Understanding Quarks, Leptons, and Particle Interactions
Explore the world of subatomic particles with topics ranging from quarks and leptons to Feynman diagrams and conservation laws. Dive into the differences between hadrons and leptons, understand the properties of quarks, and discover the intricacies of beta decay and particle interactions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
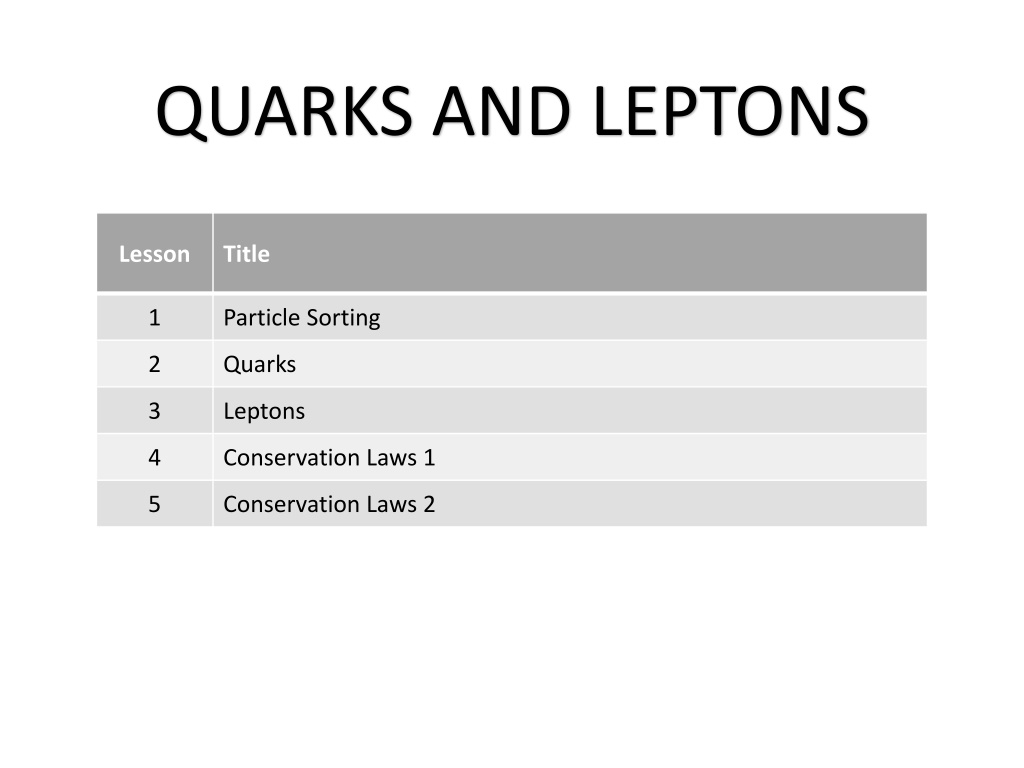
QUARKS AND LEPTONS Lesson Title 1 Particle Sorting 2 Quarks 3 Leptons 4 Conservation Laws 1 5 Conservation Laws 2
Title: Particle Sorting 1. Sketch the Feynman diagram for electron capture. 2. What is the minimum frequency of photon required to produce a proton-antiproton pair? 3. A 0.8m string fixed at both ends is oscillating in the 5th harmonic with a frequency of 25Hz. What is the wavelength of the standing wave? 4. Which force is responsible for beta decay? 5. Sketch a graph of the strength of the strong force against distance (for 0<d<3fm)
Lesson Objectives I can describe the difference between Hadrons and Leptons with reference to the fundamental forces and sort electrons, nucleons and neutrinos into these categories. C-B I can identify the 6 flavours of quarks and antiquarks and use their charged to determine the charge on a given hadron. A-A* I can distinguish between Baryons and Mesons with reference to their quark composition and sort protons, neutrons, pions and kaons into these categories. A*+
Title: Quarks 1. Sketch the 3rd harmonic in an open-closed pipe. 137??? 2. What is the specific charge on 55 3. What is the quark composition for a neutron? 4. A random Baryon has quark composition uus. What is the charge on this Baryon (as a multiple of e)? 5. An electron has KE of 1.6 x 10-19 J. What is the speed of the electron?
Lesson Objectives I can interpret the charge, baryon number and strangeness of the up, down and strange quarks. C-B I can link my understanding of beta decay to quarks and expand upon my Feynman diagrams to include them., A-A* I can recall the quark combinations for pions and kaons (mesons) and use my understanding of charge to decide which pion/kaon we are referencing. A*+
KAONS PIONS QUARK COMPOSITION QUARK COMPOSITION CHARGE KAON TYPE CHARGE PION TYPE ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? s ? ? ?
Title: Leptons 1. Sketch the Feynman diagram in terms of quarks for beta-plus decay. 2. What is the charge, quark composition and Baryon number of an anti-proton? 3. What is the minimum frequency of photon needed to produce a neutron-antineutron pair? 4. What is the difference in wavelength between the 4th and 7th harmonic on a string fixed at both ends as a multiple of the length of the string L? 5. Describe the behaviour of the strong forces between 0 and 3fm.
Lesson Objectives I can distinguish between muons, electrons and their corresponding neutrinos. C-B I can identify lepton number for a given lepton/anti-lepton and can use its conservation to identify whether or not a decay is possible. A-A* I can recall the decay equations for muon decay and give an explanation as to why muons cannot decay into anti- muon neutrinos. A*+
Title: Conservation Laws 1 1. Show that the lepton number and charge are conserved in beta-plus decay. 2. What angle of incidence is required inside a material with refractive index of 1.7 to produce an angle of refraction of 90o in air? 3. The diameter of a cylindrical wire is measured to be 3.2 0.05 mm. What is the cross- sectional area of the wire (give the absolute uncertainty in your answer)? 4. What are the base units of Resistance? 5. What is the specific charge of a Nitrogen-20 nucleus?
Lesson Objectives I can identify what is conserved in reactions involving the strong and weak forces. C-B I can check the conservation of charge, baryon number and lepton number in strong and weak interactions. A-A* I can check for conservation of strangeness and identify which interactions require me to do so. A*+
Worked Example 1. The following decay is by the weak interaction. Is it possible? K+ + n 0 + + 2. The following decay is by the strong interaction. Is it possible? ? + ? ?+ + ??
Title: Conservation Laws 2 1. Is the following decay by the weak interaction possible? 2. What are the base units of potential difference? 3. An object is experiencing two forces (25N North and 16N East). What is the Force experienced by the object? Give the direction of the force as a bearing. 4. What wavelength of photons are produced when a positron annihilates and electron? 5. Define Specific Charge.
Lesson Objectives I can identify what is conserved in reactions involving the strong and weak forces. C-B I can check the conservation of charge, baryon number and lepton number in strong and weak interactions. A-A* I can check for conservation of strangeness and identify which interactions require me to do so. A*+






















