorization methods, along with the capabilities of conceptualization beyond classification and clustering. Comparison of human a
0 views • 21 slides
Discrete Mathematics Learning Goals and Examples in Propositional Logic
Explore the learning goals in discrete mathematics focusing on translating English sentences to propositional logic, evaluating compound propositions, forming converses and contrapositives, and determining consistency. Dive into examples of conditional statements, converse, inverse, contrapositive,
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Calculus: From MVT to FTC with Lin McMullin
Join Lin McMullin in exploring the transition from the Mean Value Theorem (MVT) to the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC). Discover the significance of MVT, Fermat's Theorem, Rolle's Theorem, and the Mean Value Theorem, all crucial concepts in calculus. Engage in graphical explorations, proving m
0 views • 45 slides
Introduction to Propositional Logic: Formalization and Reasoning
Understanding formalization in propositional logic involves replacing atomic propositions with propositional variables and natural language connectives with logical connectives. The process abstracts from internal proposition structure, reducing meaning to True or False. The language allows formaliz
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Rolle's Theorem and The Mean Value Theorem in Calculus
Rolle's Theorem states that for a continuous and differentiable function on a closed interval with equal function values at the endpoints, there exists at least one point where the derivative is zero. The Mean Value Theorem asserts that for a continuous and differentiable function on an interval, th
0 views • 5 slides
Introduction to Analysis: Mean Value Theorem and Related Theorems
This resource delves into key concepts such as the Mean Value Theorem, Fermat's Theorem, Rolle's Theorem, Extreme Value Theorem, local maximums, and more. It presents important results and explores proofs in the context of analysis.
0 views • 71 slides
Introduction to Applying Pythagorean Theorem in Right Triangles
In this lesson, we will learn how to apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths of right triangles. The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Through examples and practice problems,
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Propositional Proof Complexity and Lower Bounds
Studies focus on the intractability of propositional proof complexity, exploring the power of proof systems to verify tautologies. Discussion on known lower bounds and challenges in proving hardness of certain tautologies.
0 views • 23 slides
Propositional Theorem Proving Methods Overview
The overview covers essential techniques in propositional theorem proving including the resolution algorithm, Horn clauses, forward and backward chaining, and effective propositional model checking. It discusses methods such as resolution closure, completeness of resolution, and the significance of
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Propositional and Notional Attitudes in Logic and Natural Language Processing
Explore the intricate concepts of propositional and notional attitudes in the context of logic and natural language processing. Dive into the distinctions between belief, knowledge, seeking, finding, solving, wishing, and wanting within the realms of individual intensions and hyper-intensions. Under
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic in Artificial Intelligence
Covering the syntax, semantics, and logical inference in propositional logic for Artificial Intelligence. Learn about atomic sentences, logical connectives, operator precedence, and how to determine the truth value of sentences in a particular model. Dive into the rules and computations involved in
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Binomial Theorem: Expansion, Examples, and Applications
Binomial theorem is a powerful mathematical concept used to expand expressions involving binomials. This presentation explores the basics of binomial expansion, formulae for positive, negative, and fractional indices, along with examples demonstrating its application. By leveraging the binomial theo
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Automated Theorem Proving in Lean
Dive into the world of automated theorem proving in Lean with a focus on formal verification, history, and the use of logic and computational methods. Explore how programs can assist in finding and verifying proofs, as well as the significance of interactive theorem provers. Discover the evolution o
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding LRU Competitiveness Theorem
The Lemma states that if a page is ejected by the LRU algorithm after being touched in a request sequence, there is a fault in the offline algorithm. The Theorem extends this to show that for any segment where LRU incurs k faults, the offline algorithm also has a fault. The proof involves examining
0 views • 8 slides
Triangles Inequalities and The Hinge Theorem
Understanding the inequalities in triangles using the Hinge Theorem. The theorem explains how the length of the third side of a triangle relates to the included angles and congruent sides in different triangle configurations. Explore problems that involve applying the Hinge Theorem and its converse
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding NP-Completeness: Cook-Levin Theorem and Clique Problem
Today's lecture delved into NP-completeness, focusing on the Cook-Levin Theorem and the Clique Problem. NP-completeness is defined as a language that is in NP and all other languages in NP are polynomial-time reducible to it. The Cook-Levin Theorem states that SAT, a Boolean satisfiability problem,
0 views • 10 slides