Understanding Basic Terminology and Classification of Carbohydrates
This lesson covers the fundamental terminology and classification of carbohydrates, including monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are essential chemical compounds comprising carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with diverse classifications based on their structure and composition. Explore the basic units of carbohydrates and their significance in nature.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
LESSON LESSON- -1 1 BASIC TERMINOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION OF BASIC TERMINOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHYDRATES CARBOHYDRATES
Objectives: Objectives: Know the basic terminology related to carbohydrates of different nature. Know the classifications of carbohydrates available in nature.
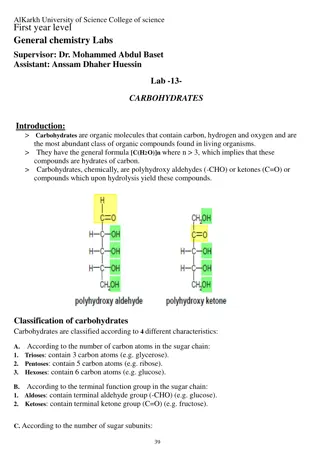
Basic terminology related to carbohydrates Basic terminology related to carbohydrates Carbohydrate Carbohydrate the the name name derived derived from from the the French French word word hydrate hydrate de de carbone carbone , , a a neutral neutral chemical chemical compounds compounds comprising comprising the the elements elements carbon, carbon, hydrogen hydrogen and and oxygen oxygen having having empirical empirical formula formula (CH (CH2 2O)n, O)n, where where n n is is 3 3 or or more, more, however, however, carbohydrate carbohydrate group group contains contains polyhydroxy polyhydroxy aldehydes, aldehydes, ketones, ketones, alcohols, alcohols, acids acids or or any any compound compound that that yield yield these these on on its its hydrolysis hydrolysis. . Monosaccharides Monosaccharides the the Greek Greek word word monos monos single single and and sacchar sacchar sugar , sugar , also also called called simple simple sugar, sugar, so, so, it it is is the the simplest simplest form form of of sugar sugar and and most most basic basic units units of of carbohydrates carbohydrates which which can t can t be be further further hydrolysed hydrolysed to to simpler simpler chemical chemical compounds compounds. .
Cont Cont .. .. Sugar Sugar is is restricted restricted to to those those carbohydrates carbohydrates containing containing less less than than ten ten monosaccharide monosaccharide residues residues (e (e. .g g. ., , glucose, glucose, fructose fructose etc) etc). . Oligosaccharides Oligosaccharides the the Greek Greek word word oligos oligos- - a a few few is is often often used used to to include include all all sugars sugars other other than than the the monosaccharides monosaccharides (e (e. .g g. ., , sucrose, sucrose, lactose lactose etc) etc). . Polysaccharides Polysaccharides the the polymers polymers of of monosaccharide monosaccharide units units (glycans) (glycans) and and are are classified classified into into two two groups, groups, homoglycans homoglycans (single (single type type of of monosaccharide monosaccharide unit) unit) and and heteroglycans heteroglycans (mixtures (mixtures of of monosaccharides monosaccharides and and derived derived products), products), such such as as cellulose, cellulose, hemicellulose, hemicellulose, starch starch etc etc. .
Cont Cont . . Cellulose Cellulose is is one one of of the the major major structural structural carbohydrates carbohydrates of of plant plant cell cell walls walls which which can can be be utilized utilized by by microorganisms microorganisms in in the the rumen rumen as as major major dietary dietary source source. . Hemicellulose Hemicellulose is is a a polysaccharide polysaccharide found found in in plant plant cell cell walls, walls, which which is is more more complex complex in in structure structure than than sugars sugars but but less less complexes complexes than than cellulose cellulose. . Lignin Lignin is is not not a a carbohydrate carbohydrate but but closely closely associated associated with with this this group group of of compounds, compounds, which which is is major major structural structural component component of of mature mature plant plant and and made made up up of of many many phenylpropanoid phenylpropanoid units units associated associated in in a a complex complex cross cross- - linked linked. .
