Understanding Coeliac Disease and Modified Diets for a Healthier Lifestyle
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the body's ability to process gluten, leading to various symptoms like abdominal pain, fatigue, and nutrient deficiencies. Following a modified diet, such as a vegetarian or gluten-free diet, can help manage these symptoms and promote better health. The dietary guidelines for individuals with Coeliac Disease include avoiding gluten-containing foods like wheat, barley, oats, and rye, and incorporating gluten-free alternatives like rice and corn. By making conscious food choices and being aware of suitable and unsuitable foods, individuals can effectively manage Coeliac Disease and improve their overall well-being.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet
Test Your Knowledge True or False Q1. Coeliac disease is a lifelong autoimmune condition. True or False Q2. Abdominal pain and diarrhoea are possible symptoms of coeliac disease. True or False Q3. Gluten causes the body s defence system to form hormones which mistakenly attack the villi of the small intestine. True or False Q4. Rye is a naturally gluten-free food. True or False Q5. Corn(maize) and rice should be avoided by individuals with coeliac disease. True or False
Modified Diets (HL) Definition Any diet altered to include or exclude certain foods or nutrients Reasons for modifying a diet? Personal Choice vegetarianism Health reasons diabetes; obesity; bowel disorders
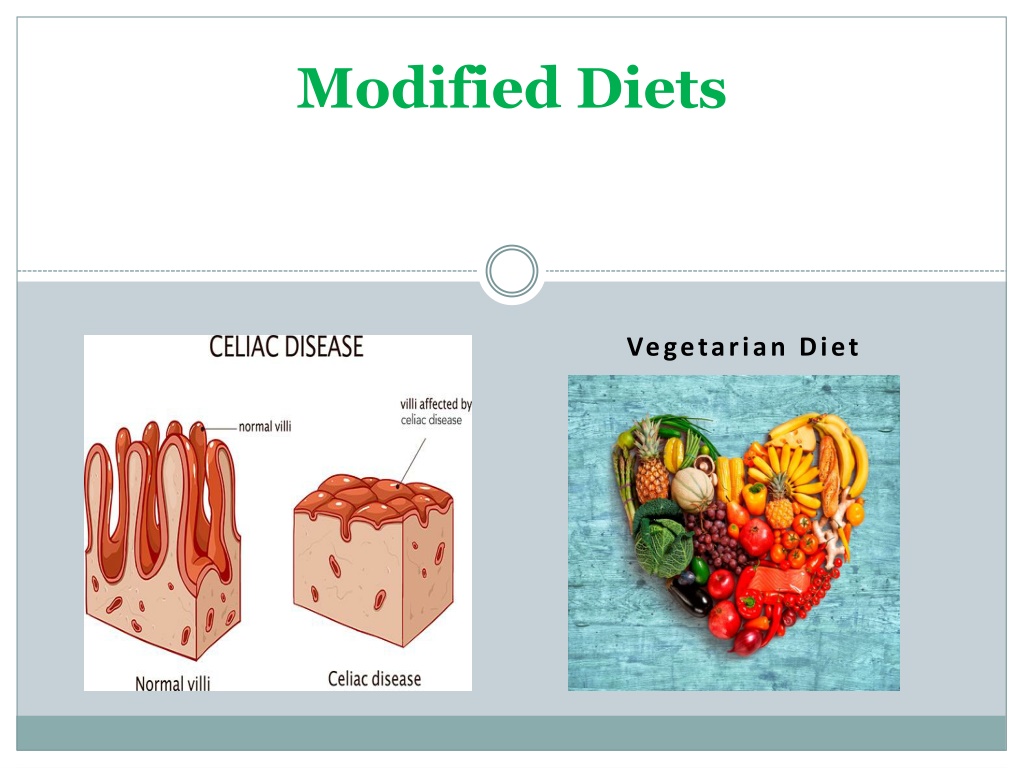
Modified Diets Coeliac Disease Definition An autoimmune condition that causes the immune system to mistake gluten as a threat to the body. The body s defence system then forms antibodies that attack the villi on internal surface of small intestine. This damage disrupts the body s ability to absorb nutrients from food, leading to malnourishment
Modified Diets Coeliac Disease Symptoms Nausea and vomiting Diarrhoea Bloating and abdominal pain Weight loss Tiredness and fatigue Slow growth in children due to lack of nutrients
Modified Diets Coeliac Disease Dietary Guidelines for those with Coeliac Disease Omit all foods containing gluten(wheat, barley, oats and rye) Include more rice and corn (naturally gluten- free) in the diet, to ensure a balanced diet Use a range of gluten-free foods eg gluten-free bread, breakfast cereals Read ingredient lists on food labels carefully, especially processed foods and check to see if the foods carry the gluten-free symbol
Modified Diets Coeliac Disease Foods Suitable gluten- free foods (natural) Suitable gluten- free foods (processed) Unsuitable foods containing gluten Fish Meat Rice Yoghurt Cheese Eggs Vegetables Fruit Commercial gluten- free versions of bread, pasta, biscuits and cakes Biscuits Bread Sausages Cakes Soups Sauces eg roux sauce Breaded/battered fish, poultry products
Learning Check Define coeliac condition. Name three foods which should be avoided by a person with coeliac condition.
