BRIDGE EXPANSION JOINT
Bridge expansion joints are crucial components that provide continuity between different parts of bridge structures, accommodating movements caused by various factors like thermal deformation and traffic loads. They come in different types based on movement ranges and construction methods, such as s
5 views • 34 slides
Faults in the Earth's Crust
Stresses in the earth's crust can lead to the formation of faults, where rocks are displaced due to relative movement. Faults can vary in size and shape, with different types such as normal faults. Movement along fault planes can be either translational or rotational. This classification helps in un
2 views • 12 slides
Metal Alloys Forming Operations: Forging, Casting, and More
Metal alloys undergo forming operations like forging, rolling, extrusion, and casting to change their shape through plastic deformation. Hot working and cold working processes are utilized to enhance mechanical properties. Techniques such as sand casting, die casting, and investment casting are empl
0 views • 18 slides
2D Geometric Transformations for Computer Graphics
In this lecture on 2D Geometric Transformations, Assistant Professor Dr. Samsun M. BA ARICI covers topics such as translation, rotation, scaling, homogeneous representations, and coordinates. The lecture delves into basic transformations like reflection and shearing, as well as practical application
3 views • 81 slides
TPC Mechanical Support Considerations for ILD Integration Task Force Meeting
During the ILD Integration Task Force meeting, discussions revolved around the deformation of the TPC under weight and pressure, fixation points for hanging the TPC, considerations for supporting the TPC with the Cryostat or HCAL, and dealing with potential service clashes. Challenges and preference
0 views • 5 slides
True Stress and Strain in Materials
In materials engineering, the use of true stress and true strain provides a more accurate representation of material behavior, especially in regions undergoing deformation like necking. True stress considers the instantaneous cross-sectional area, accounting for changes in the material's strength du
0 views • 15 slides
Axial Deformation in Mechanics of Materials
In the study of mechanics of materials, axial deformation is analyzed by simplifying real structural elements. This approach involves approximations that are generally satisfactory and work due to factors like allowable stress design, factor of safety, and statistical analysis of strength. Saint-Ven
0 views • 9 slides
Ocean Basins and Their Characteristics
Ocean basins are vast submarine regions that cover a significant portion of the Earth's surface, hosting the majority of the planet's water. These basins exhibit various features such as ocean ridges, deep-sea trenches, and seismic ridges. The ocean floor is constantly evolving due to plate tectonic
1 views • 18 slides
Plate Tectonics: Evolution of the Earth
Explore the dynamic process of plate tectonics shaping the Earth's crust through the movement of tectonic plates, subduction zones, divergent and convergent boundaries. Discover how seafloor spreading creates new oceanic crust, and learn about the geological features formed by these processes.
0 views • 25 slides
The Goldschmidt System in Geology
Explore the Goldschmidt System in geology, which classifies chemical elements based on their preferred host phases. Learn about lithophile elements concentrated in the Earth's crust and the elemental composition of the crust. Discover the significance of chondrites in meteorites and the foundational
0 views • 11 slides
Minerals and Rocks in Earth's Crust
Explore the fascinating world of minerals and rocks in Earth's crust in Chapter 5. Learn about the characteristics of minerals, the most common rock-forming minerals, and how they shape our planet. Discover the distinction between silicate and nonsilicate minerals and their abundance in the crust. G
1 views • 47 slides
Unveiling Earth's Riches: Resources, Minerals, and Sustainability
Australia is known for its abundant natural resources, including coal, gas, minerals, and metals. However, the country faces challenges with water scarcity. The Earth's crust holds valuable resources essential for everyday items and fuels. Understanding the importance of using resources wisely for a
0 views • 16 slides
Efficient Dynamic Skinning with Low-Rank Helper Bone Controllers
This research explores efficient dynamic skinning methods using low-rank helper bone controllers to achieve robust, simple, and high-performance skin deformation in computer graphics. By investigating linear blend skinning techniques and helper bone rigs, the study aims to address the wishlist of ga
2 views • 29 slides
Plate Tectonics and Earth's Crust