Basic functions of carbohydrates Basic functions of carbohydrates It It is is the the most most abundant abundant group group of of organic organic compounds compounds in in the the globe globe. . Serve Serve as as a a source source of of energy energy for for normal normal life life processes processes of of different different categories categories of of animals animals. . Insoluble Insoluble fractions fractions such such as as cellulose cellulose and and hemicellulose hemicellulose are are most most important important in in providing providing structural structural support support and and protection protection for for living living plants plants. . Used Used as as energy energy sources sources and and as as a a precursor precursor of of more more complex complex compounds compounds. . Make Make up up 75 75% % of of dry dry weight weight of of several several plants plants. . Many Many animals animals primarily primarily depend depend on on CHO CHO for for their their survivability, survivability, Important Important for for nutritional nutritional as as well well as as economic economic point point of of view view. .
Classification of carbohydrate Classification of carbohydrate Based on the numbers of sugar units and carbon atoms per sugar unit Based on the numbers of sugar units and carbon atoms per sugar unit 1 1. . Monosaccharides Monosaccharides (single (single glycose glycose unit) unit) Trioses Trioses (C (C3 3H H6 6O O3 3) ) - - Glyceraldehyde Glyceraldehyde and and Dihydroxyacetone Dihydroxyacetone Tetrose Tetrose (C (C4 4H H8 8O O4 4) ) - - Erythrose Erythrose Pentoses Pentoses (C (C5 5H H10 10O O5 5) ) - - Ribose, Ribose, Arabinose, Arabinose, Xylose, Xylose, and and Xylulose Xylulose Hexoses Hexoses (C (C6 6H H12 12O O6 6) ) - - Glucose, Glucose, Galactose, Galactose, Mannose, Mannose, and and Fructose Fructose
Cont.... Cont....
Cont.... Cont.... 2 2. . Oligosaccharides Oligosaccharides ( (2 2 to to 10 10 glycose glycose units) units) Disaccharides Disaccharides (C (C12 12H H22 22O O11 11) ) - - Sucrose, Sucrose, Maltose, Maltose, Cellobiose, Cellobiose, and and Lactose Lactose Trisaccharides Trisaccharides (C (C18 18H H32 32O O16 16) ) - - Raffinose Raffinose Tetrasaccharides Tetrasaccharides (C (C24 24H H42 42O O21 21) ) - - Stachyose Stachyose Pentasaccharides Pentasaccharides (C (C30 30H H52 52O O26 26) ) - - Verbascose Verbascose
Cont.... Cont....
Cont.... Cont.... 3 3. . Polysaccharides Polysaccharides (> (> 10 10 glycose glycose units) units) Homoglycan Homoglycan (single (single glycose glycose units) units) Pentosans Pentosans (C (C5 5H H8 8O O4 4)n )n - - Arabans Arabans and and Xylans Xylans Hexosans Hexosans (C (C6 6H H10 10O O5 5)n )n - - Glucans Glucans Starch Starch ( ( - -linked), linked), Dextrins Dextrins ( ( - -linked), linked), Glycogen Glycogen ( ( - -linked), linked), and and Cellulose Cellulose ( ( - -linked) linked) Fructans Fructans Inulin, Inulin, and and Levan Levan Galactans Galactans Mannans Mannans
Cont.... Cont.... Heteroglycan Heteroglycan ( (2 2- -6 6 dissimilar dissimilar kinds kinds of of glycose glycose units) units) Pectins Pectins ( ( - -linked), linked), Hemicellulose Hemicellulose ( ( - -linked), linked), Gums Gums & & Mucilages Mucilages and and Mucopolysaccharides Mucopolysaccharides 4. Specialized compounds 4. Specialized compounds Chitin Chitin Lignin (not a true carbohydrate) Lignin (not a true carbohydrate)
Cont.... Cont.... Amylose Amylose Amylopectine Amylopectine Glycogen Glycogen Cellulose Cellulose
Cont.... Cont....
