Understanding Electric Current, Charge, and Circuits
Explore the basics of electricity, circuit symbols, and concepts like current flow, charge, and resistance in this educational content. Learn about conventional current versus electron flow, equations linking charge, current, and time, and practical circuit applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
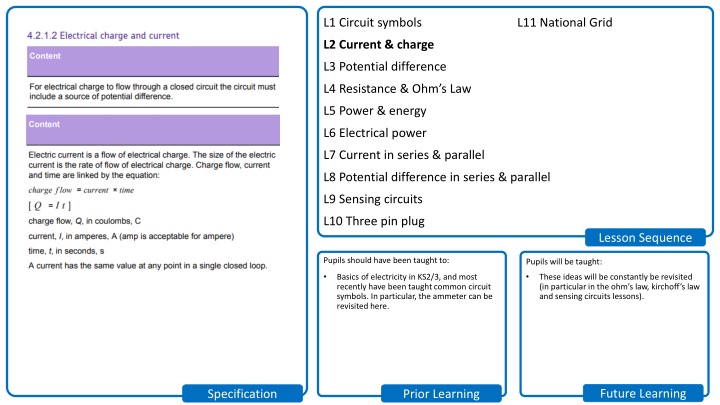
L1 Circuit symbols L11 National Grid L2 Current & charge L3 Potential difference L4 Resistance & Ohm s Law L5 Power & energy L6 Electrical power L7 Current in series & parallel L8 Potential difference in series & parallel L9 Sensing circuits L10 Three pin plug Lesson Sequence Pupils should have been taught to: Pupils will be taught: Basics of electricity in KS2/3, and most recently have been taught common circuit symbols. In particular, the ammeter can be revisited here. These ideas will be constantly be revisited (in particular in the ohm s law, kirchoff s law and sensing circuits lessons). Future Learning Specification Prior Learning
SciDoc Charge & current Charge & current Last Lesson Last Term Last Year Stretch & Challenge I do We do You do Test I do We do You do Do Now
SciDoc Keywords Learning Objectives Keywords Charge Coulomb Electron Current Ampere Ammeter Recall what the charges particles flowing through a metal wire are. Recall the definition of current. Apply an equation to calculate charge, current and time in common circuits. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do Do Now
Charged particles (electrons) flow through metal wires. SciDoc Stretch: If each electron has a charge of -1.6 10-19 C, how many electrons are there in one coulomb? Charge has units of Coulombs (C) and each electron carries a charge of -1.6 10-19 C. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
Current is the rate of flow of charge (i.e. how much charge is flowing every second). SciDoc Stretch: A circuit contains a battery and a thermistor. Draw a circuit that could measure the current flowing in the circuit. Current has units of Amps (A) and is measured by an ammeter (which goes in series). I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Conventional current vs electron flow Conventional current vs electron flow We say that conventional current flows from positive to negative. However like charges ________. So electrons are repelled by the negative terminal and move from negative to positive. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc T/N: Charge & current T/N: Charge & current Charge, current and time are linked by the equation: Q = I t I = Current (Amps, A) Q = Charge (Coulombs, C) t = Time (s) Stretch: Re-arrange to give equations for I and t. From one of the equations, why do you think current is defined how much charge is flowing each second? I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Example question 1 Example question 1 Calculate the charge when 10 Amps passes a point in 8 seconds. Write the formula: Q = I x t Write the variables Q = I = 10 t = 8 Write the equation Q = 10 x 8, which is Q = 80 C I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Example question 2 Example question 2 Calculate the current when 4 C of charge passes a point in 8 seconds. Write the formula: Q = I x t Write the variables Q = 4 I = t = 8 Rearrange the formula Q/t = I Put the numbers in 4/8 = Q which means Q = 0.5C I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Worksheet Worksheet Complete the worksheet! I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Basic answers Basic answers 0.4A 0.8A 2A 2.14A 3A 25A 750C 1000C 12 C 1000C 4550C Q = I t 20s 150s 50s 20.8s 60s t = Q I I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Medium answers Medium answers 0.58 A 1620 C 162 C 240 5400 180 0.67 A 168 C 10800 C 7200 300 420 I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Hard answers Hard answers I = Q t = 1000 240 = 0.42 A Q = I t = 0.01 0.5 = 0.005 A t = Q I = 0.3 0.002 = 150 s Q = I t = 0.5 600 = 300 C I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Struggle time! Struggle time! Exam question so exam conditions! You have 8 minutes. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO: