Understanding Enamel Pearls and Fluorosis: Dental Abnormalities Explained
Enamel pearls are small spherical projections on root surfaces that can lead to plaque retention and gum disease if left untreated. They are caused by abnormal enamel formation during tooth development. On the other hand, fluorosis is marked by enamel hypomineralization due to excessive fluoride ingestion, resulting in white or brown specks on teeth. Different stages of severity can be diagnosed using the Dean's Index.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
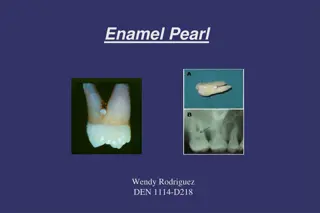
Natalee Carela WNH 20 January 2020 ENAMEL PEARL
WHAT IS AN ENAMEL PEARL? Enamel pearls appear as a small, spherical projection on root surfaces Mainly occurs on permanent dentition but it can also affect primary dentition Most commonly found at the Cementoenamel Junction and the furcation area of molars Will appear radiopaque on radiographs
ETIOLOGY Enamel Pearls are caused when ameloblasts migrate to the root s surface and causes enamel to be abnormally formed over the cemental root surface This abnormality occurs during the appositional stage of odontogenesis
EFFECTS OF ABNORMALITY Enamel Pearls can enhance plaque and biofilm retention This bacterial accumulation can eventually lead to inflammation, gum disease, periodontal pockets and bone loss
DENTAL HYGIENE CARE Radiographs must be carefully analyzed to be able to identify and diagnose enamel pearls before the development of periodontal disease These pearls can be confused with calculus when exploring BUT it will not dislodge when scaling. Attempting to forcefully remove it may result in a broken instrument tip instead.
Natalee Carela Jan.2020 FLUOROSIS
DEFINITION AND ETIOLOGY Fluorosis is a developmental disturbance marked by increased porosity of the enamel (hypomineralization) It may appear as white or dark brown specks /streaks and rough pitted enamel Damage to the enamel is permanent and there is various stages of severity, diagnosed using the Dean s Index It is caused by the ingestion of high levels of fluoride during enamel development Some examples: Drinking fluoridated water, using fluoride tablets and ingesting fluoride toothpaste
STAGES OF FLUOROSIS MODERATE MODERATE SEVERE SEVERE MILD MILD
ROLE OF DENTAL HYGIENISTS Educate the patient about Fluorosis and its possible causes Some treatment options available for Fluorosis include removing the stains through tooth whitening , veneers and bonding