Zener Diodes in Analog Electronics
Zener diodes are heavily doped semiconductor devices designed to operate in reverse bias conditions. They exhibit the Zener effect where breakdown occurs, allowing current flow in the reverse direction. These diodes maintain a constant voltage (Zener voltage) across them, making them useful as voltage regulators. Explore the working principles, characteristics, and differences between Zener breakdown and avalanche breakdown in this informative guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dr. Umayal Ramanathan College for Women, Karaikudi. Accredited with B+ Grade by NAAC Affiliated to Alagappa University (Run by Dr. Alagappa Chettiar Educational Trust) Class: III B.Sc., Physics 7BPH5C1 ANALOG ELECTRONICS Ms. MS. Kalaivani Assistant Professor, Department of Physics & EC URCW Department of Physics, URCW
Unit I Semiconductor Diodes and Regulated Power Supplies Zener Diode Department of Physics, URCW
What is zener diode? Zener effect Working of Zener diode V I characteristics of zener diode Zener Breakdown Vs Avalanche Breakdown What is Voltage Regulator? Applications of Zener Diode Department of Physics, URCW
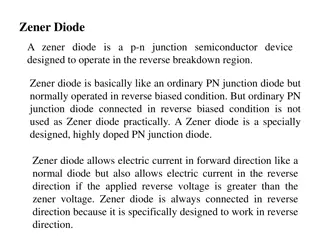
What is zener diode? Zener diode is heavily doped p-n junction diode which operates in reverse bias condition and in breakdown region. Department of Physics, URCW
Zener Effect: Zener diodes, also known as breakdown diodes are heavily doped semiconductor devices that are designed to operate in the reverse direction. When the voltage across its terminals is reversed and the potential reaches the Zener Voltage (knee voltage), the junction will break down and the current flows in the reverse direction. This effect is known as the Zener Effect. Department of Physics, URCW
Working of Zener diode: As the reverse voltage applied to the Zener diode increases, it reaches the breakdown voltage at which Zener current increases to a large value. In the breakdown region, further increase in reverse voltage will not increase the voltage across the Zener diode, it only increases the current. Thus, a constant voltage called Zener voltage (Vz) is maintained across the Zener diode when the supply voltage changes. Hence, it acts as a voltage regulator. As the reverse voltage reaches a certain value, the reverse current increases to a large value, but the voltage across the diode remains a constant. This is the break down voltage Vz. Department of Physics, URCW
V I characteristics of zener diode: Department of Physics, URCW
Zener Breakdown Vs Avalanche Breakdown The process of applying high voltage and increasing the free electrons or electric current in semiconductors and insulating materials is called an avalanche breakdown. The process in which the electrons move across the barrier from the valence band of p-type material to the conduction band of n-type material is known as Zener breakdown. This is observed in Zener diodes having a Zener breakdown voltage Vz of 5 to 8 volts. Zener diode exhibits negative temperature coefficient. i.e., breakdown votage decreases as temperature increases. This is observed in Zener diode having a Zener breakdown voltage Vz greater than 8 volts. Avalanche diode exhibits positive temperature coefficient. i.e., breakdown voltage increases with increase in temperature. Department of Physics, URCW
What is Voltage Regulator? A voltage regulator is a device that regulates the voltage level. It essentially steps down the input voltage to the desired level and keeps it in that same level during the supply. This ensures that even when a load is applied the voltage doesn t drop. The voltage regulator is used for two main reasons and they are: To vary or regulate the output voltage To keep the output voltage constant at the desired value in spite of variations in the supply voltage. Department of Physics, URCW
Applications of Zener Diode Zener diode as a voltage regulator: Zener diode is used as a Shunt voltage regulator for regulating voltage across small loads. The breakdown voltage of Zener diodes will be constant for a wide range of current. Zener diode is connected parallel to the load to make it reverse bias and once the Zener diode exceeds knee voltage, the voltage across the load will become constant. Department of Physics, URCW
Zener diode in over-voltage protection: When the input voltage is higher than the Zener breakage voltage, the voltage across the resistor drops resulting in a short circuit. This can be avoided by using the Zener diode. Zener diode in clipping circuits: Zener diode is used for modifying AC waveform clipping circuits by limiting the parts of either one or both the half cycles of an AC waveform. Department of Physics, URCW





 undefined
undefined