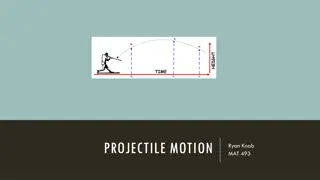
Understanding Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
Physics Bachelor's Degree Specializations Overview
Explore different specializations within a Physics Bachelor's degree program for the 2021-2022 academic year, including general physics, astronomy, computational physics, materials physics, and optics and lasers. Each specialization offers a unique set of courses and opportunities for students inter
2 views • 9 slides
Understanding Curvilinear Motion with Cylindrical Coordinates in Physics
Cylindrical coordinates, specifically the r- coordinate system, are useful in describing curvilinear motion. This system helps explain motion in relation to a fixed origin, making it ideal for scenarios involving rotation or changes in angle. By using radial and transverse unit vectors, positions, v
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Position, Motion, and Displacement in Physics
Position in physics refers to a place or location within a coordinate system, crucial for describing an object's motion through time. It involves factors like observer frame, coordinates, and whether the object is at rest or in motion. Motion is defined by an object's position, speed, direction, and
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
2 views • 25 slides
Enhancing Physics Education: Future Physics Leaders Initiative
The Future Physics Leaders program, a national education project managed by the Institute of Physics, aims to support specialist physics teachers, Newly Qualified Teachers (NQTs), and non-specialist physics teachers in England. By offering professional development, matched timetabling, and mentoring
0 views • 10 slides
Empowering Physics Teachers: Innovations in Professional Development
Discover the latest updates and initiatives in physics teacher training and support programs led by Robin Griffiths and the Institute of Physics (IOP). From stimulating physics networks to nurturing future physics leaders, these projects aim to enhance teaching practices, support disadvantaged stude
7 views • 11 slides
Comprehensive Overview of GES Physics Syllabus Aligned with Khan Academy Resources
Explore the GES Physics syllabus divided into Mechanics, Thermal Physics, Waves, Electricity and Magnetism, Atomic and Nuclear Physics, and Electronics. The syllabus covers a wide range of topics from introductory physics concepts to advanced topics in thermodynamics, optics, electromagnetism, quant
1 views • 5 slides
UIL Physics Capital Conference 2019 Topics & Questions Overview
The UIL Physics Capital Conference 2019 featured various physics topics and questions ranging from teaching quantum physics to dogs to fields like astronomy, measurement, uniform motion, forces, energy, and more. The event covered a wide array of physics concepts, and the directed study text focused
1 views • 25 slides
Understanding Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
Understanding Motion in Computer Games: Lecture #11 Movement
Explore the fundamentals of motion in computer games through Lecture #11 Movement. Delve into concepts like Newton's Laws, vectors, motion terms, and handling various forces to enhance your grasp on gaming physics. Discover how to apply basic rules of motion, obtain continuous input from keyboards,
0 views • 81 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion in Physics
A projectile, acted upon by gravity, follows a parabolic path in projectile motion. By choosing appropriate coordinates and strategies, analyzing motion along vertical and horizontal axes becomes manageable. Key formulas and strategies help in determining components of velocity, maximum height, time
5 views • 25 slides
Physics Chapter 6: Circular Motion Overview
Learn about circular motion in physics, covering concepts like centripetal acceleration, uniform circular motion, and Newton's laws applied to rotational motion. Get ready for the upcoming midterm with key equations provided and practice exams available on the class web page.
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Balanced and Unbalanced Forces in Physics
Forces play a crucial role in determining an object's motion. Balanced forces have a net force of 0 N, resulting in no change in motion, while unbalanced forces lead to a change in motion. Inertia, the resistance to changes in motion, and the concept of combining forces are also important in underst
2 views • 30 slides
Understanding Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
2 views • 12 slides
Master's Programs at University of Strasbourg - Faculty of Physics & Engineering
Explore the Master's programs offered at the Faculty of Physics & Engineering, University of Strasbourg (Unistra) with specializations in Astrophysics, Condensed Matter Physics, Radiation Physics, Subatomic Physics, and Cell Physics. The curriculum includes a strong theoretical background, specializ
2 views • 13 slides
Understanding Circular Motion Concepts in Physics
Explore the fundamentals of uniform circular motion, centripetal acceleration, and tangential velocity with real-world examples. Learn how to calculate velocities and accelerations in circular motion scenarios, and understand the difference between tangential speed and velocity in rotating systems.