Explore the differences between oceanic and continental crust, the distinctions of lithosphere and asthenosphere, the dynamics of convergent and divergent boundaries, as well as the concepts of folding and faulting in geological formations. Delve into the characteristics of oceanic crust versus ocea
0 views • 10 slides
Laplacian Deformation in Engineering and Applied Science
Laplacian deformation is a technique used in non-rigid registration to account for shape variance and improve fitting between source and target shapes. This method involves minimizing the distance and distortion terms to achieve accurate alignment. Intrinsic and extrinsic methods are discussed, wher
0 views • 53 slides
Thermal and Mechanical Simulation of Beryllium Window for MICE 201 MHz Cavity
Conducted thermal and mechanical simulations using TEM3P for the beryllium window of the MICE 201 MHz cavity. Analysis focused on temperature distribution, frequency shifts, thermal deformation control, and stress considerations under varying operation conditions and material properties. Detailed in
0 views • 11 slides
Aeroelasticity: Deformation and Aerodynamic Forces
Aeroelasticity explores the intricate relationship between the deformation of elastic structures in an airstream and the resulting aerodynamic forces. This field of study is vital for predicting and managing interactions between structural mechanics and aerodynamics in aircraft design. Historical in
4 views • 15 slides
Basics of Metal Forming Processes
Metal forming processes play a crucial role in shaping products, with casting, machining, joining, and deformation being the primary methods. Each process has its advantages and limitations, catering to different needs for accuracy, material wastage, complexity, and production quantities. Understand
0 views • 22 slides
Earth's Internal Structure: A Geographical Perspective
Deep parts of Earth's interior are studied indirectly through geophysics, including seismic waves, magnetic fields, gravity, and heat. Seismic studies reveal Earth's layers - crust, mantle, and core - each with distinct properties and compositions. The lithosphere, comprising the upper mantle and cr
0 views • 12 slides
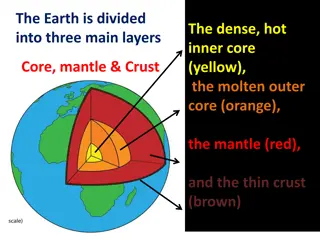
Journey to the Earth's Layers
The Earth's structure consists of four main layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin, rocky layer we see on the surface, while the mantle is a solid layer that flows like a viscous liquid. The outer core is a hot, melted layer of iron and nickel, and the inner cor
2 views • 10 slides
Journey to the Center of the Earth: Unveiling the Layers
Delve into the depths of the Earth with Dr. A.V. Tejankar to explore the three main layers - Crust, Mantle, and Core. Discover how the Earth's composition and physical properties vary across these layers, resembling the layers of an egg. Uncover the secrets of the Earth's interior, from the thin but
0 views • 15 slides
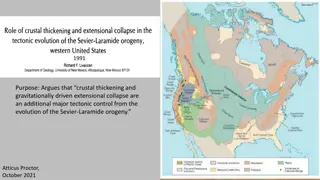
Tectonic Controls of the Sevier-Laramide Orogeny
The Sevier-Laramide orogeny was influenced by crustal thickening and gravitational extensional collapse. The tectonic model proposed suggests that conductive heating from subduction weakened the crust, leading to compression, uplift, and lateral growth. Deformation persisted from the Cretaceous to t
0 views • 8 slides
Earth's Changing Crust: Landforms, Rocks, and Minerals
The Earth's crust is in constant motion due to plate tectonics, which results in various landforms, rocks, and minerals. This movement is driven by forces such as tension, compression, and shear, causing earthquakes, mountains, and volcanic activity. Through processes like weathering and erosion, th
0 views • 26 slides
Crust Deformation: Forces, Stress, and Isostatic Adjustments
The Earth's crust undergoes various forms of deformation such as bending, tilting, and breaking due to forces like compression, tension, and shearing. Isostatic adjustments play a role in areas with mountain ranges, causing the crust to bend up and down. As mountain ranges erode, the crust lightens
0 views • 9 slides
Displacement, Deformation, and Normal Strain in Mechanics of Materials
Displacement and deformation in materials play a crucial role when loads are applied, leading to normal strain. This lecture discusses the concepts of displacement, deformation, and strain, covering topics such as types of strain, strain units, normal strain calculations, and the orientation of norm
0 views • 7 slides
Deformation and Strain in Engineering
Deformation occurs when a force is applied to a body, causing changes in its shape and size. Normal strain refers to the elongation or contraction of a line segment per unit length, while shear strain is the change in angle between two originally perpendicular line segments. Cartesian strain compone
0 views • 6 slides
Speckle Tracking Echocardiography Basics
Speckle tracking echocardiography is a method analyzing speckle artifacts in ultrasound images to obtain information on myocardial motion and deformation. By tracking speckles in the ventricle wall, parameters like motion displacement, velocity, strain, and strain rate can be measured. Deformation c