Classification based on dietary forms Classification based on dietary forms 1. Free (not associated with the cellular structure of food) 1. Free (not associated with the cellular structure of food) Lactose Lactose milk milk Fructose Fructose honey honey Trehalose Trehalose haemolymph haemolymph
Cont.... Cont.... 2. Intracellular (inside the cell) 2. Intracellular (inside the cell) Soluble Soluble dissolved in the cytosol of the cell dissolved in the cytosol of the cell Storage polysaccharides Storage polysaccharides Starches Starches - Amylose ( Amylose ( - -1,4 glucose polymer) 1,4 glucose polymer) - Amylopectin ( Amylopectin ( - -1,4 and - Glycogen ( Glycogen ( - -1,4 and 1,4 and - -1,6 glucose polymer) 1,4 and - -1,6 glucose polymer) 1,6 glucose polymer) 1,6 glucose polymer) Fructans Fructans - Levans ( Levans ( - -2,6 fructose polymer) 2,6 fructose polymer) - Inulins Inulins ( ( - -2,1 fructose polymer) 2,1 fructose polymer)
Cont.... Cont.... 3 3. . Cell Cell wall wall Cellulose Cellulose ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 glucose glucose polymer) polymer) Hemicellulose Hemicellulose ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 xylose xylose polymer) polymer) Pectin Pectin ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 galacturonic galacturonic acid acid polymer) polymer) Gums Gums ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 and and - -1 1, ,3 3 polymers polymers of of numerous numerous sugars) sugars) Lignin Lignin - - phenylpropenoid phenylpropenoid polymers polymers (not (not a a carbohydrate) carbohydrate) 4 4. . Chitin Chitin ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 N N- -acetylglucosamine acetylglucosamine polymer) polymer) Exoskeleton Exoskeleton Cell Cell wall wall
Salient details about important carbohydrates Salient details about important carbohydrates 1 1. . Monosaccharides Monosaccharides Trioses, Trioses, glyceraldehyde glyceraldehyde & & dihydroxyacetone dihydroxyacetone are are important important intermediates, intermediates, plays plays a a significant significant role role in in energy energy metabolism metabolism. . Pentoses Pentoses exist exist as as polymers, polymers, pentosans, pentosans, and and small small fraction fraction as as a a free free form form. . o It It is is associated associated with with cell cell walls walls (hemicellulose) (hemicellulose). . o After After getting getting fermentation fermentation by by microbes, microbes, they they contribute contribute to to energy energy pool pool. .
Cont.... Cont.... Ribose Ribose arise arise in in a a number number of of compounds/intermediates compounds/intermediates such such as as ATP, ATP, ADP, ADP, DNA, DNA, RNA, RNA, etc etc. . and and also also in in several several vitamins vitamins and and coenzymes coenzymes. . o It It can can be be synthesized synthesized by by animals animals. . Glucose Glucose occur occur in in free free as as well well as as in in combined combined form form in in plants, plants, fruits, fruits, honey, honey, blood, blood, lymph lymph and and cerebrospinal cerebrospinal fluid fluid. . o Major Major component component of of many many oligosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides polysaccharides and and glucosides glucosides. . o Significant Significant source source of of energy energy (probably (probably the the most most important important sugar) sugar). . o White White crystalline crystalline solid solid in in pure pure state state and and soluble soluble in in water water. . o End End product product of of starch starch digestion digestion. .
Cont.... Cont.... Galactose Galactose is is constituent constituent of of the the disaccharide disaccharide lactose lactose (occurs (occurs in in milk) milk). . o It It doesn t doesn t occur occur free free in in nature nature except except as as a a breakdown breakdown product product during during fermentation fermentation. . o Arises Arises as as a a component component of of the the anthocyanin anthocyanin pigments, pigments, galactolipids, galactolipids, gums gums and and mucilages mucilages. . o Some Some people people lack lack the the enzyme enzyme namely namely phosphogalactose phosphogalactose uridyl uridyl transferase, transferase, results results in in accumulation accumulation of of galactose galactose and and condition condition is is referred referred as as galactosemia galactosemia. .
Cont.... Cont.... Fructose Fructose is is fruit fruit sugar sugar or or laevulose, laevulose, occurs occurs free free in in green green leaves, leaves, fruits fruits and and honey honey. . They They are are one one of of the the sugar sugar units units of of sucrose sucrose and and fructans fructans. . It It is is the the sweetest sweetest of of sugars, sugars, and and may may be be important important in in piglet piglet diets diets. . The The free free form form is is white white crystalline crystalline solid solid nature nature and and sweeter sweeter taste taste than than sucrose sucrose and and the the sweet sweet taste taste of of honey honey is is due due to to this this sugar sugar. .