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Physics Misconceptions and Newton's Laws
Cognitive scientists have shown that physics students often hold misconceptions about motion that hinder their learning. Overcoming these misconceptions involves self-reflection, critical thinking, and evaluation. Newton's laws of motion play a significant role in understanding the concepts. Questio
0 views • 56 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
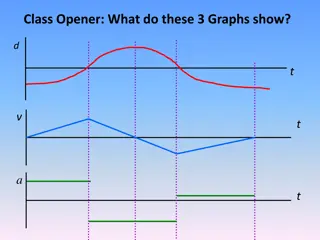
Understanding Kinematics in Physics: Equations, Graphs, and Definitions
Exploring kinematics in physics involves studying the motion of objects through equations, graphs, and definitions. Key concepts include position, distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration, along with scalar and vector quantities. Equations like s = (u + v)t and v = u + at are crucia
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Kinematics in Physics: The How and Why of Motion
Explore the fascinating world of kinematics in physics through the concept of motion, acceleration, and free-fall. From constant acceleration to projectile motion, unravel the principles behind bodies in motion. Delve into the discoveries of scientists like Galileo and experience free-fall demonstra
0 views • 21 slides
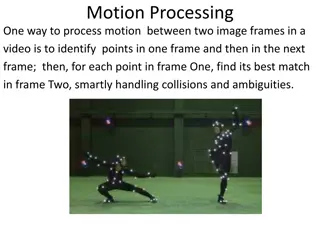
Understanding Motion Processing and 2D Motion Modeling
Processing motion between image frames can be done by identifying points and finding their best matches in the next frame. Another approach based on physics and mathematics has grown in popularity. This theoretical approach now produces better results, as seen in the expected output from Optical Flo
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
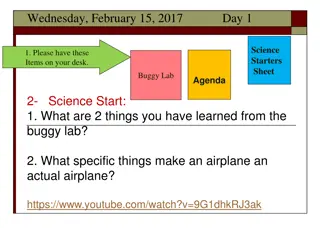
Science Starters for Motion Maps and Buggy Lab Agenda
Explore the world of motion maps and delve into the concepts of velocity and direction with engaging activities such as the Buggy Lab. Discover how to interpret motion maps and analyze different types of motion patterns. Enhance your understanding of physics with hands-on experiments and interactive
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Kinematics of Particles: Understanding Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of rectilinear motion, analytical relationships of velocity and acceleration, and solve practical problems involving acceleration and distance calculations in physics. Dive into scenarios such as a car race, a baseball player running to first base, and a subway train braking bet
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion in Physics
Projectile motion is the motion of an object near the Earth's surface influenced by gravity. This concept has a historical background from Aristotle to Galileo and Newton, with forces like gravity and air resistance playing crucial roles. Models with and without air resistance are discussed, leading
0 views • 19 slides
Welcome to Physics 100! Basic Concepts of Physics
This physics course, led by Instructor Neepa Maitra, covers fundamental concepts of physics based on Paul G. Hewitt's book. It includes topics such as Newton's laws, momentum, energy, rotation, and more. The course structure, grading system, and important notes are outlined, along with details on cl
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides
Evolution of Motion Theories: Aristotle to Einstein
Explore the progression of motion theories from Aristotle's belief in a force for motion to Galileo's discoveries on gravity, Newton's laws of motion, and Einstein's theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Discover how our understanding of motion has evolved over the centuries, shaping the way
0 views • 20 slides