Kinematics of Particles: Understanding Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of rectilinear motion, analytical relationships of velocity and acceleration, and solve practical problems involving acceleration and distance calculations in physics. Dive into scenarios such as a car race, a baseball player running to first base, and a subway train braking between stops. Enhance your understanding of motion in physics through various examples and exercises.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
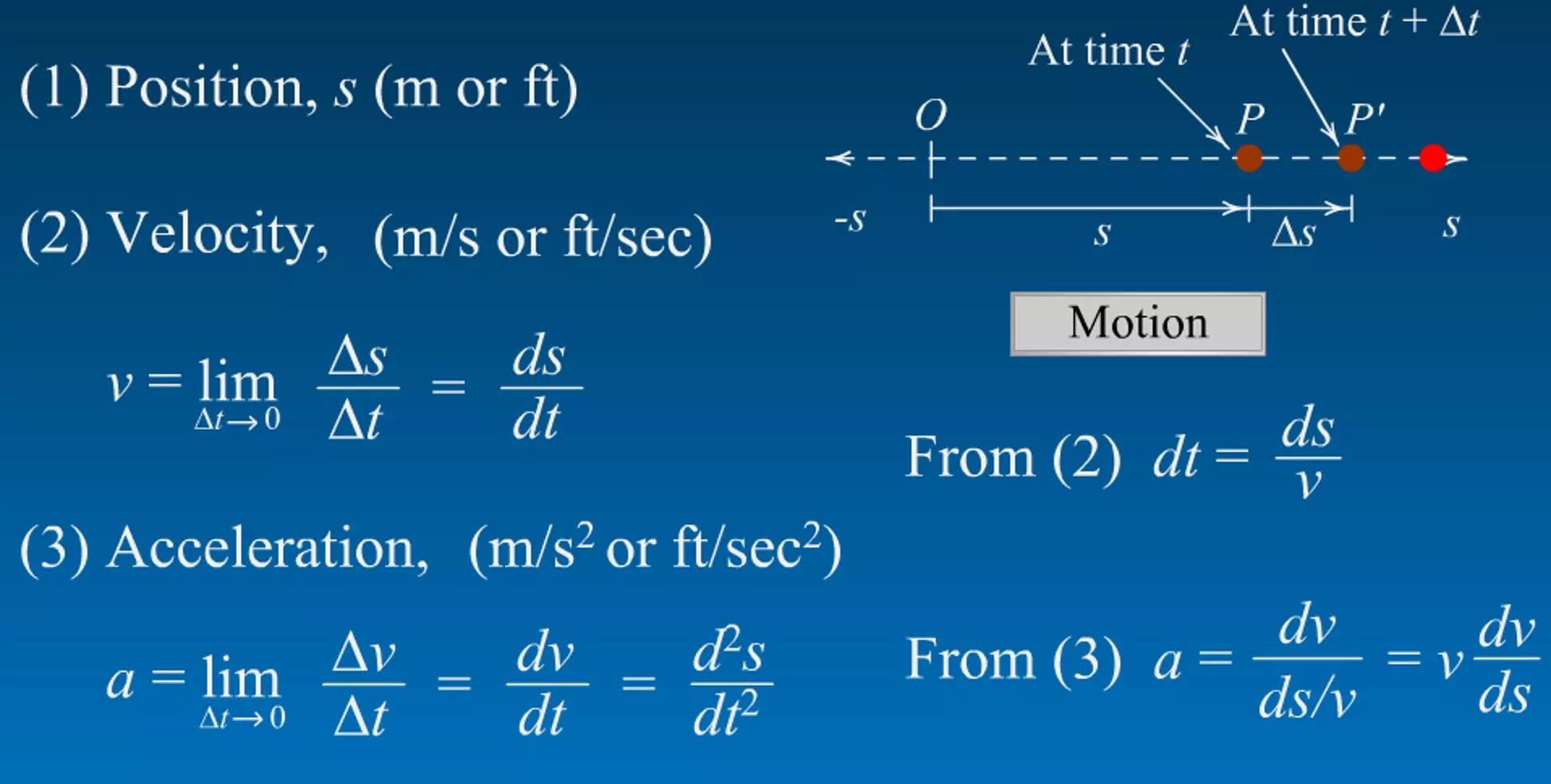
Chapter 2 kinematics of particles Class Lecture 2: Tuesday, August 25, 2015 Today s Objective: Rectilinear motion
Problem 2.14 In the pinewood-derby event shown, the car is released from rest at the starting position A and then rolls down the incline and on to the finish line C. If the constant acceleration down the incline is 9 ft/s2and the speed from B to C is constant, determine the time duration for the race. The effects of the small transition area can be neglected.
Problem 2. 15 Starting from rest at home plate, a baseball player runs to first base (80 ft away). He uniformly accelerates over the first 10 ft to his maximum speed, which is then maintained until he crosses first base. If the overall run is completed in 4 sec, determine his maximum speed, the acceleration over the first 10 ft, and time duration of the acceleration.
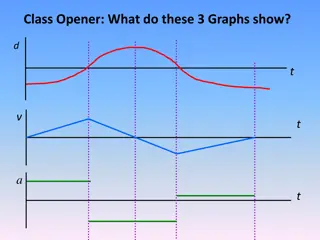
Problem 2/48 A subway train travels between two of its stops with the acceleration schedule shown. Determine the time interval ? during which the train brakes to a stop with deceleration of 2 m/s2 and find the distance s between stations.