Cont.... Cont.... Glucose Glucose Fructose Fructose Galactose Galactose Ribose Ribose
Cont.... Cont.... 2 2. . Oligosaccharides Oligosaccharides Maltose Maltose consists consists of of two two - -D D- -glucose glucose residues residues linked linked in in the the - -1 1, ,4 4 positions positions. . o They They are are produced produced from from starch starch during during the the germination germination of of barley barley by by the the action action of of the the enzyme enzyme amylase amylase. . o It It is is soluble soluble in in water, water, but but not not as as sweet sweet as as sucrose sucrose. . Sucrose Sucrose is is - -D D- -glucose glucose and and - -D D fructose fructose joined joined by by an an - -1 1, , 2 2 linkage linkage and and has has no no active active reducing reducing group group. . o It It is is most most abundantly abundantly occurring occurring disaccharide disaccharide in in plants plants o Major Major sources sources are are sugar sugar cane, cane, beets, beets, molasses, molasses, fruits, fruits, tree tree sap, sap, etc etc. . o They They are are easily easily hydrolysed hydrolysed by by the the enzyme enzyme sucrase sucrase or or by by dilute dilute acids acids. .
Cont.... Cont.... Lactose Lactose is is formed formed from from - -D D- -glucose glucose and and - -D D- -galactose, galactose, joined joined together together by by a a - -1 1, ,4 4 linkage linkage. . o They They are are synthesized synthesized by by mammary mammary gland gland in in mammals mammals. . o Streptococcus Streptococcus lactis lactis, , is is responsible responsible for for souring souring milk milk by by converting converting the the lactose lactose into into lactic lactic acid acid. . o Lactase Lactase is is an an enzyme enzyme and and abundantly abundantly available available in in young young animals animals. . o However, However, chickens chickens have have no no lactase lactase activity, activity, but but can can utilize utilize at at low low levels levels of of lactose lactose via via fermentation fermentation in in the the hind hind gut gut. .
Cont.... Cont.... Cellobiose Cellobiose is is composed composed of of two two - -D D- -glucose glucose residues, residues, joined joined through through a a - -1 1, ,4 4 linkage linkage o It It can t can t be be fragmented fragmented by by mammalian mammalian digestive digestive enzymes, enzymes, but but can can be be split split by by microbial microbial enzymes enzymes. . o It It does does not not exist exist naturally naturally as as a a free free sugar, sugar, and and is is a a basic basic repeating repeating unit unit of of cellulose cellulose. .
Cont.... Cont.... 3 3. . Polysaccharides Polysaccharides Starch Starch is is reserve reserve carbohydrate carbohydrate of of seeds, seeds, fruits, fruits, tubers, tubers, roots roots etc etc. . o It It is is quantitatively quantitatively a a major major source source of of energy energy for for animals animals. . o Differ Differ in in their their chemical chemical composition composition have have amylose amylose ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 linkage) linkage) and and amylopectin amylopectin ( ( - -1 1, ,4 4 & & - -1 1, ,6 6 linkages) linkages). . o In In most most starch, starch, amylopectin amylopectin is is the the main main component, component, which which accounts accounts about about 70 70- -80 80 % % of of the the total total starch starch component component. . o Insoluble Insoluble in in cold cold water, water, but but in in water water hot hot it it swells swells & & eventually eventually gelatinise gelatinise. . o Iodine Iodine reactions reactions gives gives a a deep deep blue blue colour colour for for amylose, amylose, whereas, whereas, amylopectin amylopectin solutions solutions produce produce a a blue blue- -violet violet or or purple purple colour colour. .
Cont.... Cont.... Dextrin Dextrin is is an an intermediate intermediate product product of of the the hydrolysis hydrolysis of of starch starch and and glycogen glycogen and and called called - -limit limit dextrins dextrins because because of of inability inability of of - -amylase amylase to to break break - -1 1, ,6 6 bonds bonds. . o They They are are soluble soluble in in water water and and produce produce gum gum- -like like solutions solutions. . o It It can can be be hydrolysed hydrolysed at at the the brush brush boarder boarder by by - -dextranase dextranase. . o Dextrin Dextrin gives gives a a characteristic characteristic flavour flavour to to foods foods. .
Cont.... Cont.... Glycogen Glycogen is is a a group group of of highly highly branched branched polysaccharides polysaccharides. . o Isolated Isolated from from animals animals or or microorganisms microorganisms and and frequently frequently called called animal animalstarch starch . . o They They occur occur in in the the liver, liver, muscle muscle and and other other animal animal tissues tissues and and plays plays an an essential essential role role in in energy energy metabolism metabolism. .
