Volvo EC55-2 Compact Excavator Service Repair Manual Instant Download
Please open the website below to get the complete manualnn// n
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
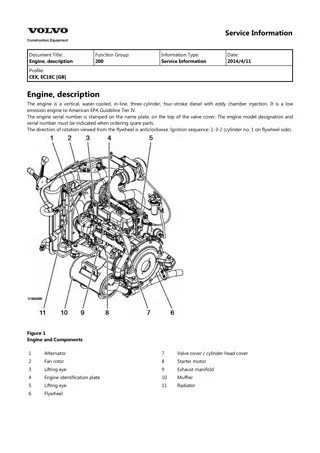
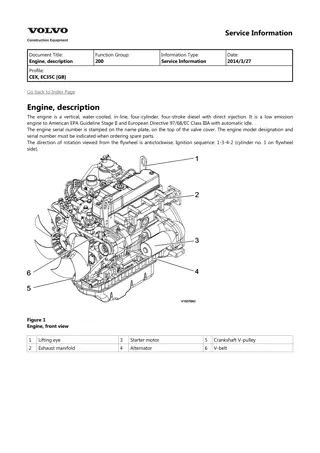
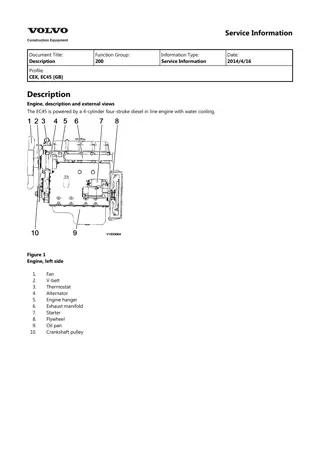
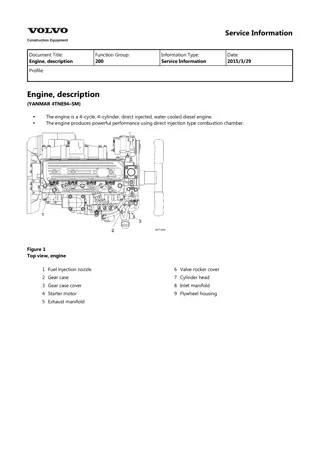
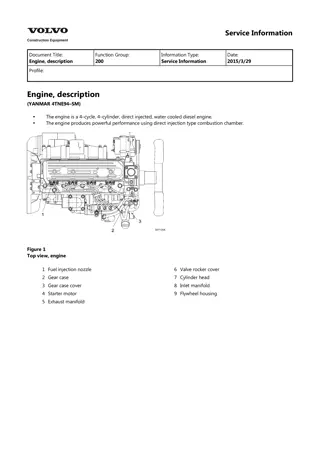
Service Information Document Title: Adjusting operation Function Group: 210 Information Type: Service Information Date: 2014/4/10 Profile: Adjusting operation Perform adjusting operation as follows after the maintenance job : Supply the fuel oil, lubricating oil and coolant. CAUTION Check the levels of the lubricating oil and coolant again after test running (for about 5 minutes) and add as required. Start the engine, and carry out idling at a low revolution (from 700 to 900 rpm) for a few minutes. Run in the engine for about five minutes at the rated revolution (no load). Check for coolant, fuel or oil leaks and existence of abnormal vibration or noise. Also check the oil pressure, coolant temperature and exhaust gas color. Adjust the no load minimum and maximum revolutions according to the specifications. Long storage Observe the following instructions when the engine is to be stored for a long period without operation : Always drain cooling water in a cold season or before a long storage. (This is unnecessary when antifreeze is used.) CAUTION Negligence of water draining will cause the water remaining inside the engine to freeze and expanded, damaging the engine cooling system components. Coolant draining procedure 1. 2. 3. 4. Remove the radiator cap. Loosen the draining cock under the radiator to drain coolant. Loosen the drain cock on the side of the engine block to drain coolant. After draining coolant, tighten the radiator cap and drain plug and cocks. Remove all mud, dust, oil deposits and thoroughly clean the engine and attached components. Perform the nearest periodic inspection before the storage. Drain or fill the fuel oil fully to prevent condensation in the fuel tank. Disconnect the battery cable from the battery negative terminal. Cover the silencer, air cleaner and electric parts with PVC cover to prevent water and dust from depositing or entrance. Select a well ventilated location without moisture and dust for storage. Perform battery recharging once a month during storage to compensate for self discharge.
