Understanding Osmosis in Cell Membranes
This quiz explores the concept of osmosis in cell membranes, focusing on the movement of water into outermost cells of roots by osmosis and its implications on cell sap. It covers topics such as active transport, diffusion, pressure in cell contents, and the role of water movement in maintaining the water/salt balance in organisms. The quiz challenges understanding and knowledge of cellular processes related to water and solute movement across membranes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
2.2.6 Movement through Cell Membranes Follow-Me iQuiz
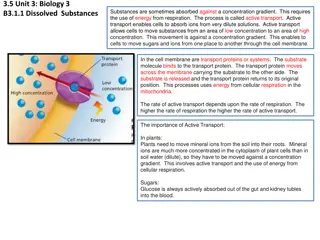
Q. Water enters the outermost cells of the root by osmosis. What does this tell you about the cell sap of these outermost cells? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Osmosis has been described as a special case of diffusion. Explain why. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is meant by a selectively permeable membrane? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
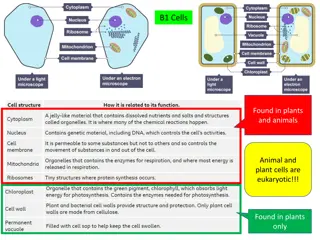
Q. Give locations in a cell at which there is a selectively permeable membrane. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is diffusion? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Why is diffusion alternatively known as passive transport? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain the biological basis for the use of high sugar or high salt concentrations in the preservation of food. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What did you use as the selectively permeable membrane in your investigation of osmosis? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is active transport? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name two substances that enter a human muscle cell by diffusion. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest an advantage to the cell of having a selectively permeable membrane. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain the term turgor. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give an example of osmosis in plants. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name a substance found in a plant cell vacuole. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give a feature of a plant cell that allows it to remain turgid for long periods. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. True or False. Plant cell walls are fully permeable. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Water for photosynthesis enters the roots of plants by what process? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest a way in which turgor is of value to plants. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the terms used in biology to describe the movement of substances through cell membranes. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What process is responsible for the uptake of minerals in a plant? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is meant by osmoregulation? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where precisely does water enter a plant? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. The drooping of the leaves of a plant resulting from loss of turgidity due to lack of water is known as Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In which tissue does water ascend through the plant? Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Active transport Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Substances can be allowed or prevented in or out Active transport Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to Allowing some substances to pass through Support Allowing some substances to pass through Support Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane area of lower concentration Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Vacuole; Cell wall; Cell sap Bacteria lose water by osmosis, this leads to inactivity or death No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing No energy (ATP) required Chloroplast; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Vacuole Visking tubing Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Osmosis Water movement between cells or from soil to root Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Water movement between cells or from soil to root Osmosis Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Water; Sugar; Sap; Salt(s); Protein Oxygen; Glucose; Water; Amino acids; Phosphate; Iron Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Pressure of cell contents on cell wall FALSE TRUE Wilting Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem Lower water concentration; Higher solute concentration Root hairs Xylem
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again