Explaining the Earth's Tilt and Seasonal Changes
The Earth's tilt causes seasonal changes, leading to winter in the hemisphere tilted away from the Sun, resulting in colder weather due to reduced sunlight. Understanding the tilt helps explain why seasons vary across different parts of the same hemisphere, impacting temperatures and daylight length. Explore the differences between seasons, the effects of Earth's tilt on weather patterns, and how globes depict this tilt. Discover why the UK experiences seasons due to Earth's 23.5-degree tilt, affecting sunlight distribution throughout the year.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
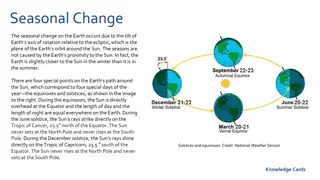
*The seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth. Winter happens on the part of the Earth which is tilted away from the Sun. The tilt makes the days shorter and reduces the amount of sunlight that falls on that part of Earth's surface, so that the weather is colder.
WHY DO WE HAVE SEASONS?
Wednesday 1st July 2020 WALT: explain how the Earth s tilt leads to seasonal changes Success criteria: I can describe how the Earth orbits around the Sun while it is turning on its axis. I can explain how the tilt of the Earth s axis causes seasons. I can use my pictures or models to explain why a season is not exactly the same in different parts of the same hemisphere. Key vocabulary: autumn, axis, equinox, hemisphere, northern, North Pole, orbit, rotation, solstice, southern, South Pole, spring, summer, sunrise, sunset, temperature, tilt, winter
What are the differences between the seasons? What is it like in each season? What kinds of weather do you expect in spring? Summer? Autumn? Winter? How do temperatures change from one season to another? Does anything else change? Have you heard people say the days are getting longer or the nights are drawing in ? What do they mean? I need you write our ideas draw them this is where you share your ideas :
Why do globes always show the Earth tilted? Is it really tilted or is this just for models? Scientists think another planet bumped into the Earth billions of years ago and made it tilt. The Earth is tilted at an angle of 23.5 . This is the reason we have seasons in the UK. The tilt angles Earth s northern hemisphere towards the Sun in the summer and away from it in winter, with midway points in spring and autumn. Which hemisphere is the UK in?
Do all parts of the globe get the same amount of light? What season would we have when the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun? The tilt of the Earth, with its influence on seasonal change, is a difficult concept for children to understand. It may be demonstrated with a torch and a globe as shown here, but it is hard to see that the globe is less brightly lit where the rays fall on it at a low angle. Imagine if we use an overhead projector to represent the Sun and a globe mounted on its tilted stand for the Earth. If someone walks round the Sun with the globe to show how it orbits the Sun, at the same time spinning it on its axis to show its daily movement, you can observe what happens to the way the light falls on the globe. The directions in which the poles point must remain the same. In winter, the North Pole is angled away from the Sun, and northern regions get very little sunlight and therefore become very cold. The globe and torch can be used to model this, and to show why the Sun looks low in the sky during the winter. It can also show how Arctic regions become permanently dark, with the Sun never rising at all.
Why Do We Have Different Seasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WgHmqv_-UbQ Mechanism of The Seasons https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=taHTA7S_JG k In the summer, the opposite happens: the North Pole leans towards the Sun, which appears much higher in the sky. Arctic regions now have perpetual daylight - the 'midnight sun'. You can do this at home with the globe(a big ball-to represent earth) and torch(represent Sun), as can the fact that in each case the opposite happens in the Antarctic.
Task: make a poster to show the position of the Earth and the Sun during summer and winter in the UK Remember to model the Earth s rotation (remembering the tilt) and to draw a poster-sized, labelled scientific drawing with the Sun and the Earth in two different positions in the Earth s orbit; one for summer and one for winter in the UK. Use the terms summer and winter , Earth s orbit , Earth s tilt and the Sun . Can you attempt to describe the seasons that Australia, Ghana and Antarctica would have, firstly when the UK has summer and then when the UK has winter. Remember to share whether the season is the same in each of the three countries and why
Check and Remember to do today: Have you described the different seasons in the UK in terms of day length and temperature changes? Have you shown in you drawings, modelling and presentations that the Earth s axis tilts? Have you explained how the tilt of the axis causes the seasons?
Your poster page You can add the poster (no cut and paste from website please) here or submit it as image either way look forward to your vision and also remember add explanations as it is vital for today s lesson. YOU MUST DRAW TO SHOW WHAT YOU HAVE UNDERSTOOD TODAY . Have a lovely DAY!