Understanding the Significance of the Cell Cycle in Growth and Development
This resource focuses on the cell cycle in the context of growth, development, and proliferation. It covers the significance of cell division, similarities in unicellular and multicellular organisms, the importance of CDK-mediated phosphorylation, and more. Students will learn to create schematic depictions of cell cycle phases and understand the regulatory mechanisms involved in cell division.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Northeast Regional SI 2011 Yale University Group 2 Cell and Developmental Biology
Group 2: Cell and Developmental Biology Tara Mann Harvard University Peter Gergen Stony Brook University Casey Roehrig Harvard University Xinnian Chen (Facilitator) University of Connecticut Ryan Draft Harvard University Debbie Spikes Stony Brook University
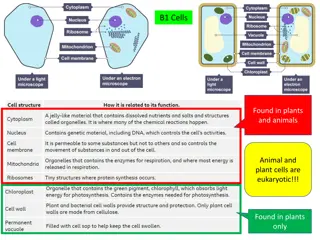
Teachable Unit: The Cell Cycle Audience: sophomore level class for majors (40 students as presented, but adaptable for 20-500) These students already know: Basic genetics Mitosis Evolution Class would have already covered: The cell is the fundamental unit of life Organelle function DNA Replication Transcription Cell signaling
Learning Goals Learning Outcomes To understand the significance of the cell cycle for growth, development, and proliferation. o To identify the similarities and differences in cell division for unicellular and multicellular organisms. o To explain why cells need to divide during both development and maintenance of multicellular organisms.
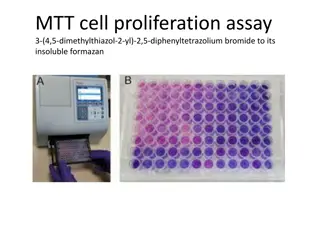
Learning Goals Learning Outcomes To understand the significance of the cell cycle for growth, development, and proliferation. o To identify the similarities and differences in cell division for unicellular and multicellular organisms. o To explain why cells need to divide during both development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. o To create a schematic depiction of the four major phases of the cell cycle. o To describe the key events that take place during the four major phases of the cell cycle. o To explain the importance of CDK-mediated phosphorylation for irreversible progression through the cell cycle. o To relate alternating levels of different cyclins to CDK activity at different points in the cell cycle. o To be able to superimpose a diagram of cyclin levels on cell cycle phases and checkpoints. o To interpret data from techniques that identify cells in different phases of the cell cycle. To know how the cellular machinery interacts to regulate the cell cycle through a tightly ordered series of events.
Learning Goals Learning Outcomes To understand the significance of the cell cycle for growth, development, and proliferation. o To identify the similarities and differences in cell division for unicellular and multicellular organisms. o To explain why cells need to divide during both development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. o To create a schematic depiction of the four major phases of the cell cycle. o To describe the key events that take place during the four major phases of the cell cycle. o To explain the importance of CDK-mediated phosphorylation for irreversible progression through the cell cycle. o To relate alternating levels of different cyclins to CDK activity at different points in the cell cycle. o To be able to superimpose a diagram of cyclin levels on cell cycle phases and checkpoints. o To interpret data from techniques that identify cells in different phases of the cell cycle. To know how the cellular machinery interacts to regulate the cell cycle through a tightly ordered series of events. o To predict how mutations in cell cycle components would alter progression through the cell cycle. o To discuss the significance of cell cycle checkpoints. o To contrast the key players and events in the spindle assembly checkpoint with those of the DNA damage checkpoint. o To explain how dysregulation of the cell cycle leads to disease. To understand how dysregulation of the cell cycle would affect the cell and organism
Learning Goals Learning Outcomes To understand the significance of the cell cycle for growth, development, and proliferation. o To identify the similarities and differences in cell division for unicellular and multicellular organisms. o To explain why cells need to divide during both development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. o To create a schematic depiction of the four major phases of the cell cycle. o To describe the key events that take place during the four major phases of the cell cycle. o To interpret data from techniques that identify cells in different phases of the cell cycle. o To explain the importance of CDK-mediated phosphorylation for irreversible progression through the cell cycle. o To relate alternating levels of different cyclins to CDK activity at different points in the cell cycle. o To be able to superimpose a diagram of cyclin levels on cell cycle phases and checkpoints. To know how the cellular machinery interacts to regulate the cell cycle through a tightly ordered series of events. o To predict how mutations in cell cycle components would alter progression through the cell cycle. o To discuss the significance of cell cycle checkpoints. o To contrast the key players and events in the spindle assembly checkpoint with those of the DNA damage checkpoint. o To explain how dysregulation of the cell cycle leads to disease. To understand how dysregulation of the cell cycle would affect the cell and organism
How do you go from one cell to two cells? ordered series of regulated events
How do you go from one cell to two cells? ordered series of regulated events
How do you go from one cell to two cells? ordered series of regulated events accurate duplication of the DNA
How do you go from one cell to two cells? ordered series of regulated events accurate duplication of the DNA division of the copies into two identical daughter cells
How do you go from one cell to two cells? ordered series of regulated events accurate duplication of the DNA division of the copies into two identical daughter cells
How do you go from one cell to two cells? ordered series of regulated events accurate duplication of the DNA division of the copies into two identical daughter cells
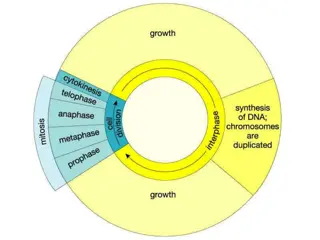
(handout) How might we depict the cell cycle as a function of time? Chromosome segregation 2x Cell Mass 1x 2x DNA content 1x Time
On your copy of the diagram, fill in the following cell cycle events: DNA synthesis, cytokinesis, and G1 Chromosome segregation Cytokinesis 2x Cell Mass 1x DNA Synthesis 2x DNA content 1x G1 Time
Which of the boxes labeled A, B, or C represents G2? Chromosome segregation Cytokinesis 2x Cell Mass 1x DNA Synthesis 2x DNA content 1x G1 A B C Time A. B. C.
Which of the boxes labeled A, B, or C represents G2? Chromosome segregation Cytokinesis 2x Cell Mass 1x DNA Synthesis 2x DNA content 1x G1 G2 Time
Which of the boxes labeled A, B, or C represents G2? Chromosome segregation Cytokinesis 2x Cell Mass 1x DNA Synthesis 2x DNA content 1x G1 S G2 M Time
S. pombe: a model system for studying cell cycle regulation G1 S G2 M
Which cell cycle step is altered in the mutant yeast cells? Wild-Type Mutant A. Early exit from G1 B. G1-S transition is blocked C. Early exit from G2 D. G2-M transition is blocked Clicker Question! Image from http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~forsburg/main4.html
Describe an experiment to distinguish between these possibilities. Wild-Type Mutant A. Early exit from G1 B. G1-S transition is blocked C. Early exit from G2 D. G2-M transition is blocked Image from http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~forsburg/main4.html
End of Tidbit: Where would we go from here? Lecture will transition into cell cycle regulatory mechanisms (cyclins, checkpoints) At the end of the lecture, a homework assignment will review the material The subsequent lecture will explore the catastrophic consequences of dysregulation in human disease
Homework Assignment Replicate a diagram for the mutant in which you show the effect on the cell cycle, cell mass, and DNA content. Wild-Type Wild-Type Mutant Mutant