Understanding Mass and Inertia in Physics
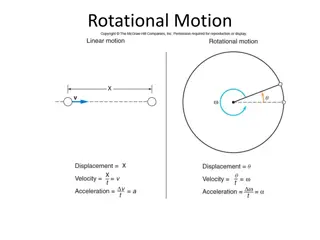
Understanding the concepts of mass and inertia in physics is essential for comprehending the behavior of objects in motion. Mass is the measure of the quantity of inertia of an object, affecting its resistance to changes in motion. In translational cases, inertia is termed as mass, measured in kilograms, while in rotational scenarios, it is known as moment of inertia, measured in kg.m2. The larger the mass or inertia, the more resistance there is to movement or change in spinning speed.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DR. RAJESH PRATAP SINGH ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR PHYSICAL EDUCATION CSJM UNIVERSITY CAMPUS , KANPUR MASS AND INERTIA
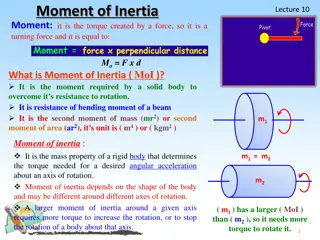
In linear (translational) cases, the inertia is called mass . The unit is (kg). The larger the mass, the tougher it is to push something to move or to slow In rotational cases, the inertia is called moment of inertia . The unit is (kg m2). The larger the Inertia, the tougher it is to swing a wheel up to fast spinning or to slow down the spinning. something down.
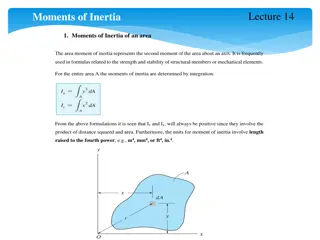
MASS THE MEASURE OF QUANTITY OF INERTIA OF AN OBJECT. MASS IS THE MEASURE OF INERTIA. SCALAR QUANTITY MAGNITUDE ONLY KILOGRAM (SI UNIT) The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion varies with mass. Mass is that quantity that is solely dependent upon the inertia of an object. The more inertia that an object has, the more mass that it has.