Understanding Ozone Depletion: Causes and Impact
The ozone layer, found in the stratosphere at 15 to 40 km altitude, plays a crucial role in absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation. However, due to the use of Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), the ozone layer has been depleted, leading to the formation of the ozone hole. This depletion is caused by chemical reactions involving chlorine atoms that destroy ozone molecules, ultimately impacting the Earth's protective layer. Learn about the process, implications, and formation of the ozone hole in this informative guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is the ozone layer and where is it found? The ozone layer is the layer of the atmosphere at an altitude of 15 to 40 km (stratosphere)
What is the function of the ozone layer? ozone absorbs ultraviolet solar radiation. What is Ozone? Ozone is a molecule made of three oxygen atoms
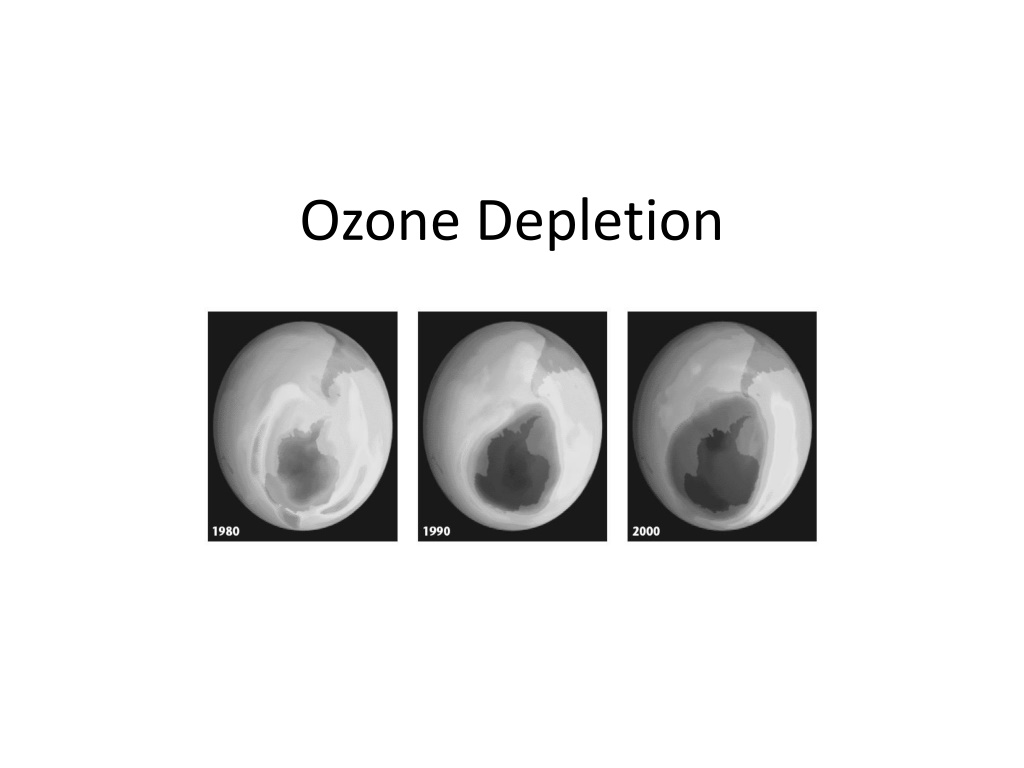
SoWhats the issue with the ozone layer? These satellite images below show the growth of the ozone hole (blue, then purple, then red) over the past two decades.
How is ozone depleted? Chloroflouorocarbons (CFC s) They are used in coolants for refrigerators and air conditioners and in cleaning solvents. They were also used as a propellant in spray cans of everyday products such as deodorants, insecticides, and paint. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are hydrocarbons in which some or all of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by chlorine and fluorine. Their use is now restricted because they destroy ozone molecules in the stratosphere
Chemical equation for this process CFCl3 + UV Light Cl + O3 ClO + O2 ClO + O Cl + O2 CFCl2 + Cl The free chlorine atom is then free to attack another ozone molecule Cl + O3 ClO + O2 ClO + O Cl + O2 and again ... Cl + O3 ClO + O ClO + O2 Cl + O2 and again... for thousands of times In this way, a chlorine atoms act as a catalyst.
