Understanding Language Components and Phonemes in Communication
Explore the components of language, from individual letters and sounds to phrases and sentences. Learn about phonemes, the sounds in spoken language, and how they vary among different languages. Engage in activities to enhance your understanding of linguistic elements in communication.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
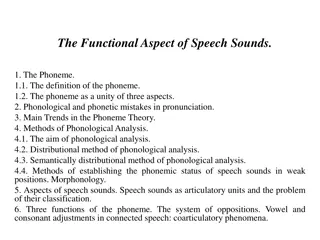
LANGUAGE In this chapter we explore: - what language is - how we use language to interact - language in the classroom.
WHAT IS LANGUAGE? Language is a tool we use to communicate with other. people: We encode what we want to say using language which is made up of a range of components. One way of looking at language is to start with the smallest component and work upwards:
- individual lettersand sounds, for example, 'c' and /k/ - combined letters and sounds, for example, 'th' - / /( )or lo! ( the') - words - 'cat', /k t/ - phrases= 'the happy cat' (noun phrase), 'sat down' (verb phrase) - clauses - 'the happy cat sat down' - sentences - 'The happy cat sat down on the muddy mat.'
What does phonemes? The individual sounds of a spoken language are called phonemes. There are two types of phoneme: vowels, for example, the / / sound in cat', and consonants, for example, the /k/ sound in cat'. As we can see, the letter is not always the same as the symbol that represents the sound.
The particular vowels and consonants we need to produce when we speak are often different or do not exist in other languages. For example: - the 'i' phonemes in English, the /I/ in 'ship', and /i:/ in 'sheep', do not exist in Italian - Spanish speakers sometimes have problems with the /b/ in 'ban' and the /v/ in 'van' since these are not distinctly separate phonemes in Spanish - to Japanese speakers / / (cat) and / /(cut) can sound similar as the Japanese 'a sound is about halfway between the two.
'Classroom' has two syllables - 'class' + "room', Syllables are made up of a vowel or a vowel + consonant combination. When a word has more than one syllable, one syllable is emphasized more than another. So, for example, in the words 'table', 'mother', 'doctor' the first syllable is emphasized or stressed, In the words 'belief", 'attack', and 'cassette', the second syllable is stressed.
Word stress can be indicated in the phonetic transcription of a word with a / / symbol before the stressed syllable, for example, 'table' /'terbl /, 'cassette -/k 'set/. Often the unstressed vowel, called the schwa, is pronounced as / / as in /k 'set/.
Underline the stressed syllable in these words. Use a dictionary if necessary. classroom, example, telephone, instructions, important, exercise, computer, conversation, explain
Underline the stressed syllable in these words. Use a dictionary if necessary. classroom, example, telephone, instructions, important, exercise, computer, conversation, explain
Open your books on page ten. Today we're going to hear a story about a clown.
Sentence stress can also change the meaning of a sentence. For example: I love you. I love you. I love you