Understanding the Efficiency and Applications of LED Technology
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. This technology operates based on charge carrier recombination at a p-n junction diode. LED efficiency is calculated as the ratio of light output to electrical input power. Common applications of LEDs include burglar alarm systems, TVs, and computers. Explore the construction and working principles of LEDs to grasp their significance in modern lighting solutions.
Uploaded on Sep 25, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
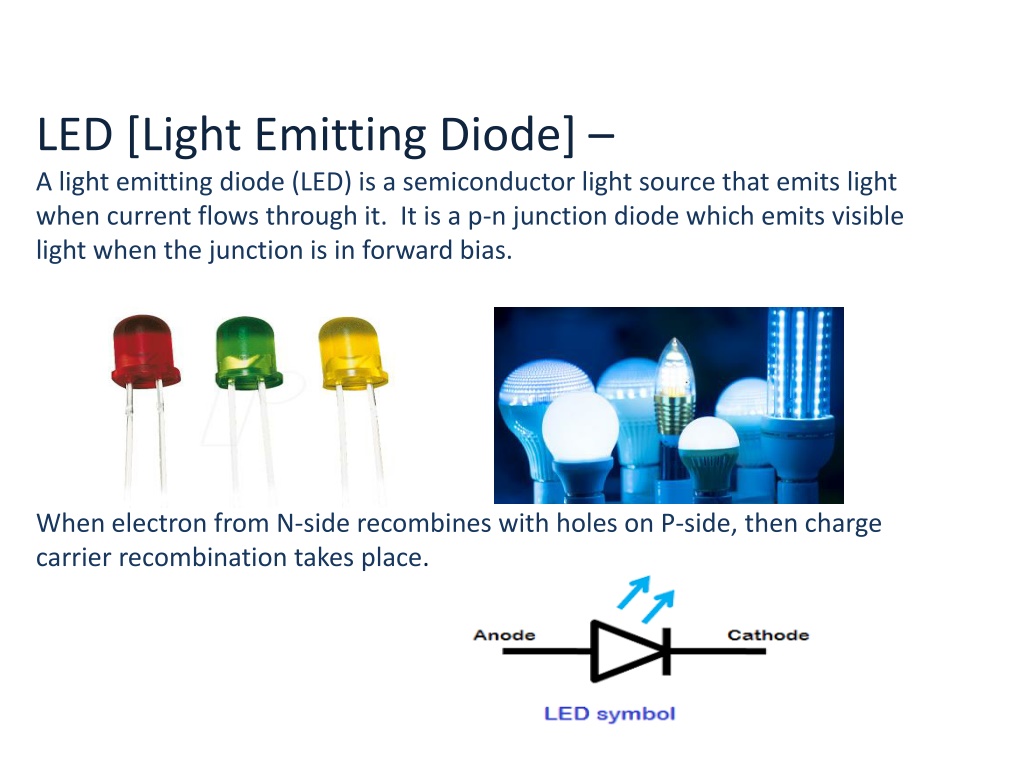
LED [Light Emitting Diode] A light emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. It is a p-n junction diode which emits visible light when the junction is in forward bias. When electron from N-side recombines with holes on P-side, then charge carrier recombination takes place.
LED Efficiency: It is defined as light output devided by the electrical input power. It is denoted by eta. Applications: 1) Burglar alarm system 2) T.V. , F.M. , Computers, etc.