1 views • 12 slides
Strain Gauges and Deformation in Beams
Explore the concepts of strain gauges and resistors, how loading deforms beams, and Da Vinci's insights on spring bending. Learn about axial strain measurement, strain proportional to resistance change, bridge circuits, and formulas for cantilever beams. Understand the importance of strain gauge att
1 views • 9 slides
Adaptive Grids Towards Interactive Tourist Map Deformation
In this Ph.D. defense by Pio Claudio under the guidance of Prof. Sungeui Yoon, the study focuses on the optimization of tourist map layouts through adaptive grids for interactive exploration. The research delves into enhancing tourist map functionality, including content-aware grid developments and
1 views • 78 slides
Description of the spectra of the lowest states for a chain
The evolution of shape in Zr isotopes is analyzed using the geometric collective model, revealing transitions between spherical and deformed shapes with configurations mixing. The collective quadrupole Bohr Hamiltonian is employed, with deformation parameters determining the nucleus's shape. The stu
1 views • 9 slides
Physics of Elastic Continua - Stress, Strain, and Waves
In this lecture, we delve into the physics of elastic continua, focusing on stress, strain, and waves in elastic media. Topics include deformation components, rotation of material, effects of strain on vectors, and more. The discussion continues with a detailed look at deformation and its components
0 views • 21 slides
The Goldschmidt System and Lithophile Elements
The Goldschmidt System in geology classifies elements based on their preferred host phases, with Lithophile elements being concentrated in the Earth's crust. This classification, developed by Victor Moritz Goldschmidt, helps us understand the composition of Chondrites and the elemental makeup of the
0 views • 11 slides
Interpreting Fault Parameters and Block Models in Crustal Deformation
Rooted in plate tectonics theory and continuum models, this study explores the caveats and interpretations of fault parameters and block models in active crustal deformation. Emphasizing the differences between block and continuum models, it delves into the nuances of fault slip rates, block rotatio
0 views • 19 slides
Prediction of Al-alloy Hot Extrudate Deformation
This project aims to develop an accurate elasto-viscoplastic constitutive model for Al-alloy heat sink extrusion to predict and minimize warpage deformation, enhancing production efficiency and cost-effectiveness in thermal management applications.
0 views • 4 slides
Analysis of Thermal Fatigue in Surface Mount Resistor Under Creep Deformation
Surface mount resistors are subjected to thermal cycling leading to thermal stresses, primarily in the solder joints. This study utilizes two fatigue models to predict the life of a surface mount resistor assembly. Detailed modeling and analysis of the solder joint, including creep deformation and s
0 views • 13 slides
Laplacian Deformation in Engineering and Applied Science
Explore Laplacian deformation techniques in the context of non-rigid registration at Washington University in St. Louis, School of Engineering and Applied Science. Learn about rigid-body transformations, iterative improvement methods, intrinsic vs. extrinsic registration, and more. Discover how non-
0 views • 53 slides
Earth's Layered Structure: Core, Mantle, Crust and More
Explore the Earth's structure divided into core, mantle, crust, and various layers with distinct characteristics. Learn about the composition and depths of the different layers in the Earth's interior.
0 views • 8 slides
Microscopic Study of Neutron Star Inner Crust
Explore the detailed analysis of the inner crust of neutron stars, including complex nuclei structures, pasta phases, and their influence on crustal oscillations and cooling processes. Various quantum methods and boundary conditions are examined to understand the properties of pasta nuclei.
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Hydrothermal Fluid Movement in Earth's Crust
Exploring the movement of hydrothermal fluids in the Earth's crust is essential for mineralization. Factors affecting fluid flow at a crustal scale, such as original and induced openings in rocks, play a significant role in the transport of metals to form ore deposits.
0 views • 4 slides
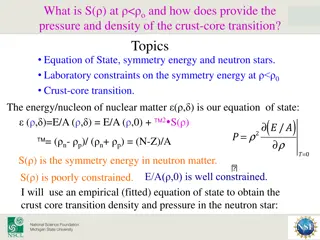
Crust-Core Transition in Neutron Stars: Symmetry Energy and Laboratory Constraints
Discover how the symmetry energy influences the pressure and density of the crust-core transition in neutron stars. Explore topics like Equation of State, Laboratory Constraints, and Symmetry Energy. Learn about adiabatic instability and spinodal decomposition, as well as the conditions at the crust
0 views • 16 slides