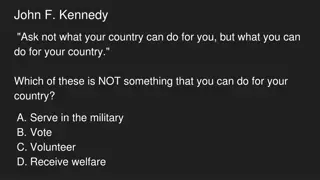
Understanding Different Forms of Government
An institution known as government establishes and enforces rules for a group of people. This institution must possess sovereignty, legitimacy, and jurisdiction. Various forms of government exist, such as dictatorship, absolute monarchy, and constitutional monarchy, each with distinct characteristics and levels of power distribution. Anarchy, the absence of formal government, and its implications are also explored in this comprehensive overview.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Government: Who has the power?
Definition of Government An institution that establishes and enforces rules for a group of people. They must have sovereignty, legitimacy, and jurisdiction.
Other Governmentish Words Sovereignty (sov-ern-tee) POWER! The government has authority to do things! Legitimacy The people ACCEPT the government s power, so it s legit! If people don t accept that the government has sovereignty, then the government can t get anything accomplished. Jurisdiction The geographic boundaries where the government has the right to make and enforce laws For example, the Texas state government doesn t have jurisdiction in Oklahoma. The United States government doesn t have jurisdiction in Mexico.
Anarchy The belief that every form of regulation or government is immoral and unnecessary. In anarchy, there are no leaders. There are anarchist groups all around the world, but there are not any countries that don t have any person or group of people exercising control. Even countries plagued with violence and chaos still have a group or opposing groups using their power (threats, violence, etc.) to get people to do what they want.
Dictatorship One person has sole power in the state The ruler of the country claims total control over all activities of the citizens. A dictator often gains power by force, does not hold himself to a constitution or previous laws, and is the only person who has to approve of decisions. Sudan, Rwanda, Nicaragua, Venezuela, Cuba, Syria, Iran, Turkmenistan, North Korea, Belarus
Absolute Monarchy A form of government in which one person inherits the throne and serves as head of state for life. Saudi Arabia, Vatican City, Swaziland
Constitutional Monarchy A form of government in which one person inherits the throne and serves as head of state for life, but it is ceremonial. There is usually a parliament and prime minister and the government is held to a constitution. These people are usually elected. The British monarchy is a good example of a constitutional monarchy. The royal family has little to do with making and enforcing laws. That is left to the British Parliament.
Democracy The power to govern is determined by the people; Decisions are made by voting The majority will always rule Rights of the minorities are not protected Most countries that we view as strict democracies are actually considered republics, or democratic republics.
Republic Government by the people through freely elected representatives; bound by the laws contained in a charter or constitution. There is still a head of state (President or Prime Minister), and he/she does have power, but the power is offset by a legislative branch, such as a congress or parliament. Most countries in the world (Including the United States) are republics. Democracy is a part of a republican government, because the people still have a part in the decisions through voting and electing representatives.
Communism Political, economic and social system in which most or all property is owned by the centralgovernment and is supposed to be shared by all the people. Equality is the idea behind communism .it doesn t usually work out that way Oftentimes in communist countries there is actually a very large disparity between the rich and the poor. North Korea, Vietnam, China,
Theocracy Religious leaders rule according to religious laws A Deity (such as God) is recognized as the supreme ruler. Other leaders interpret and enforce the laws of the Diety. Muslim countries like Iran and Saudi Arabia are based on Sharia law from the Kuran. Vatican City, headquarters of the Roman Catholic Church, is a theocracy. St. Peter s Square, Vatican City
Thank you for your purchase, I hope that you enjoy using it in your classroom! Please don t forget to leave feedback and follow my store for more great resources! https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/Rich- Resources