Introducing Turnkey's groundbreaking iPM instrument
\nIntroducing Turnkey's groundbreaking iPM instrument! Revolutionizing air quality analysis, it combines light extinction & scatter for precise airborne particle measurement. Now, track all PM size fractions simultaneously with unmatched accuracy. \nKEY FEATURES:\n1. Measures PM10, PM4 (respirable),
1 views • 2 slides
Robin Klein's Poetic Reflection on Childhood Innocence
Robin Klein's poem portrays the constant nagging of a little girl named Amanda by her mother for various perceived flaws. Amanda imagines herself as a mermaid, an orphan, and Rapunzel in response to the criticisms. The poem highlights the desire for freedom from continuous scrutiny and the impact of
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Mass and Inertia in Physics
Mass and inertia are fundamental concepts in physics. Mass is the amount of material in an object, determining its inertia - the resistance to change in motion. Objects with greater mass require more force to change their state of motion. Mass should not be confused with volume or weight, as they ar
0 views • 21 slides
Physical Science Unit 1 Test Review Game
This test review game covers various topics in physical science including concepts like floating and sinking, forces, work, inertia, acceleration, and more. It presents multiple-choice questions with explanations related to lifeguard tests, object forces, average force calculations, work calculation
1 views • 71 slides
Understanding Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships in Mathematics
Proportional relationships involve quantities having a constant ratio or unit rate, while nonproportional relationships lack this constant ratio. By examining examples such as earnings from babysitting and costs of movie rentals, we can grasp the differences between these two types of relationships.
2 views • 6 slides
Understanding Velocity vs. Speed in Physics
Velocity and speed are fundamental concepts in physics that describe how fast an object is moving and in what direction. While speed is a scalar quantity representing the rate of motion, velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. Constant velocity implies steady speed and
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Food Dehydration: Constant vs. Falling Rate Periods
Food dehydration involves constant rate periods where moisture evaporates uniformly until a critical point is reached, and then transitions to falling rate periods where drying slows down. Various drying methods and characteristics of air play crucial roles in this process, impacting the efficiency
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Objects can be in static equilibrium when at rest or dynamic equilibrium when moving at a constant speed. Equilibrium is maintained when there is no net force to change the state of motion. This equilibrium is possible when forces either cancel out or there is no force acting on the object. Friction
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Inertia and Motion in the Moving Earth
Inertia and motion in a moving Earth debunk the argument against Earth's movement using examples of birds catching worms on trees and flipping coins in moving vehicles. Objects on Earth move with Earth's motion, showcasing the principle of inertia in action.
2 views • 7 slides
Understanding Motion Under Constant Acceleration
Constant acceleration refers to motion where the speed increases by the same amount each second. It is exemplified in scenarios like free fall due to gravity, where objects experience a consistent acceleration of approximately 10 meters per second squared. This type of motion plays a significant rol
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Gas Laws: Boyle's, Charles', Gay-Lussac's, and Avogadro's Laws
Gas laws such as Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, and Avogadro's Law govern the behavior of gases under different conditions. Boyle's Law relates pressure and volume at constant temperature, Charles' Law relates volume and temperature at constant pressure, Gay-Lussac's Law relates pressu
1 views • 19 slides
Determination of Ester Hydrolysis Constant Rate by Conductivity Measurement
This study focuses on determining the ester hydrolysis constant rate through conductivity measurement, presenting a second-order reaction example. Conductivity meter is utilized for accurate monitoring. The procedure involves utilizing equal concentrations of ester and sodium hydroxide, measuring co
0 views • 6 slides
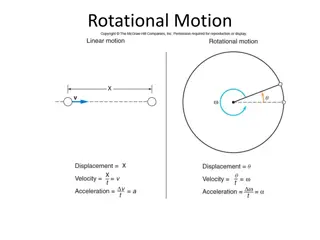
Understanding Rotational Motion in Physics
Exploring rotational motion in physics involves understanding angular velocity, torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinetic energy. This comprehensive guide covers concepts such as the conversion between degrees and radians, angular variables, Newton's second law for rotating bodies, and momen
