Effective Communication Strategies in Business Environments
Explore the various aspects of communication processes within organizations, including sender-receiver dynamics, communication channels, small group networks, upward and downward communication methods, business communication tools, information richness of channels, email and voice mail etiquette, and interpersonal communication challenges. The content delves into encoding and decoding messages, gender differences in communication, and offers insights into enhancing communication effectiveness.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
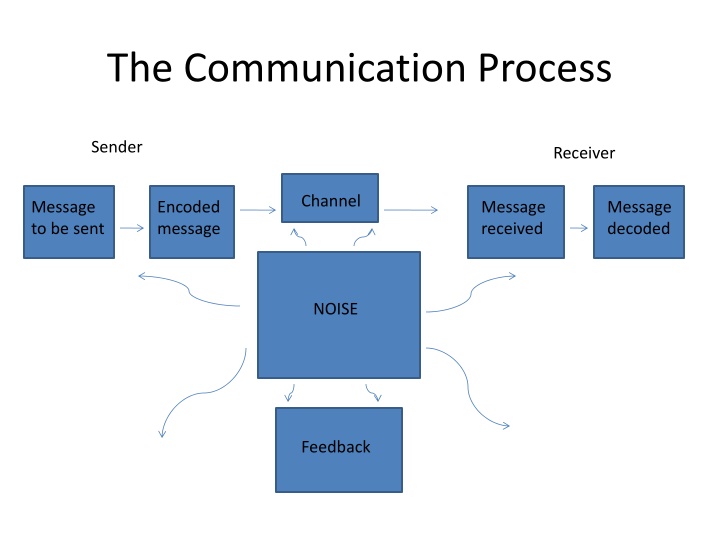
The Communication Process Sender Receiver Channel Message to be sent Encoded message Message received Message decoded NOISE Feedback
Wheel All Channel Chain
Small Group Networks and Effective Criteria Networks Criteria Chain Wheel All Channel Speed Moderate Fast Fast Accuracy High High Moderate Emergence of Leader Moderate High None Member Satisfaction Moderate Low High
Upward Communication Serial communication Attitude surveys Focus groups Exit interviews Suggestion boxes Third party facilitators 4
Downward Communication Bulletin boards Policy manuals Newsletters Intranets 5
Business Communication Memos Telephone calls Email (and IM, TM, Blogs) Voice mail Face-to-face meetings Committee meetings Videoconferencing 6
Information Richness of Communication Channels Prerecorded speeches Live speeches Formal reports, bulletins Online Discussion Groups Video conferences High Channel Richness Low Channel Richness Memos, letters Voice mail Face-to-face conversations Telephone conversations Electronic mail
Email Etiquette and Voice Mail Etiquette 8
Interpersonal Communication Three problem areas: Intended message versus message sent Message sent versus message received Message received versus message interpreted 9
Sender Receiver Encodes Message Sends Message Receives Message Decodes Message I hear her say I think she means What I want to say What I say 10
Gender Differences in Communication (Tannen, 1986 & 1990) Men Talk about major events Tell the main point Are more direct Use uh-huh to agree Are comfortable with silence Concentrate on the words spoken Sidetrack unpleasant topics Women Talk about daily life Provide details Are more indirect Use uh-huh to listen Are less comfortable with silence Concentrate on nonverbal cues and paralanguage Focus on unpleasant topics 11
Noise 12
Use of Space Intimacy zone Personal distance zone Social distance zone Public distance zone 14
Use of Time 15
Paralanguage 16
Artifacts Our office What we wear The car we drive The house we live in 17
When we have too much information, we tend to: Assimilate Sharpen Level 18
Reactions to Information Overload Omission Error Queuing Escape Use of a gatekeeper Use of multiple channels 19
Listening Styles (Geier & Downey, 1980) Leisure Inclusive Stylistic Technical Empathic Nonconforming 20
Other Factors Emotional State Bias Cognitive Ability Drugs and Alcohol 21