The Goldschmidt System in Geology
Explore the Goldschmidt System in geology, which classifies chemical elements based on their preferred host phases. Learn about lithophile elements concentrated in the Earth's crust and the elemental composition of the crust. Discover the significance of chondrites in meteorites and the foundational work of Victor Moritz Goldschmidt in geochemistry and crystal chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
AS-A level Geology The Goldschmidt System Click anywhere on the screen to move on. AS-A level Geology
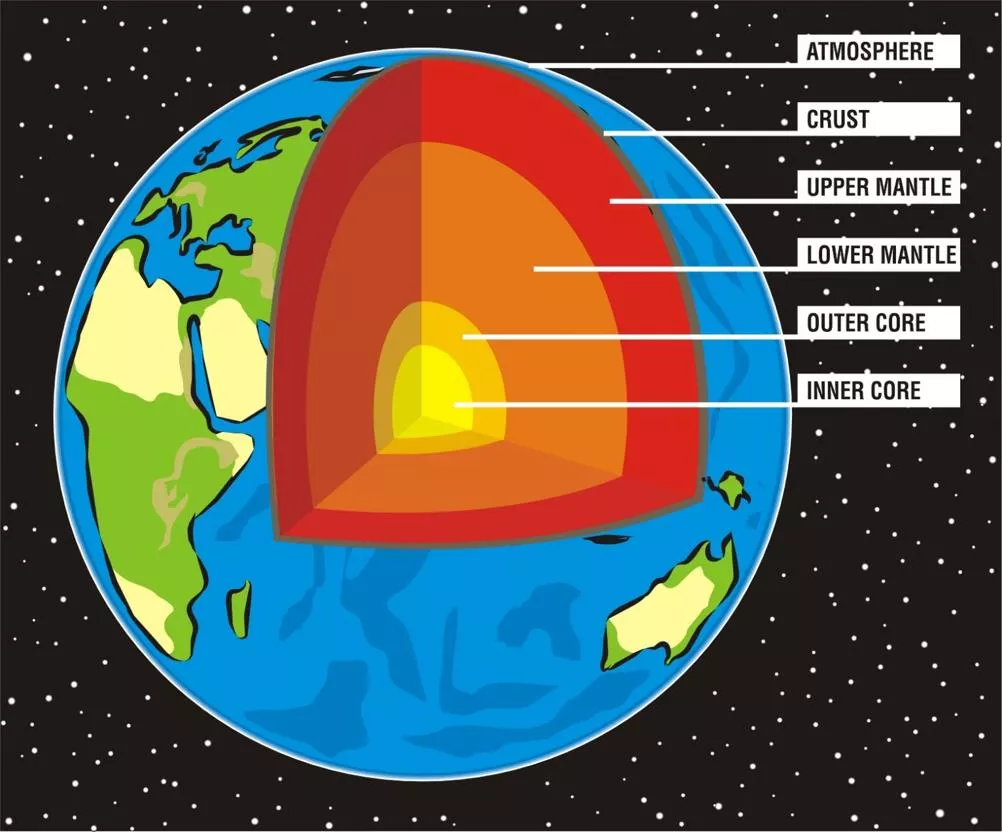
Chemistry of the Earth AS-A level Geology
Bulk composition comparable to Chondrites Chondrites are one of the stony meteorites, formed when various types of dust and small grains that were present in the early solar system accreted to form primitive asteroids Chondrites are the most common type of meteorite accounting for approximately 82% of all meteorites AS-A level Geology
The Goldschmidt Classification of Elements Swedish born mineralogist considered to be one of the founders of modern geochemistry and crystal chemistry Chemical elements on the periodic table are classified into groups according to their preferred host phases 4 groups are recognised: Lithophile, Siderophile, Chalcophile and Atmophile Victor Moritz Goldschmidt 1888 - 1947 AS-A level Geology
The Goldschmidt Classification of Elements AS-A level Geology
Lithophile Elements - Concentrated in the Crust Lithophile (rock loving) elements are found close to the Earth s surface as they combine readily with oxygen, forming compounds that do not sink into the core. The lithophile elements include: Aluminium Calcium Potassium Magnesium Sodium Oxygen Silicon Titanium AS-A level Geology
Elemental Composition of the Earths Crust Elemental Composition of the Earth s Crust 99% of the earth s crust by weight is made up of just eight elements: Oxygen Silicon Aluminium Iron Calcium Sodium Potassium Magnesium AS-A level Geology
Lithophile Elements Concentrated in the Crust Found in the silicate minerals which make up 93% of the crust by mass and constitute the common rock-forming minerals Quartz Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Mica Muscovite Mica Hornblende (Amphibole) Augite (Pyroxene) Olivine Garnet Clay Minerals (Kaolinite) AS-A level Geology
Siderophile Elements Concentrated in the Core Siderophile (iron-loving) elements High density metals Tend to sink into the Earth s core Do not combine with oxygen Dissolve readily in iron as solid solutions or in the molten state The siderophile elements include Gold Iridium Iron Molybdenum Nickel Platinum AS-A level Geology
Chalcophile Elements Trace amounts in the Crust Chalcophile (ore-loving) elements Combine readily with sulphur Form compounds that do not sink to the core Make up just 0.046% of crust by mass (More concentrated in mineral veins) Chalcophile elements include Arsenic Cadmium Copper Lead Silver Sulphur Tin Zinc AS-A level Geology
Atmophile Elements Concentrated in the Atmosphere and Hydrosphere Atmophile (atmosphere-loving) elements Also known as volatile elements Occur in gases and liquids close to the Earth s surface The atmophile elements are Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Argon Helium Neon Krypton Xenon AS-A level Geology