Understanding Electron-Phonon Interaction and Peierls Instability in Polyacetylene using SSH Model
Explore the concepts of electron-phonon interaction, Peierls instability, and the SSH model in the context of Polyacetylene. Dive into the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, electron band properties, and density of states, unraveling the fascinating world of molecular dynamics and energy calculations.
Uploaded on Nov 20, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Week 7, Electron- phonon interaction, SSH Model, Peierls instability Model for polyacetylene, Born-Oppenheimer approximation, electron band and band gap, density of states, Peierls instability
Polyacetylene (CH)n H H H H H H . . . . . . C C C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H trans: zigzag cis: armchair
Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model 1 N 2 3 = + + H H H H u2 e ph epi t0 N ( ) = + = l l , periodic B.C. H t c c + c c l N c + c + e 0 1 1 l l l = 1 l 1 2 1 2 N ( ) 2 = + = = 2 l , , H u K u u u u u M x + l N + ph 1 l l l l l = 1 l or if ..., ..., 0 otherwise = = + = + = = = if 1 l k n n n l k k l l 1 N c c u + ( ) = + = = l nk n k M c c u l nk l h.c. , H u M + epi 1 1 l l l l = 1 , , l n k l
Born-Oppenheimer approximation Fixing atomic positions to ??, compute the single electron energy ??. Fill the band to fermi level ?. Then the total energy is given by ? ?? = ?????+phonon potential energy The single electron Hamiltonian H is from (atoms are fixed) ( 0 1 l = N ) = = + l ( ) h.c. H c Hc t u u c c + + 1 1 l l l = H k k k
Single electron H + + 0 ( 0 ( 0 ( ) ( 0 ) t u u t u u 0 2 1 0 1 N + + ) ( 0 ) t u u t u u 0 2 1 0 3 2 = + ) H t u u 0 3 2 + ( ) t u u 0 0 0 1 N N or + = = + ( ( ), if ), if 1 mod 1 mod rwise t t u u u u m m n n N N 0 m n = + H 0 mn n m 0, othe = T H H
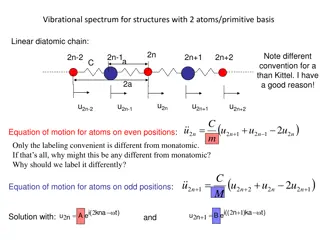
Special case, uniform displacement ??= const ?? 2?0 c c 1 k d 2 = = / iEt , , i H e c n dt ? ? ? c N ? 2?0 c c c c 1 1 2 2 = = = = , 1,2, , H E t c t c Ec l N l N c + c + 0 1 0 1 l l l l c c N N 2 Na = 1 N = = = = ikla Bloch theorem: , , 0,1,2, 1, c Ae k n n N A l ( ) = + = k 0 ika ika 2 cos( t ) E t e e ka 0 0
Odd/even displacement ??= 1??0 ?2 ?1 ?1 ?2 ?3 + 0 2 2 t u t u 0 0 0 0 + 2 0 2 0 t u t u 0 0 0 0 = 0 0 H t u 0 0 + 2 t u 0 0 0 0 or + = + + 2 2 , | , | | 1, ( | 1, ( = 1)/ 2 even 1)/ 2 odd + + herwise t u u t m n m n m n m n 0 t 0 2 t = H 0 0 1 mn 0, ot
Enlarged unit cell ?1 ?2 ?1 0 1 2 3 4 5 .. ? 1 = e k o k c c c 1 N 2 l = = = ikR , , (2 ) , a l 0,1, 1 e L R l L l l c 2 L k + 2 1 l 2 = = , 0,1,2, 1 k n n L (2 ) a L
Transform Hamiltonian ? into k-space 1 L ( ) = + + h.c. H 1 2 t c c 2 2 t c 1 2 c + + + 2 1 2 l l l l = 0 l 2 e k o k iak 0 t e c c t t e ( ) = e k o k 1 2 c c 2 iak 0 t k 1 2 ( ) ( ) ( ) c k H k c k 1BZ k 2 e k o k iak 0 t e c c t t e = = 1 2 ( ) , ( ) H k c k 2 iak 0 t 1 2
Diagonalize the k-space H c c ( ) 1 = = ( ) 0, H k I k k 2 2 i ak t t e ( )( ) + = + + = 2 2 2 i ak i ak 1 2 det 0 0 t t e t t e 1 2 1 2 + 2 i ak t t e 1 2 = + = 2 , 2 t t u t t u 1 0 0 2 0 0 ( ) 2 ( ) = + + = + 2 1 2 2 0 k 2 k 2 cos(2 ) t t 1 2 t t ak k 2 cos( t = = 0 k ), 4 sin( ) ak u ak 0 0 k
Zone folding when = 0 shift by ?/? ?? 2?0 k ? ? ? ? 2? ? 2?0 = Original Brillouin zone [ ? New BZ half smaller. ?,? one site per unit cell, lattice const 2 cos( ) k t ka = a ? ), 0 = two sites per unit cell, lattice const 2 cos( ) k t ka = 2 a 0
Gapped band structure when ? 0 ?? +2?0 = 2 2| | t t 2 1 ? 2? ? 2? 2?0 ( ) 2 = + 0 k 2 k k 2 cos( t = = 0 k ), 4 sin( ) ak u ak 0 0 k
Density of states in 1D system 2?0 dk d = = d D ( ) ( ) F ( ) 2 ( ) F F k 2 2 v k 1 v = = = , ( ) k k d dk v dk D k k ?(?) ( ) 1 , 2 t 0 ( ) = a D 2 0 2 2 2 (4 )( ) t von Hove Singularity 0, otherwise 2?0
Compute total energy E(u) 1 2 N ( ) 2 = + ( ) ( ) E u k u u + 1 k k l l = 1 k l + / a dk = ) 2 + 2 ( Na ku N k k 2 / a = d D ( ) + = 2 2 , Na Nku u u 0 1 = density of states: ( ) ( ) D k Na k (per unit length, per unit energy interval)
Density of states from the Green s function ( ) ( ) 1 = + i r ( ) Tr ( ) A E ( ) D E G E E H 1 = r in mode space: ( , , ) g n k E + i ( ) k E n ( ) = r a ( ) A E ( ) ( ) i G E G E Why the density of states D(E) is given by the spectrum function A(E), and what const we need to take so that it agrees with the previous slide?
Peierls instability ?(?)/? ?0 ?0 ? ??/?