Service Information Document Title: Compression inspection Function Group: 210 Information Type: Service Information Date: 2014/4/10 pressure Profile: Compression pressure inspection Compression pressure drop is one of major causes of increasing blowby gas (lubricating oil contamination or increased lubricating oil consumption as a resultant phenomenon) or starting failure. The compression pressure is affected by the following factors : 1. 2. 3. Degree of clearance between piston and cylinder Degree of clearance at intake/exhaust valve seat Gas leak from nozzle gasket or cylinder head gasket In other words, the pressure drops due to increased parts wear and reduced durability resulting from long use of the engine. A pressure drop may also be caused by scratched cylinder or piston by dust entrance from the dirty air cleaner element or worn or broken piston ring. Measure the compression pressure to diagnose presence of any abnormality in the engine. Compression pressure measurement method 1. 2. After warming up the engine remove the fuel injection nozzle from the cylinder to be measured. Before installing the compression gauge, cut off the fuel supply by the adjusting lever and check if fuel comes out while rotating the flywheel manually. Install the compression gage and compression gage adapter at the cylinder to be measured. 3. Figure 1 Measuring the compression pressure 1. Compression gauge CAUTION Do not forget to install a gasket at the tip end of the adapter. 4. 5. Install the compression gage and compression gage adapter at the cylinder to be measured. Crank the engine by the starting motor until the compression gage reading is stabilized. Standard compression pressure Standard : 35 1 kgf/cm2 (497 14.2 psi) Limit : 27 kgf/cm2 (383.4 psi) Difference among cylinders : 2 ~ 3 kgf/cm2 (28.4 ~ 42.6 psi) Engine speed and compression pressure
Figure 2 Engine speed and compression pressure P : Compression pressure N : Engine speed Check items When the measured compression pressure is below the limit value, inspect each part by referring to the table below. Compression pressure check items Item Air cleaner element Cause Clogged element Broken element Defect at element seal portion Excessive or no clearance Incorrect valve clearance Gas leak from gasket Corrective action Clean the element Replace the element Valve clearance Valve timing Cylinder head gasket Adjust the valve clearance Adjust the valve clearance Replace gasket Retighten the cylinder head screws to the specified torque Lap the valve seat Replace the inlet/exhaust valve Inlet/exhaust valve Valve seat Gas leak due to worn valve seat or foreign matter Sticking valve Gas leak due to scoring or wear Piston Piston ring Cylinder Perform honing or boring/honing and use an oversized part
https://www.ebooklibonline.com Hello dear friend! Thank you very much for reading. Enter the link into your browser. The full manual is available for immediate download. https://www.ebooklibonline.com
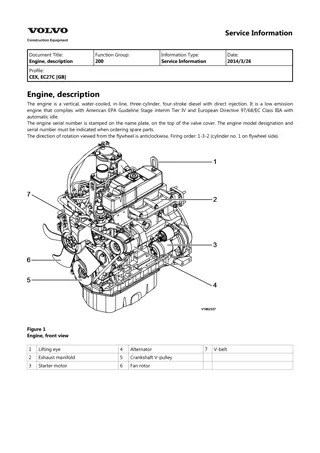
Service Information Document Title: Cylinder disassembly/assembly Function Group: 2111 Information Type: Service Information Date: 2014/4/10 head, Profile: Cylinder head, disassembly/assembly Disassemble in the order of the numbers shown in the illustration. (service point) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Remove the alternator assembly. (service point 1) Remove the fan, pulley and V belt. Remove the thermostat case. (service point 2) Remove the fuel filter and fuel oil piping. (service point 3) Remove the oil level gauge assembly. Remove the oil filter. (service point 4) Remove the fuel injection pipes. (service point 5) Remove the intake manifold assembly. Remove the exhaust manifold assembly. Remove the rocker cover. Remove the rocker shaft assembly, push rods and valve caps. (service point 6) Remove the cylinder head assembly and head gasket. (service point 7) Remove the fuel injection valves and fuel return pipe. (service point 8) Remove the intake/exhaust valves, stem seals and valve springs. (service point 9) Remove the rocker arms from the rocker shaft. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. For assembly, reverse the procedure. Service points Point 1 Disassemble : Loosen the mounting screw while supporting the alternator. CAUTION Do not tilt the alternator toward the cylinder block in a haste since it may damage the alternator or pinch a finger. Reassemble : The belt deflection shall be between 10 ~ 15 mm (7 ~ 9 mm for a new belt). Figure 1 V belt tension 1. 2. 3. Cooling water pump Crankshaft pulley Alternator
