Ocular Presentation in Diseases of Central Nervous System - MBBS Lecture
Ophthalmologist Dr. Sanjeev Kumar Mittal from AIIMS Rishikesh discusses the ocular manifestations of intracranial lesions, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis by ophthalmologists. Symptoms include headaches, vision changes, seizures, and more, while signs may include visual field defects, papilledema, and cranial nerve palsies. The lecture highlights the crucial role ophthalmologists play in detecting and referring patients with CNS-related eye issues.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ocular Presentation in Diseases of central Nervous system MBBS Lecture Dated 28-02-2018 Dr. Sanjeev Kumar Mittal Professor & Head, Dept of Ophthalmology All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh
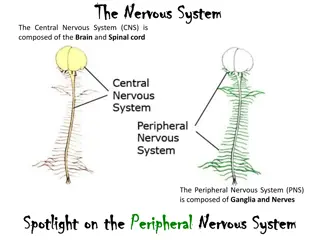
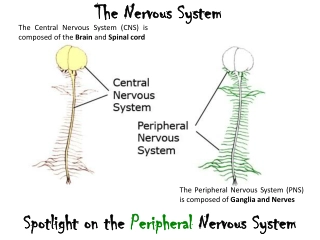
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Intracranial lesions may cause: -serious ocular signs and symptoms -neurological complications (raised ICT) -cranial nerve impairment or brain compression 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
INTRODUCTION Intracranial lesions may cause: -serious ocular signs and symptoms -neurological complications (raised ICT) -cranial nerve impairment or brain compression >50 % - present to an ophthalmologist initially 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
INTRODUCTION Intracranial lesions may cause: -serious ocular signs and symptoms -neurological complications (raised ICT) -cranial nerve impairment or brain compression >50 % - present to an ophthalmologist initially Ophthalmologists play a vital role in early diagnosis and proper referral. 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
HOW DO THE PATIENT PRESENT ? 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
CLINICAL PRESENTATION SYMPTOMS: Headache Diminution of Vision Seizures Behavioural and psychiatric changes Vertigo Paresis Dysphasia, dementia, deafness, tinnitus, ataxia, and diplopia etc. 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
CLINICAL PRESENTATION SIGNS(one or more of following depending upon location and size) Vision Visual field defects Proptosis Pupillary defect Papilloedema Optic atrophy 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
CLINICAL PRESENTATION SIGNS: Nystagmus Gaze palsy Paralytic squint [Cranial Nerve palsies-VI, VII, IV] 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Intracranial lesions MENINGITIS ENCEPHALITIS BRAIN ABSCESS NEUROSYPHILIS INFECTIONS 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Intracranial lesions INTRACRANIAL ANEURYSMS ISCHEMIC AND CIRCULATORY DISORDERS CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA AND HAEMORRAHGES HYDROCEPHALOUS 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
INTRACRANIAL ANEURYSMS- 2 to 3 % in the region of circle of willis 1. Congenital weakness in the wall 2. Post traumatic 3. Post infection Carotico-cavernous fistula 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA AND HAEMORRAHGES Transient ischaemic attacks Cerebral strokes Intra cerebral hematoma Sub arachnoid haemorrhage 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
HYDROCEPHALOUS Congenital acquired 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Intracranial lesions MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS DEMYLENATING LESIONS NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA SCHILDER'S DISEASE 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Loss of sensory or motor function of different parts of body Optic neuritis Sudden DV 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA Bilateral Optic neuritis with Lumbar / thoracic myelitis 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
SCHILDER'S DISEASE, DIFFUSE SCLEROSIS OPTIC RADIATION, RBN, Muscle palsy, Nystagmus 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Chronic Progressive Ophthalmoplegia friedreich s disease [hereditary ataxia] 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Intracranial lesions CONCUSSION INJURY TO BRAIN HEAD INJURY CEREBRAL CONTUSION FRACTURE BASE OF SKULL 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Intracranial lesions PRIMARY OPTIC TUMOURS SECONDARY TUMOURS ICSOLS HAMETOGENOUS LESION GRANULOMATOUS LESION PARASITIC CYST 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
most common types in adults pituitary adenoma meningioma craniopharyngioma 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF ICSOL OCULAR FEATURES Frontal lobe tumours(gliomas, meningiomas) 1 Slight bulging of eye ball (ipsilateral).If extension into chiasm -foster kennedy syndrome ,papilloedema,optic atrophy,psychic changes, Alteration in character and temperament Frontal lobe and optic nerve pushed up(simulates pituitary tumour) Olfactory groove tumours (meningiomas) 2 Sphenoidal ridge tumours (meningiomas) 3 Proptosis Pituitary tumours (adenomas) 4 Optic nerve ischemia then atrophy, Bitemporal heminopia, Colour field defective Suprasellar (Rathke s pouch) tumours (craniopharyngioma) Median area tumours (Meningiomas) 5 Papilloedema, diplopia(VI nerve involvement 6 Paralysis of V.VI,VII ,Homonymous hemianopia, Papilloedema Temporal lobe tumours (Gliomas, meningiomas) Occipital tumours 7 Contralateral homonymous hemianopia(Incongruous) 8 Congruous field defects Cerebellar tumours (medulloblastoma) 9 Coarse horizontal nystagmus,Bilateral papilledema,diplopia(VI nerve palsy) Paralysis of V.VI,VII 10 Cerebellopontine angle tumours (Neuromas, neurofibromas, or gliomas in connection with acoustic and vestibular nerves) 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Extra-ocular disturbances. (a) Sensory. (b) Motor. (c) Psychic (d) Endocrinal. 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
HOW DO WE CLINICALLY APPROACH........ 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
CLINICAL APPROACH HISTORY......v.v important Presenting complaint Past Family Personal habits OPHTHALMOLOGICAL: Vision (BCVA) Visual fields and colour perception Pupillary reflexes Displacement of the eyeball. 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
CLINICAL APPROACH Extraocular movements(gaze palsy, paralytic squint or nystagmus) Dilated fundus examination with IO( papilloedema, papillitis, optic nerve atrophy, retinal haemorrages, arteritis, atherosclerotic changes ,etc..) 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
HOW TO INVESTIGATE...??? 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
investigations BASELINE CBC with ESR URINE ROUTINE AND MICROSCOPY Special Investigations- MRI brain with orbit CT scan Fundus flurorescein angiography B- scan VER 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
investigations And other special investigations(if needed): Viral markers Mantoux test for Tuberculosis CSF analysis VDRL for syphilis Orbital biopsy FNAC of lesion X-Rays if needed Angiography Doppler ultrasonography 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Summary Detailed neuro- ophthalmic evaluation Judicious use of neuroimag ing CORRECT DIAGNOSIS and Careful history Investigations TREATMENT 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
Source Text-Kanski, Parson s, Samar Basak, Pradeep Sharma Photographs- above , Archives & Website 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh
The End 30-09-2024 Dr.Sanjeev Kumar Mittal,AIIMS Rishikesh