How Does the Ozone Hole Form? Polar stratospheric clouds form at altitudes of about 21,000 m during the Arctic and Antarctic winter or early spring, when air temperatures drop below 80 C. During the dark polar winter, strong circulating winds over Antarctica, called the polar vortex, separate cold air from surrounding warmer air. The air within the vortex grows extremely cold. When sunlight returns to the South Pole in the spring, molecular chlorine is split into two chlorine atoms by UV radiation. On the surfaces of polar stratospheric clouds, the products of CFCs are converted to molecular chlorine. The chlorine atoms rapidly destroy ozone. The destruction of ozone causes a thin spot, or ozone hole, which lasts for several months.
If ozone is also being produced as air pollution, why does this ozone not repair the ozone hole in the stratosphere? Ozone is very chemically reactive. It can chemically burn your lungs (Good up high bad near by) Ozone produced by pollution breaks down or combines with other substances in the troposphere long before it can reach the stratosphere to replace ozone that is being destroyed
Why is a hole in the ozone a problem? UV light is dangerous to living things because it damages DNA, the genetic material that contains the information that determines inherited characteristics. As the amount of ozone in the stratosphere decreases, more UV light is able to pass through the atmosphere and reach Earth s surface. Exposure to UV light makes the body more susceptible to skin cancer, and may cause other damaging effects to the human body.
What are the effects of thinning ozone layer on humans? As the amount of ozone decreases, more UV light is able to pass through the atmosphere and reach Earth s surface. UV light damages DNA Exposure to UV light makes the body more susceptible to skin cancer, and may cause other damaging effects to the human body.
High levels of UV light can kill single- celled organisms called phytoplankton that live near the surface of the ocean disrupt ocean food chains and reduce fish harvests Decrease in phytoplankton could cause an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Effects of ozone thinning on animals and plants UV light could be especially damaging for amphibians, such as toads, because they lay eggs that lack shells in the shallow water of ponds and streams. UV light at natural levels kills many eggs of some species by damaging unprotected DNA. UV light can damage plants by interfering with photosynthesis. This damage can lower crop yields
What have we done to protect the ozone layer? 1987 1992 Montreal Copenhagen group of nations made an agreement, called the Montreal Protocol, to sharply limit their production of CFCs. _ At a second conference in Copenhagen, Denmark in 1992, developed countries agreed to eliminate most CFCs by 1995
2007 was the 20thanniversary of the Montreal Protocol: "The Montreal Protocol has been a resounding success," said Richard Stolarski, a speaker at the symposium from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. "The effect can be seen in the leveling off of chlorine compounds in the atmosphere and the beginning of their decline." Since the Montreal Protocol was signed on Sept. 16, 1987, more than 100 nations have agreed to limit the production and release of compounds, notably human- produced chlorofluorocarbons, known as CFCs. CFCs and a list of other compounds are known to degrade the layer of ozone in the stratosphere that shields life from the sun's ultraviolet radiation. That process gives rise to the ozone hole above Antarctica.
Other forms of Pollution. NOISE!!! A sound of any kind is called a noise. Some noises are unnecessary and can cause noise pollution. Health problems that can be caused by noise pollution include loss of hearing, high blood pressure, and stress. Noise can also cause loss of sleep, which may lead decreased productivity at work and in the classroom.
Other forms of Pollution. LIGHT!!!!! Light pollution does not present a direct hazard to human health, but it does negatively affect our environment. The use of inefficient lighting in urban areas is diminishing our view of the night sky. In urban areas, the sky is often much brighter than the natural sky.
Describe in 1 sentence what is happening in the diagram below. The hole in the ozone has grown significantly over the past two decades over the continent of antarctica
What causes ozone depletion? A - Acid Rain B - Volatile Organic Compounds C - Chloroflourocarbons D - Thermal Inversion
What happens to chlorine after it breaks down one molecules of ozone? A It move on to break down another molecule of ozone B It creates acid rain C It destroys aquatic ecosystems D It disappears
What does good up high bad near by mean? Ozone in the stratosphere is helpful because it protects us from harmful UV radiation Ozone on the ground level is toxic to humans and breaks down before reaching the stratosphere so it can t be used to replace the missing ozone
What are some effects on people from ozone depletion? UV rays can cause genetic damage that can lead to skin cancer or other health problems
What have we done about the hole in the ozone layer? A - We are moving ground level ozone into the stratosphere B - CFC s were no longer produced and later banned from use C We are cleaning up the CFC s from the atmosphere over antarctica D - Nothing