Techniques in Ocular Examination for Gaze and Visual Fixation
Explore various techniques for assessing ocular alignment, range of motion, and eye movement in patients through sessions focusing on gaze testing, visual fixation, saccades, and smooth pursuit. Learn how to identify abnormalities such as nystagmus, saccadic movements, and pursuit asymmetries to aid in diagnosing neurological conditions affecting eye coordination and control.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
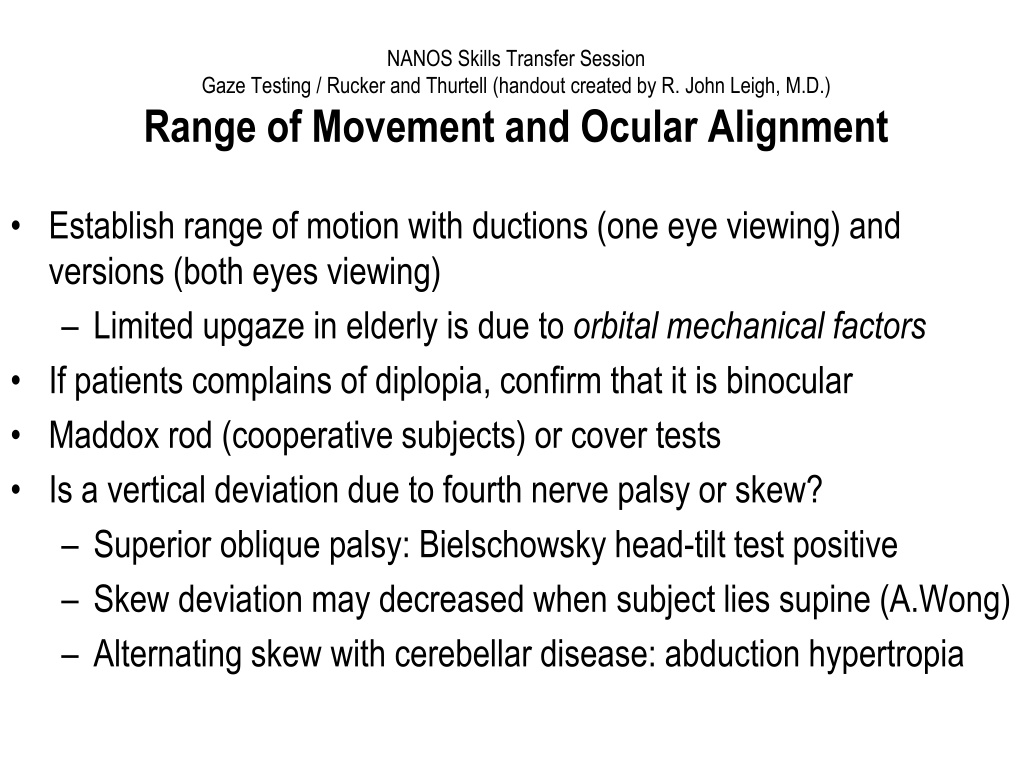
NANOS Skills Transfer Session Gaze Testing / Rucker and Thurtell (handout created by R. John Leigh, M.D.) Range of Movement and Ocular Alignment Establish range of motion with ductions (one eye viewing) and versions (both eyes viewing) Limited upgaze in elderly is due to orbital mechanical factors If patients complains of diplopia, confirm that it is binocular Maddox rod (cooperative subjects) or cover tests Is a vertical deviation due to fourth nerve palsy or skew? Superior oblique palsy: Bielschowsky head-tilt test positive Skew deviation may decreased when subject lies supine (A.Wong) Alternating skew with cerebellar disease: abduction hypertropia
NANOS Skills Transfer Session Visual Fixation Before formal gaze testing, with eyes in central position, look for nystagmus or uncalled-for saccades, by: Simple visual inspection Ophthalmoscope Frenzel goggles or high positive lens in darkness/flashlight In eccentric gaze: Look for gaze-evoked nystagmus (will affect interpretation of smooth pursuit), and then rebound nystagmus Determine the position of the eyes under closed lids by noting corrective movements when patients open their eyes (e.g., lateropulsion in Wallenberg's syndrome)
NANOS Skills Transfer Session Saccades Test (horizontal and vertical): Spontaneous saccades (e.g., during conversation) Saccades to non-specified targets Look right, left, up, down Saccades between two fixed visual targets e.g., pen, nose Rapid self-paced saccades between two fixed targets Antisaccades Eye-head saccades between two fixed visual targets Quick phases of optokinetic or rotational nystagmus Note: Initiation (prolonged reaction time, need to blink or make head movement) Speed (distinct from range of movement) Accuracy (look for corrective saccades indicating hypo- or hypermetria) Trajectory ( round-the-houses sign) Conjugacy (especially adduction slowing lag in INO)
NANOS Skills Transfer Session Gaze Testing / R. John Leigh, M.D. Smooth Pursuit and Eye-Head Tracking - 1 Instruct the patient to track a small moving target smoothly, horizontally and vertically; start slowly and progressively increase speed Look for corrective saccades that indicate an inappropriate smooth pursuit gain: If pursuit is deficient (low gain), corrective saccades will be catch-up If pursuit is too fast (increased gain), corrective saccades will be back-up If pursuit is in wrong direction, corrective saccades (off-axis) Use a small optokinetic drum or tape: To bring out pursuit asymmetries To detect inverted optokinetic nystagmus in congenital nystagmus Use a large mirror to induce smooth tracking in uncooperative patients
NANOS Skills Transfer Session Smooth Pursuit and Eye-Head Tracking - 2 Assess active, smooth eye tracking, looking for corrective saccades Test cancellation/suppression of the vestibulo-ocular reflex by rotating the patient in a chair while attempting to fixate a target moving with their head: Look for corrective saccades Useful to evaluate smooth tracking in patients with gaze-evoked nystagmus
NANOS Skills Transfer Session Vergence Note that during natural behavior, we combine vergence with saccades There are two main stimuli to convergence disparity (fusion) and accommodative (near) Conventional testing combines disparity and accommodative stimuli by asking patients to fixate a target brought in along the mid-sagittal plane toward the bridge of their nose To test vergence to accommodation: With one eye covered with a semi-opaque Spielmann occluder, the other eye alternately fixes upon near and distant targets aligned on this viewing eye. Note movements of eye under cover. To test vergence to disparity: Place a prism in front of one eye; then remove it. Note pupillary changes during vergence movements