Mastering Microscope Focusing Techniques
Understand the essential parts of a light microscope, the magnification process, general procedures for handling a microscope, focusing techniques for specimens, and the relationship between magnification and field of view. Learn how to avoid damaging the microscope and achieve optimal results during observations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Care Parts Focusing
Light Microscope - uses compound (2) lenses to magnify objects. The lenses bend or refract light to make the object beneath them appear closer.
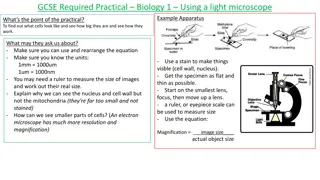
Eyepiece BodyTube RevolvingNosepiece Arm ObjectiveLens Stage StageClips CoarseFocus FineFocus Diaphragm Light Base
Magnification Your microscope has 3 magnifications (objective lenses): o o o High Scanning Low Each objective has its magnification labeled. In addition to this, the _______ ______ (eyepiece) has a magnification of __X. To calculate total magnification, ________ the ocular x objective. multiply Ocular Lens 10
General Procedures Make sure all backpacks and materials are out of the aisles and off the tops of desks. Store with cord wrapped around microscope and the scanning objective clicked into place. Carry by the base and arm with both hands.
Focusing Specimens 1. Always start with the Scanning Objective. 2. Place your specimen in the center of your field of view. 3. Use the Coarse Knob to focus. 4. Next, use the Fine knob until clear. 5. Once you've focused on Scanning, switch to Low Power. 6. Repeat steps 3-4. 7. Now, switch to High Power. 8. At this point, ONLY use the ____ ___________ _____ to focus specimens. Fine Adjustment Knob
Recap 1. Scanning --> use coarse and fine knob 2. Low power --> use coarse and fine knob 3. High power --> use fine knob only DO NOT SKIP STEPS!!!! What will happen if I use the course knob under high power? The slide or lens could crack
Field of View view Field of View: the area a person can _____ through a microscope. circle It is represented by a _______. RELATIONSHIP: As magnification __________, field of view __________. decreases increases As you switch from scanning (40X) to high power (100X), the area you see through the microscope gets smaller. We can see better detail with higher powers of magnification, but we cannot see as much of the image.
The lens inverts the image of the object inside the microscope. _________ means that the image appears upside down and backward compared with the actual object. Inverted This means that the slide must be moved in the opposite direction that you want the image to move. Ex. If you move the slide to the right on stage, as you look through the microscope the slide appears to move ____. left
Making a Wet Mount Slide 1. Get a clean slide and coverslip from your teacher. 2. Place ONE drop of water in the middle of the slide. 3. Place the specimen into the water. 4. Place the edge of the cover slip on one side of the water drop at a 45 angle. 5. Slowly lower the cover slip on top of the drop. THIS PREVENTS AIRBUBBLES.
Staining Specimens Scientists stain specimens to see parts of the cell more clearly. 1. Put a drop of stain (iodine) on a slide. Caution: methylene blue will stain clothes and skin. 2. Place specimen in the center of drop of stain. 3. Place a coverslip onto the slide.
Drawing Specimens 1. Use pencil - you can erase and shade areas 2. All drawings should include clear and proper labels (and be large enough to view details). Drawings should be labeled with the specimen name and magnification. 3. Specimens should be drawn to scale - Ex. if your specimen takes up the whole viewing field, make sure your drawing reflects that.
Practice Drawing should have: Fewer cells at a larger size
Cleanup 1. Store microscopes with the scanning objective in place. 2. Wrap cords and cover microscopes. *Double check to make sure you didn't leave a slide 3. Place microscopes in their designated location (probably a cabinet)
Troubleshooting Occasionally you may have trouble with working your microscope. Here are some common problems and solutions. 1. Image is too dark! Adjust the diaphragm, make sure your light is on. 2. There's a spot in my viewing field, even when I move the slide the spot stays in the same place! Your lens is dirty. Use lens paper, and only lens paper to carefully clean the objective and ocular lens. The ocular lens can be removed to clean the inside. The spot is probably a spec of dust. 3. I can't see anything under high power! Remember the steps, if you can't focus under scanning and then low power, you won't be able to focus anything under high power. Start at scanning and walk through the steps again. 4. Only half of my viewing field is lit, it looks like there's a half-moon in there! You probably don't have your objective fully clicked into place..
Quiz Over the Microscope 1. When focusing a specimen, you should always start with the ___________________ objective. 2. When using the high power objective, only the ________ ___________ knob should be used. 3. The type of microscope used in most science classes is the _________________ microscope 4. What part of the microscope can adjust the amount of light that hits the slide? ______________________________
5. You should carry the microscope by the ________ and the __________. 6. The objectives are attached to what part of the microscope (it can be rotated to click the lenses into place): _______________ ________________ 7. You should always store your microscope with the ________________ objective in place. 8. A microscope has an ocular objective of 10x and a high power objective of 50x. What is this microscope's total magnification? ____________