Argentina Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Overview
The Argentina Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (arg-ADNI) is a comprehensive program focusing on the early detection and characterization of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and related conditions. The initiative involves inviting and following patients through various stages, including baseline assessments, follow-ups at different intervals, and conducting screenings for different cognitive conditions. Several publications have highlighted the findings and contributions of the initiative towards understanding AD better. Ongoing research is also exploring neuropsychology and functional assessments in the context of AD.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
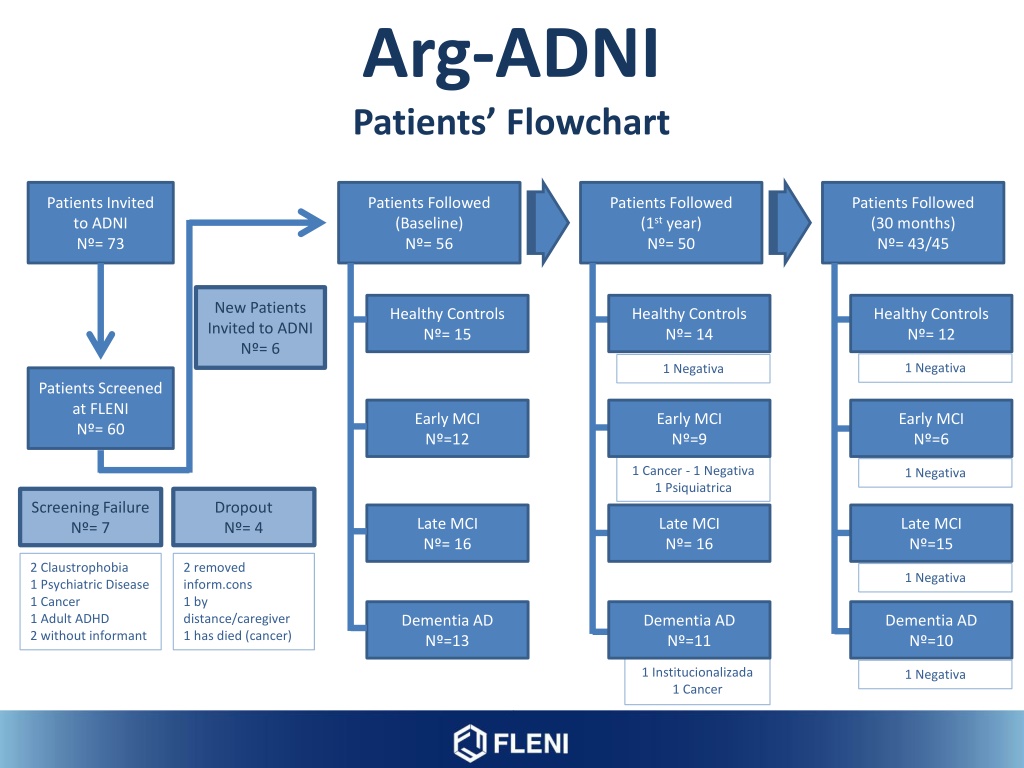
Arg-ADNI Patients Flowchart Patients Invited to ADNI N = 73 Patients Followed (Baseline) N = 56 Patients Followed (1styear) N = 50 Patients Followed (30 months) N = 43/45 New Patients Invited to ADNI N = 6 Healthy Controls N = 15 Healthy Controls N = 14 Healthy Controls N = 12 1 Negativa 1 Negativa Patients Screened at FLENI N = 60 Early MCI N =12 Early MCI N =9 Early MCI N =6 1 Cancer - 1 Negativa 1 Psiquiatrica 1 Negativa Screening Failure N = 7 Dropout N = 4 Late MCI N = 16 Late MCI N = 16 Late MCI N =15 2 Claustrophobia 1 Psychiatric Disease 1 Cancer 1 Adult ADHD 2 without informant 2 removed inform.cons 1 by distance/caregiver 1 has died (cancer) 1 Negativa Dementia AD N =13 Dementia AD N =11 Dementia AD N =10 1 Institucionalizada 1 Cancer 1 Negativa
Arg-ADNI News Follow-up 60 months Projected Follow-up Baseline Follow-up 60 month NPS Ass Alz Costs Survey MRI CSF A -tau (Optional) PET PiB PET-tau AV-1451 Healthy Controls 15 12 Early MCI 12 6 Late MCI 16 15 Dementia AD 13 10 TOTAL 56 43
Arg-ADNI Results Baseline Follow-up Follow-up Total N NPS Ass MRI CSF A -tau PET FDG PET PiB Follow- up 1 year Follow- up 30 month Follow- up 60 month Healthy Controls 15 15 15 11 15 15 13 12 2 Early MCI 12 12 12 7 10 8 10 6 1 Late MCI 16 16 16 14 16 15 16 15 1 Dementia AD 13 13 13 8 12 9 11 10 1 40 53 50 TOTAL 56 56 56 50 43 5 (71%) (95%) (89%)
Arg-ADNI Publications Published 2016 Creation of the Argentina-Alzheimer s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Mar a Julieta Russo, Gustavo Sevlever et al. Alzheimer s & Dementia 2014:10 S84 S87. Concordance Between 11C-PIB-PET and Clinical Diagnosis in a Memory Clinic. American Journal of Alzheimer s Disease & Other Dementias 2015:30(6) 599-606. Cognitive reserve and A 1-42 in mild cognitive impairment (Argentina-Alzheimer s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative). Paula Harris, Ricardo Allegri, et al. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 2015:11 2599 2604. Predicting episodic memory performance using different biomarkers: results from Argentina. Julieta Russo, Ricardo Allegri et al. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2016 vol. 12 pp. 2199-2206 Published 2017 Adding Recognition Discriminability Index to the Delayed Recall Is Useful to Predict Conversion from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer's Disease in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Russo, MJ; Campos, J; V zquez, S; Sevlever, G; Allegri, RF; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Front Aging Neurosci, 2017 vol. 9 pp. 46
Arg-ADNI Publications In development Argentina Alzheimer s disease neuroimaging initiative (arg-ADNI): Neuropsychology after one-year follow up. Patricio Chrem Mendez, Ricardo Allegri et al. Functional assessment in Argentina-ADNI: comparison and diagnostic utility of the Everyday Cognition (ECog) versus Functional Assessment Questionnaire (FAQ). Julieta Russo, Ricardo Allegri et al.