Replace the belt with a new one if cracked, worn or damaged. Carefully prevent the belt from being smeared with oil or grease. Figure 2 Tension adjustment 1. 2. 3. Adjuster Alternator Adjust the V belt tension by inserting a bar Point 2 Reassemble : Check the thermostat function. Point 3 Reassemble : Replace the fuel filter element with a new one. Disassemble : Cover the fuel pipe opening with tape to prevent intrusion of foreign matter. Point 4 Reassemble : Replace the oil filter with a new one. After fully tightening the filter manually, retighten it with a filter wrench by 3/4 turn. Point 5 Disassemble : Cover the fuel injection pipe and pump inlets and outlets with tape or the like to prevent intrusion of foreign matter. Point 6 Disassemble : Keep the removed push rods by attaching tags showing corresponding cylinder numbers. Reassemble : Always apply oil to the contact portions of the push rods and valve clearance adjusting screws. Point 7 Disassemble :
Loosen the cylinder head screws in two steps in the illustrated order. Figure 3 Head screw disassembly order 1. Fan side Place the cylinder head assembly on card board to prevent any damage to the combustion face. Reassemble : Replace the head gasket with a new one. Uniformly install the head screws manually after applying oil on the threads and seat portions. Figure 4 Head screw tightening order 1. Fan side They shall be tightened in two steps in the reverse of the order for disassembly. Tightening torque : First step : 5 ~ 6 kgf m (36.1 ~ 43.3 lbf ft) Second step : 10.5 ~ 11.5 kgf m (75.8 ~ 83.0 lbf ft) Point 8 Disassemble : Carefully remove the fuel injection valve so as not to leave the tip end protector from being left inside the cylinder. Reassemble : Replace the fuel injection valve protector with a new one. Point 9 Disassemble : When removing each inlet/exhaust valve from the cylinder head, use a valve spring compressor and compress the valve spring and remove the valve cotter. Figure 5 Valve spring compressor Keep each removed inlet/exhaust valve after attaching a tag showing the corresponding cylinder number. If cotter burr is seen at the shaft of each inlet/exhaust valve stem, remove it with an oil stone and extract the valve from the cylinder head. Reassemble :
Replace the stem seal with a new one when an intake/exhaust valve is disassembled. Carefully install each valve after oil application so as not to damage the stem seal. Different stem seals are provided for the intake and exhaust valves. Do not confuse them since those for exhaust valves are marked with yellow paint. After assembling the intake/exhaust valve, stem seal, valve spring, seat, and cotter, tap the head of the valve stem lightly for settling. Do not forget to install the valve cap.
Service Information Document Title: Cylinder inspection measurement Function Group: 2111 Information Type: Service Information Date: 2014/4/10 head, parts and Profile: Cylinder head, parts inspection and measurement Cylinder head Clean the cylinder head, mainly the combustion surface, valve seats and intake/exhaust ports, remove carbon deposit and bonding agent, and check the surface state. Appearance check Check mainly discoloration and crack. If crack is suspected, perform dye check. Combustion surface distortion Apply a straight edge in two diagonal directions and on four sides of the cylinder head, and measure distortion with a feeler gage Figure 1 Distortion at combustion surface 1. 2. Straight edge Feeler gauge Combustion surface distortion, unit : mm (in) Standard 0.05 (0.002) or less Limit 0.15 (0.0059) Distortion Valve sink Measure with the valve inserted to the cylinder head. Combustion surface distortion, unit : mm (in) Standard 0.5 0.7 (0.0197 0.0276) 0.6 0.8 (0.0236 0.0315) Limit 1.0 (0.0394) 1.1 (0.0433) Valve sink Inlet Exhaust
Figure 2 Valve sink 1. Depth micrometer Figure 3 Valve sink depth 1. Valve sinking depth Seat width Figure 4 Valve seat width 1. Vernier callipers Valve seat width, unit : mm (in) Standard 1.3 (0.0512) 2.2 (0.0866) Limit 2.0 (0.0787) 3.0 (0.1181) Seat width Inlet Exhaust Seat contact Apply a thin coat of bluing on the valve seat. Insert the valve in the cylinder and push it against the seat to check seat contact. Standard : Continuous contact all around
Figure 5 Valve seat contact 1. Seat Valve guide Mainly check damage and wear on the inside wall. Apply supply part number 129150 11810 when replacing the part. Figure 6 Valve guide inside diameter 1. Measuring positions Valve guide inside diameter, unit : mm (in) Standard 7.965 ~ 7.980 (0.3136 ~ 0.3142) 8.015 ~ 8.030 (0.3156 ~ 0.3161) 0.035 ~ 0.065 (0.0014 ~ 0.0026) 7.955 ~ 7.970 (0.3132 ~ 0.3138) 8.015 ~ 8.030 (0.3156 ~ 0.3161) 0.045 ~ 0.075 (0.0018 ~ 0.0030) Limit 7.915 (0.3116) 8.100 (0.3189) 0.185 (0.0073) 7.905 (0.3112) 8.100 (0.3189) 0.195 (0.0077) Inlet valve Stem outside diameter Guide inner diameter Clearance Stem outside diameter Guide inner diameter Clearance Exhaust valve Inlet/exhaust valve Mainly clean and check damage and wear at the valve stem and seat. Seat contact : See above. Stem outside diameter : See above.
