Mammalian Tooth Structure: Vertical Section Overview
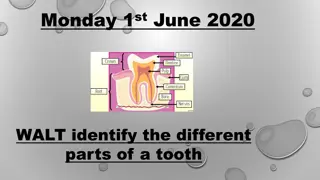
Mammalian teeth consist of hard tissues (enamel, dentine, cementum) and soft tissue (tooth pulp). The enamel is the hardest, dentine surrounds the pulp cavity, and cementum covers the dentine and connects to the alveolar bone. Tooth pulp provides support, nourishment, and defense mechanisms. Supporting tissues include the periodontium, gingiva, and tooth alveolus, each playing a vital role in maintaining tooth structure and function.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHAPTER 1. MAMMALIAN HISTOLOGY 1.2. Digestive system 1.2.Vertical Section of tooth T.Y.B.Sc. ZOOLOGY SEMESTER V COURSE XIII Histology, Pathology, Toxicology and Biostatistics
1.2. Digestive System : Vertical Section of Tooth Mammalian tooth is made up of two components i.e. hard tissues and soft tissues. The hard components are enamel, Dentine and cementum Soft tissue is tooth pulp. The supporting tissues are peridontium, Gingiva, and alveolar bone. 1. Enamel Hardest tissue; resistant to abrasion; less porous; contains fluorides. Synthesized during developmental stages and does not regenerate. Colour in young stages Bluish white. Colour in adult stages yellowish . 2. Dentine Hard calcified tissue forming crown and root of tooth. Surrounds pulp cavity. Produced by odontoblast cells. Ectomesenchymal in origin
3. Cementum Thin layer of mineralized tissue. Covers the dentine Connects the alveolar bone by periodontal ligaments. Produced by cementoblast cells. There are two types of cementum 1. Acellular- covers entire root surface 2. Cellular- found at the apex of root .
3. Soft tissues : Tooth Pulp Contains 75% water and 25% organic matrix. Fills the dental cavity. Comprised of loose connective tissue. It is made up of pulpal fibroblasts and free cells like histiocytes, plasma cells, antigen p[resenting cells and leucocytes. Provides nourishment and support. Also important in defense mechanism through immune cells. 4. Supporting tissues of the tooth a. Periodontoum : Strong flexible connection of bones; it is dense connective tissue present between cementum and alveolar bone. b. Gingiva (Gum): composed of lamina epithelialis made up of squamous epithelium and lamina propria made up of dense connective tissue. There are two type of gingiva i.e. free and attached gingiva. c. Tooth Alveolus (Socket): Suppports and protects the teeth. Part of mandible or maxilla. Composed of compact lamellar bone and spongy bone.