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore Sir Isaac Newton's foundational principles of motion through engaging visuals and real-world examples. Discover how inertia, force, and acceleration shape the dynamics of objects in motion, as explained by Newton's First and Second Laws. Delve into the concept of inertia and the relationship
2 views • 13 slides
Understanding Small Gasoline Engine Performance
This chapter explores the intricacies of measuring and optimizing internal combustion engine performance, focusing on calculating functional horsepower through various formulas and measurements. It delves into the combustion process in a small gasoline engine, detailing how the air/fuel mixture igni
0 views • 66 slides
Understanding Gravity and Inertia: Key Concepts in Motion
Exploring the principles of inertia and gravity, this content delves into how objects resist changes in motion and the force that attracts objects towards each other. From Newton's Law of Gravity to the dynamics of free fall and weight, learn how these fundamental concepts shape our understanding of
0 views • 21 slides
Constant-Time Algorithms for Sparsity Matroids
This paper discusses constant-time algorithms for sparsity matroids, focusing on (k, l)-sparse and (k, l)-full matroids in graphic representations. It explores properties, testing methods, and graph models like the bounded-degree model. The objective is to efficiently determine if a graph satisfies
0 views • 21 slides
Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data for Constant-Volume Systems
This content delves into the analysis and interpretation of data from constant-volume batch reactors in constant-density reaction systems. It covers integral methods for analyzing data, considerations for irreversible reactions, and the behavior of zero-order and first-order reactions. The text also
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Inertial and Non-Inertial Frames of Reference
Frames of reference play a crucial role in describing and observing motion. In physics, there are two main types of frames of reference: inertial and non-inertial. An inertial frame is one that moves at a constant velocity, where Newton's first law holds true. Such frames have specific characteristi
0 views • 14 slides
Challenges in Constant-Round Public-Coin Zero-Knowledge Proofs
The paper discusses the implausibility of constant-round public-coin zero-knowledge proofs, exploring the limitations and complexities in achieving them. It delves into the fundamental problem of whether such proofs exist, the challenges in soundness error reduction, and the difficulties in parallel
0 views • 20 slides
Newton's First Law of Motion: Inertia and Forces
Understanding the concept of inertia in motion, the role of forces in maintaining or changing motion, and analyzing net forces applied to objects. Also explores scenarios where forces are balanced or unbalanced, affecting the motion of objects.
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Rotational Motion: Linear vs. Angular Speed
Exploring the concept of rotational motion, this content delves into the comparison between linear speed (tangential speed) and rotational speed (angular speed). It discusses how the linear speed varies based on distance from the axis of rotation, while the rotational speed remains constant for all
0 views • 27 slides
Exploring the Cosmological Constant as a Classical Eigenvalue
The concept of the cosmological constant, its implications in the standard cosmological model, and its relation to dark energy are discussed in this scientific exploration. The discussion delves into whether the cosmological constant is truly constant or varies in space and time, and its role in gra
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Rotational Inertia and Conservation of Momentum
Rotational inertia symbolized as I is crucial in quantifying the torque needed for rotation, depending on mass distribution. Torque, rotational inertia, and mass influence an object's spinning motion, affecting stability and speed. Exploring why wheels keep spinning, ice skaters rotate faster when a
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion: Inertia, Forces, and Acceleration
Delve into the fundamentals of Newton's first and second laws of motion, exploring concepts such as inertia, the relationship between forces and acceleration, and the procedure for solving force problems. Discover how objects behave when left to themselves, and grasp the significance of forces in ch
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Rotational Inertia and Torque in Physics
Rotational inertia symbolizes how difficult it is to change the rotation of an object. It depends on mass distribution from the axis, shape, and mass. Torque needed to start rotation is proportional to rotational inertia. Smaller rotational inertia leads to faster rotational acceleration. Examples a
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Solubility Product Constant for Slightly Soluble Salts
