Understanding Noise in Communication Systems
Noise in communication refers to unwanted energy that interferes with signal reception and transmission. It can be categorized as external or internal noise, each with various subtypes like atmospheric noise and shot noise. Recognizing and managing different types of noise is essential for ensuring clear and effective communication.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
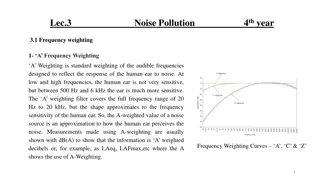
What is Noise noise is defined as the unwanted form of energy which tends to interface with the proper reception and the reproduction of transmitted signals. Electronic Devices unwanted random addition to the signal are considered as Noise. Their are various types of Noise presents. The Acoustic Noise is observed when the signals are converted into sound which is generally know as snow in TV or video Images. In signalling processing or computing noise can be considered random unwanted data without meaning that is, data that is not being used to transmit signal, but is simply produced as an unwanted by-product of other activities.
Classification of Noise: There are several way to classify Noise, but conveniently Noise is classified as 1) External Noise 2) Internal Noise
External Noise: External noise is defined as the type of Noise which is general externally due to communication system. External Noise are analysed qualitatively. Now, External Noise may be classified as a) Atmospheric Noise : Atmospheric Noise is also known as static noise which is the natural source of disturbance caused by lightning, discharge in thunderstorm and the natural disturbances occurring in the nature. b) Industrial Noise : Sources of Industrial noise are auto- mobiles, aircraft, ignition of electric motors and switching gear. The main cause of Industrial noise is High voltage wires. These noises is generally produced by the discharge present in the operations.
External Noise (continue) c) Extraterrestrial Noise : Extraterrestrial Noise exist on the basis of their originating source. They are subdivided into i) Solar Noise ii) Cosmic Noise
Internal Noise Internal Noise are the type of Noise which are generated internally or within the Communication System or in the receiver. They may be treated qualitatively and can also be reduced or minimized by the proper designing of the system. Internal Noises are classified as 1) Shot Noise : These Noise are generally arises in the active devices due to the random behaviour of Charge particles or carries. In case of electron tube, shot Noise is produces due to the random emission of electron form cathodes. 2) Partition Noise : When a circuit is to divide in between two or more paths then the noise generated is known as Partition noise. The reason for the generation is random fluctuation in the division. 3) Low- Frequency Noise : They are also known as FLICKER NOISE. These type of noise are generally observed at a frequency range below few kHz. Power spectral density of these noise increases with the decrease in frequency. That why the name is given Low- Frequency Noise.
Internal Noise (continue) 4) High- Frequency Noise : These noises are also known TRANSIT- TIME Noise. They are observed in the semi-conductor devices when the transit time of a charge carrier while crossing a junction is compared with the time period of that signal. 5) Thermal Noise : Thermal Noise are random and often referred as White Noise or Johnson Noise. Thermal noise are generally observed in the resistor or the sensitive resistive components of a complex impedance due to the random and rapid movement of molecules or atoms or electrons