Modified Diets Vegetarianism Definition The practice of not eating meat or fish, especially for moral, religious, or health reasons
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diets Lacto vegetarian diets Milk and dairy products allowed No eggs meat or fish Lacto-ovo vegetarian diets Milk, dairy products and eggs allowed No meat and fish Pesco-vegetarian diets Milk, dairy products eggs and fish allowed No meat HL Pollo-vegetarian diets Milk, dairy products eggs and poultry allowed No red meat or fish Vegan diets Plant based foods only No milk, dairy products, eggs, meat and fish
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet Reasons for choice Health low in saturated fat, higher in dietary fibre Religion/culture Buddists follow a vegetarian diet (believe killing animals is wrong) Sensory factors some people do not like th smell, appearance, taste and texture of meat and fish Economic cheaper as meat and fish excluded from diet Family a person may have adapted eating habits as a child as a result of other family members practicing a vegetarian diet Ethics wrong to kill/harm animals; disagree with intensive farming practices eg. caged hens
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet Dietary Guidelines Each meal should be nutritionally balanced Suitable meat alternatives TVP(textured vegetable protein); tofu; mycoprotein eg. Quorn Milk, cheese and yoghurt should be included in vegetarian dishes for calcium and HBV protein Combine two or more LBV protein foods to create complete proteins in the diet Include fortified products eg milk to increase intake of B12 and calcium consumption Use vegetable stock cubes in soups and sauces instead of chicken, fish or beef Vegans should include dairy food alternatives eg soya milk adequate calcium and Vitamin D intake Omit animal fats from the diet eg butter, use vegetable oils instead eg. olive oil
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet Advantages Reduces risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes reduced saturated fat intake Reduces incidence of bowel disorders higher fibre intake Reduced reliance on processed food so less so sugar and salt intake reduced risk of high blood pressure(hypertension) and type 2 diabetes Higher intake of vitamins and minerals due to a higher consumption of fresh produce eg fruit and vegetables.
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet Consider the following nutrients to avoid deficiencies Protein Vitamin B12 Include soya beans/soya products HBV protein Include eggs and dairy products in vegetarian diets Include meat alternatives eg TVP; tofu; mycoprotein Use fortified products eg soya milk and breakfast cereals prevent deficiency Combine 2 or more LBV protein foods to create complete proteins Supplements may be necessary in some cases
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet Consider the following nutrients to avoid deficiencies Zinc Iron Include dairy products and eggs in vegetarian diets Both haem and non-haem sources of iron should be included eg. green leafy vegetables and cereals as well as pulses Include green leafy vegetables, legumes and bread in vegetarian and vegan Include foods rich in Vitamin C eg. citrus fruits to enhance iron absorption Include some fortified products such as cereals, soya milk and breakfast cereals
Modified Diets Vegetarian Diet Consider the following nutrients to avoid deficiencies Vitamin D Calcium Include eggs and dairy products in vegetarian diets Include green leafy vegetables as well as nuts and seeds in vegetarian and vegan diets Include fortified foods eg. soya milk and breakfast cereals Dairy products should be included in vegetarian diets Supplements may be required in certain cases
Learning Check Explain the term lacto-vegetarian. Name 2 protein alternatives suitable for the diet of a vegetarian. State 2 specific dietary requirements of a lacto- vegetarian diet. In relation to each nutrient listed recommend two good sources for a vegan diet. Protein Calcium Iron