Solubility product constant (Ksp) is a special constant that describes the solubility of slightly soluble salts like potassium acid tartrate (KHT) and silver chloride (AgCl) in solution. This experiment aims to determine Ksp for KHT and explore factors affecting Ksp such as temperature and common io
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Forces and Equilibrium in Physics
Forces in physics can be categorized into contact forces and field forces, measured in units like Newtons (N). Inertia, mass, weight, and equilibrium are fundamental concepts in understanding the behavior of objects under different conditions. An object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Mass and Inertia in Physics
Understanding the concepts of mass and inertia in physics is essential for comprehending the behavior of objects in motion. Mass is the measure of the quantity of inertia of an object, affecting its resistance to changes in motion. In translational cases, inertia is termed as mass, measured in kilog
0 views • 8 slides
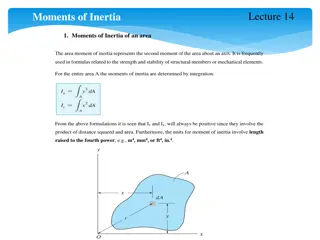
Understanding Moments of Inertia in Structural Mechanics
Moments of inertia of an area play a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of structural members and mechanical elements. This includes concepts such as area moment of inertia, parallel-axis theorem, and radius of gyration. The integration process, positive nature, and units of mome
0 views • 5 slides
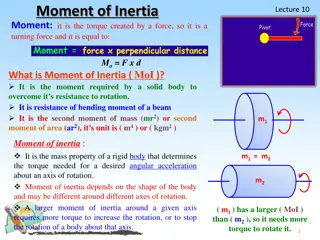
Understanding Moment of Inertia and its Importance in Mechanics
Moment of Inertia (MoI) is a crucial concept in mechanics, representing a body's resistance to rotation. It depends on the shape of the object and influences the torque required for rotation. This property plays a significant role in structural mechanics and stress analysis, contributing to understa
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Power System Inertia in Inverter-Dominated Networks
This study explores the impact of high levels of instantaneous inverter-based renewable energy penetration on power system inertia. It delves into fundamental concepts of energy balance, frequency control, load/frequency characteristics, and the importance of system inertia in maintaining grid stabi
0 views • 20 slides
Moment of Inertia Calculations in Engineering Mechanics - Problems and Solutions
The content covers problems related to calculating moments of inertia in engineering mechanics, specifically focusing on triangular areas, shaded areas, and circles. Detailed step-by-step solutions are provided for each problem, including determining moments of inertia about different axes and findi
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Area Moment of Inertia and Centroidal Axis in Mechanics
Explore the concept of area moment of inertia and centroidal axis in mechanics through detailed explanations and visual representations. Learn how to determine moment of inertia, locate the centroid, and understand the principles behind mass moment of inertia. Dive into the calculation methods and p
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Rotational Kinetic Energy and Moment of Inertia
Rotational kinetic energy arises from the motion of mass in a rotating object, while moment of inertia quantifies an object's resistance to rotational motion. This concept is crucial for analyzing the energy and stability of rotating systems. The content explains the calculation of kinetic energy fo
0 views • 7 slides
Optimus Prime's Transformation Challenge: Angular Momentum and Moment of Inertia Exploration
Dr. Mark Huntress, a Chemistry and Physics professor, devises a transformative assignment on rotation. As Optimus Prime aims to rotate as fast as possible with minimal external forces, students explore whether he should transform into a disk, ring, or solid sphere. Through a four-part exploration in
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Rotational Dynamics in Physics
General announcements for a physics class covering topics on rigid bodies, torque, moment of inertia, and rotational Newton's second law. Learn about the importance of moment of inertia, calculating rotational inertia, and the application of Rotational N2L in problem-solving exercises. Explore the r
0 views • 21 slides
Experimental Determination of Moment of Inertia in Rotational Dynamics Lab
In this university lab experiment, students apply known torques to various objects to measure angular accelerations and determine their moments of inertia. The setup involves rotating discs and rods with masses, using a rotational sensor for data collection. Important steps include measuring diamete
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Power System Stability: Synchronous Machines and Dynamics
Power system stability is crucial for maintaining synchronism and continuity. It includes steady-state and transient stability, with dynamics of synchronous machines playing a key role. Different types of disturbances can affect stability, requiring a system's ability to adjust and return to normal
0 views • 73 slides