Comparison of Simeprevir vs. Telaprevir in HCV Genotype 1 Non-Responders
The ATTAIN study compared simeprevir and telaprevir in previous non-responders with genotype 1 HCV. The study included 379 patients with simeprevir and 384 with telaprevir, focusing on SVR12 as the primary endpoint. Baseline characteristics, treatment regimens, patient disposition, and virologic outcomes were analyzed. The study aimed to demonstrate non-inferiority of simeprevir compared to telaprevir in achieving SVR12. Results indicated comparable efficacy between the two treatment groups, with both regimens showing tolerable safety profiles. Detailed analyses of patient demographics and treatment responses were provided. The study also examined NS3 sequencing data to identify emerging mutations post-treatment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
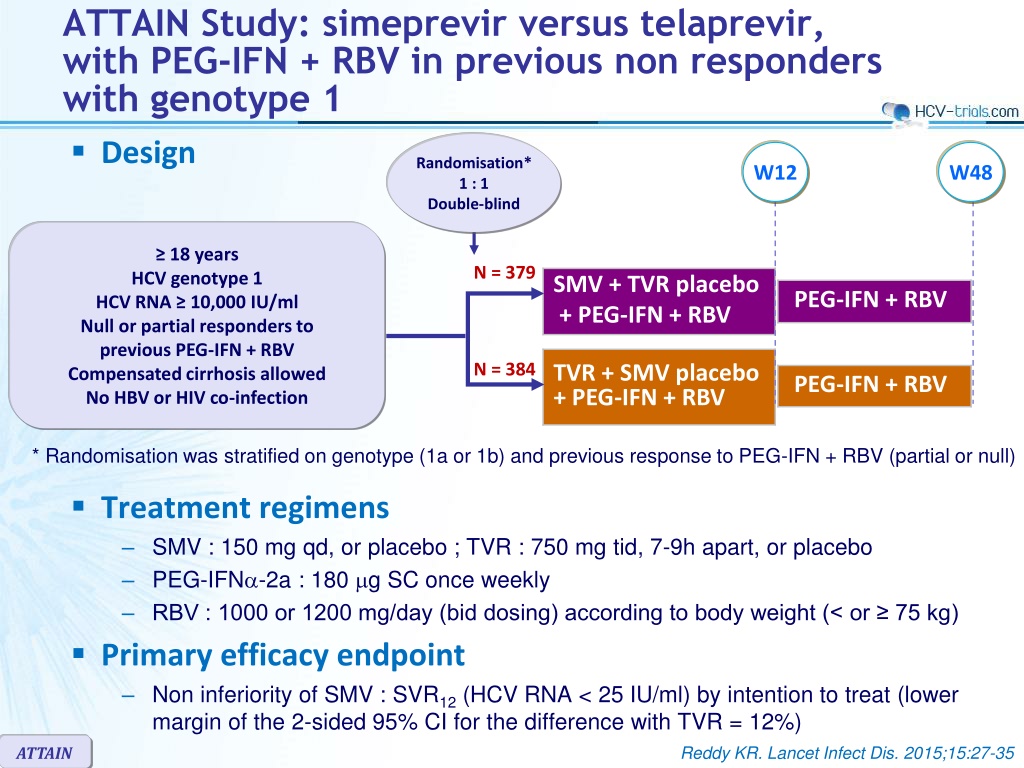
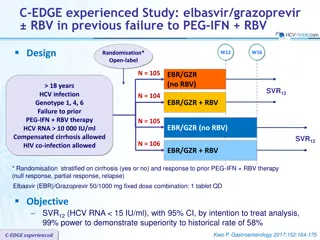
ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1 Design Randomisation* 1 : 1 Double-blind W12 W48 18 years HCV genotype 1 HCV RNA 10,000 IU/ml Null or partial responders to previous PEG-IFN + RBV Compensated cirrhosis allowed No HBV or HIV co-infection N = 379 SMV + TVR placebo + PEG-IFN + RBV PEG-IFN + RBV N = 384 TVR + SMV placebo + PEG-IFN + RBV PEG-IFN + RBV * Randomisation was stratified on genotype (1a or 1b) and previous response to PEG-IFN + RBV (partial or null) Treatment regimens SMV : 150 mg qd, or placebo ; TVR : 750 mg tid, 7-9h apart, or placebo PEG-IFN -2a : 180 g SC once weekly RBV : 1000 or 1200 mg/day (bid dosing) according to body weight (< or 75 kg) Primary efficacy endpoint Non inferiority of SMV : SVR12(HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) by intention to treat (lower margin of the 2-sided 95% CI for the difference with TVR = 12%) Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35 ATTAIN
ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1 Baseline characteristics and patient disposition SMV N = 379 50 36% TVR N = 384 52 42% Median age, years Female Genotype 1a (Q80K present /Q80K absent) 1b Other IL28B CC genotype HCV RNA log10IU/ml, median Metavir fibrosis score F0-F2 / F3-F4 Prior treatment with PEG-IFN + RBV Null response Partial response Discontinued treatment, n Adverse event Lost to follow-up Withdrawal 43% (23% / 77%) 57% < 1% 4% 6.56 56% / 44% 42% (17% / 83%) 57% 1% 5% 6.57 55% / 45% 62% 38% 21 0 10 11 62% 38% 29 4 6 19 Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35 ATTAIN
ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1 SVR12(HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) % 100 TVR SMV 80 70 68 67 64 55 60 54 46 44 44 40 39 40 34 27 26 20 N 379 384 234 238 145 146 124 133 37 27 215 220 215 220 0 All Previous null response Previous partial response 1a Q80K- 1a Q80K+ 1b Cirrhosis difference : - 1.1% (95% CI : -7.8 to 5.5) SMV TVR On treatment failure 34% 20% Viral breaktrough 22% 20% Relapse 17% 17% Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35 ATTAIN
ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1 NS3 Sequencing SMV TVR Sequencing available 148/176 failures 134/176 failures Emerging mutations 142/148 111/134 80 122 155 168 36 54 155 156 Main mutations detected (positions) Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35 ATTAIN
ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1 Adverse events, N (%) SMV, N = 379 12 (3%) 72 (19%) 14 (4%) 8 (2%) TVR, N = 384 39 (10%) 84 (22%) 21 (5%) 33 (9%) AE leading to treatment discontinuation Grade 3 adverse event Grade 4 adverse event Serious adverse event Adverse event of interest Rash (any type) Pruritus Photosensitivity Neutropenia Anemia Dyspnea Increased bilirubin Additional AE in 20% of patients in either group Fatigue Pyrexia Headache Nausea 81 (21%) 122 (32%) 8 (2%) 69 (18%) 51 (13%) 27 (7%) 30 (8%) 119 (31%) 170 (44%) 1 (< 1%) 52 (14%) 144 (38%) 36 (9%) 28 (7%) 120 (32%) 81 (21%) 95 (25%) 64 (17%) 146 (38%) 94 (24%) 111 (29%) 109 (28%) Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35 ATTAIN
ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1 Summary SMV + PEG-IFN + RBV showed non-inferiority with regard to SVR12 to TVR + PEG-IFN + RBV in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection and compensated liver disease who were null or partial responders to previous treatment with PEG-IFN + RBV Non-inferiority was met for null or partial responders separately as well Rates of on-treatment failure, viral breakthrough, and relapse were similar between the two treatment groups The incidence of adverse events deemed at least possibly related to SMV or TVR was noticeably lower in the SMV group, and most adverse events were grade 1 or 2 Serious adverse events were infrequent and less common in the SMV group, and fewer patients needed to discontinue SMV compared with TVR because of an adverse event Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35 ATTAIN