Understanding DNA Fragment Analysis Through Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments based on size. By casting a gel and running an electric current through it, terminated DNA fragments can be separated and visualized using isotopes. This process allows for the analysis of DNA fragments differing in size by just one base pair. Techniques such as linear PCR and cycle sequencing in the 1980s paved the way for more efficient DNA amplification methods.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
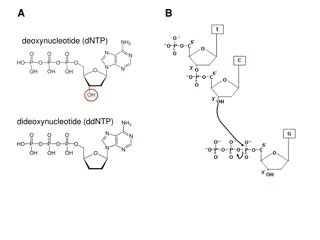
After synthesis, a polyacrylamide gel was cast Acrylamide is neurotoxic until polymerized
The terminated fragments are separated according to size on the gel. After electrophoresis, the gel is dried and exposed to photographic film. The decay of Isotope-labeled dCTP (filled circles) produces photons, that blacken the film. PAGE allows us to distinguish DNA fragments that differ in size by only one base pair large small
A C G T
1980s: Linear PCR is used to generate more products from less template Cycle sequencing is a simple method in which successive rounds of denaturation, annealing, and extension in a thermal cycler result in linear amplification of extension products. From applied biosystems.com