Figure 7 Valve stem outside diameter 1. Measuring positions Valve head thickness Figure 8 Valve head thickness 1. Thickness Valve head thickness, unit : mm (in) Standard 1.71 (0.0673) 1.65 (0.0650) Limit 1.00 (0.0394) 1.00 (0.0394) Inlet Exhaust Valve stem bend Limit : 0.01 mm (0.0004 in) Overall length Figure 9 Valve bend and length 1. Length Valve overall length, unit : mm (in) Standard 115 (4.53) 115 (4.53) Limit 114.5 (4.50) 114.5 (4.50) Inlet Exhaust Valve spring Mainly inspect damage and corrosion.
Valve spring, unit : mm (in) Standard 47.5 (1.87) Limit 1.2 (0.047) Free length Inclination Figure 10 Valve spring free length Figure 11 Valve spring inclination Valve rocker arm Mainly inspect valve head cap contact surface, inside surface defects and wear. Slight surface defects shall be corrected with an oilstone Figure 12 Rocker arm hole diameter Rocker arm hole diameter, unit : mm (in) Standard 18.50~18.52 (0.7283~0.7291) 18.47~18.49 (0.7272~0.7280) 0.01~0.05 (0.0004~0.0020) Limit 18.57 (0.7311) 18.44 (0.7260) 0.13 (0.005) Arm hole diameter Shaft outside diameter Clearance
Valve rocker arm shaft Mainly inspect seizure and wear at the surface in sliding contact with the arm. The rocker shaft diameter shall be as specified in above. Figure 13 Rocker shaft outside diameter Push rod Mainly inspect the surface in contact with the tappet and adjusting screw. Slight defects shall be corrected with an oilstone. Bend limit : 0.03 mm (0.0012 in) or less Figure 14 Push rod bend 1. Thickness gauge Valve clearance adjusting screw Mainly inspect the surface in contact with the push rod. Slight defects shall be corrected with an oilstone. Rocker arm spring Mainly inspect surface defects and corrosion. Valve seat correction CAUTION Always check the oil clearance between the valve and valve guide before correcting the valve seat. If it exceeds the limit, replace the valve or valve guide first to make the clearance satisfy the standard. After correction, wash the valve and the cylinder head sufficiently with diesel oil to remove all grinding powder or compound. If the seat surface is slightly roughened : perform (A) and (B) following. If the seat is heavily roughened but the width is almost normal, correct with a seat grinder or seat cutter first. Then perform lapping (A) and (B) following.
Figure 15 Cylinder head correction angle 1. 2. 3. Seat angle Seat width Seat cutter Seat cutter angle, unit : degree Inlet 120 Exhaust 90 Seat cutting angle If the seat is heavily roughened and the width is much enlarged, grind the seat inner surface with a seat grinder whose center angle is 40then grind the seat outer surface with a grinder whose center angle is 150 to make the seat width match the standard. Then perform seat correction as described above, and then carry out lapping (A) and (B) below. Grinding wheel angle, unit : degree 1 40 2 150 Grinding wheel angle (A) : Lap the valve and seat with a mixture of valve compound and engine oil. (B) : Lap with engine oil only. Figure 16 Seat grinder 1. 2. Grinder Grindstone
Figure 17 Valve lapping Valve guide replacement Use a valve guide extraction tool and extract the valve guide from the cylinder head. Figure 18 Valve guide replacement 1. 2. 3. 4. Cylinder head Valve guide Projection Valve guide extracting & inserting tool Put liquid nitrogen or ether, (or alcohol) with dry ice added in a container and put the valve guide for replacement (Part No. 129150 11810) in it for cooling. Then insert it in with a valve guide inserting tool. WARNING Do not touch the cooled valve guide with bare hands to avoid skin damage. Check the inside diameter and finish to the standard inside diameter as required with a reamer. Check the projection from the cylinder head. Projection : 14.7 ~ 15.0 mm (0.5787 ~ 0.5906 in) Valve stem seal replacement Always use a new seal after the intake/exhaust valve disassembly. Since the exhaust valve is marked with yellow paint, do not confuse the intake and exhaust valves.
Figure 19 Stem seal insertion 1. 2. 3. 4. Valve stem seal inserting tool Stem seal Valve guide Cylinder head Apply engine oil to the lip. Push with the inserting tool for installation.
Service Information Document Title: Exploded head Function Group: 2111 Information Type: Service Information Date: 2014/4/10 view, cylinder Profile: Exploded view, cylinder head Figure 1 Exploded view, cylinder head
Service Information Document Title: Cylinder disassembly/assembly Function Group: 2121 Information Type: Service Information Date: 2014/4/10 block, Profile: Cylinder block, disassembly/assembly Disassemble in the order of the numbers in the illustration. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Perform steps 1 to 12 in the cylinder head disassembly procedure. Perform steps 1 to 12 in the gear train disassembly procedure. Remove the oil pan. (service point 1) Remove the lubricating oil suction pipe. Remove the piston w/rod. (service point 2) Remove the mounting flange. (service point 3) Remove the bearing metal caps. (service point 4) Remove the crankshaft. (service point 5) Remove the tappets. Remove the pistons and rings. (service point 6) Remove the oil seal from the mounting flange. (service point 7) 10. 11. For assembly, reverse the procedure. Service points Point 1 Oil pan Disassembly : Sealant is applied to the oil pan mounting surface on the block. Carefully operate so as not to damage or distort the bonding surface. Reassembly : Apply sealant (Part No. 977770 01212) before reassembly. Point 2 Piston with rod Disassembly : Measure the connecting rod side gap. Standard : 0.20 ~ 0.40 mm (0.0079 ~ 0.0157 in) Figure 1 Connecting rod side gap 1. 2. Crankshaft Feeler gauge
Suggest: If the above button click is invalid. Please download this document first, and then click the above link to download the complete manual. Thank you so much for reading
Carefully remove the carbon deposit on top of the cylinder so as not to damage the inner side of the cylinder. Set the piston at the BDC (Bottom Dead Center) position and remove the connecting rod cap. Then set the piston at the TDC (Top Dead Center) position, and push the connecting rod big end with the wooden shaft of a hammer. Proceed carefully so as not to cause the cylinder block catch the rod big end. Set the rod caps and crankpin metals in their correct combinations. Reassembly : Apply oil especially carefully to the sliding contact surfaces of the pistons, rods and rings. Use the piston insertion tool to insert each piston with rod in the cylinder block and install the bearing metal cap. Tightening torque : Rod screw : 5.5 ~ 6 kgf m (39.7 ~ 152.4 lbf ft) (lubrication oil applied) Point 3 Mounting flange Disassembly : Place the engine on a stable base with the cylinder block upper surface facing down, and remove the mounting flange carefully so as not to damage the combustion surface. Reassembly : Apply sealant (Part No. 977770 01212) and install the mounting flange by matching the two dowel pins. After assembly, rotate the engine with its mounting flange on the bottom side. WARNING Unforeseen injury may arise due to falling or slipping when raising or reversing the engine. Carefully operate so as not to lose balance. Point 4 Journal bearing cap Disassembly : Before removing the journal bearing, measure the crankshaft side gap. Standard : 0.11 ~ 0.21 mm (0.0043 ~ 0.0083 in) Figure 2 Crankshaft side gap Reassembly : If the side gap exceeds the standard, replace the thrust bearing with an oversize one. Crankshaft side gap 0.25 Oversize 129900 02370 (Upper) 129900 02360 (Lower) 2.055 ~ 2.105 (0.0809 ~ 0.0829 ) Standard thickness, mm (in) Disassembly :
https://www.ebooklibonline.com Hello dear friend! Thank you very much for reading. Enter the link into your browser. The full manual is available for immediate download. https://www.ebooklibonline.com