Cont.... Cont.... Beta Beta glucan glucan is is a a polymer polymer of of D D- -glucose, glucose, joined joined with with - -1 1, ,3 3 and and - -1 1, ,4 4 linkages linkages. . o Found Found in in barley barley (about (about 5 5- -8 8% %) ) where, where, starch starch and and protein protein are are enclosed enclosed within within the the endosperm endosperm cell cell walls, walls, that that consist consist of of - -glucans glucans and and arabinoxylans arabinoxylans. . o Forms Forms a a viscous viscous solution solution in in the the gastrointestinal gastrointestinal tract, tract, thereby thereby interfere interfere the the digestion digestion process process. . o Dietary Dietary - -glucanase glucanase supplementation supplementation is is beneficial beneficial in in barley barley- -based based poultry poultry diets diets. . o However, However, in in case case of of swine swine results results have have been been very very inconsistent inconsistent. .
Cont.... Cont.... Cellulose Cellulose is is the the most most abundant abundant carbohydrate carbohydrate in in nature nature and and main main structural structural component component of of plant plant cell cell wall wall. . o Polymer Polymer of of - -1 1, ,4 4- -linked linked D D- -glucose, glucose, have have 6 6 carbon carbon atoms atoms in in the the trans trans position position. . o Held Held together together by by both both inter inter and and intra intra- -molecular molecular hydrogen hydrogen bonding, bonding, which which results results in in a a tightly tightly bound bound and and crystalline crystalline structure structure. . o Hydrolysed Hydrolysed only only by by microbial microbial enzymes, enzymes, and and has has limited limited use use in in nonruminant nonruminant species species. .
Cont.... Cont.... Hemicellulose Hemicellulose is is a a complex, complex, heterogenous heterogenous mixture mixture of of different different polymers polymers of of monosaccharides monosaccharides and and found found in in plant plant cell cell wall wall. . o Mainly Mainly composed composed of of D D- -glucose, glucose, D D- -galactose, galactose, D D- -mannose, mannose, D D- -xylose xylose and and L L- -arabinose arabinose units, units, which which joined joined together together by by various various glycosidic glycosidic linkages linkages. . o Less Less resistant resistant to to hydrolysis hydrolysis in in comparison comparison with with others, others, but but more more easily easily utilized utilized than than cellulose cellulose because because of of less less hydrogen hydrogen bonding bonding. .
Cont.... Cont....
Cont.... Cont.... Chitin Chitin is is the the only only known known example example of of a a homoglycan homoglycan containing containing glucosamine glucosamine. . o It It is is a a linear linear polymer polymer of of acetyl acetyl- -D D- -glucosamine glucosamine. . o Chitin Chitin is is widely widely occurring occurring in in lower lower animals animals (abundant (abundant in in crustacea, crustacea, fungi, fungi, green green algae, algae, etc) etc). . o Probably Probably the the most most abundant abundant polysaccharide polysaccharide of of nature nature after after cellulose cellulose. .
Cont.... Cont.... Exudate Exudate gums gums and and acid acid mucilage mucilage are are produced produced from from wounds wounds of of plants, plants, and and may may arise arise as as natural natural exudations exudations from from bark bark and and leaves leaves. . o Occur Occur naturally naturally as as salt, salt, especially especially of of calcium calcium and and magnesium, magnesium, and and in in some some cases cases as as acetate acetate. . o Gum Gum arabic arabic (acacia (acacia gum) gum) on on hydrolysis hydrolysis yields yields arabinose, arabinose, galactose, galactose, rhamnose rhamnose and and glucuronic glucuronic acid acid. .
Cont.... Cont.... Hyaluronic Hyaluronic acid acid and and chondroitin chondroitin are are consisting consisting of of an an amino amino sugar sugar and and D D- -glucuronic glucuronic acid acid. . o Hyaluronic Hyaluronic acid acid contains contains acetyl acetyl- -D D- -glucosamine glucosamine & & present present in in the the skin, skin, synovial synovial fluid fluid & & umbilical umbilical cord cord & & also also play play an an important important part part in in lubrication lubrication of of joints joints. . o Chondroitin Chondroitin contains contains galactosamine galactosamine in in place place of of glucosamine glucosamine and and sulphate sulphate esters esters of of chondroitin chondroitin are are major major structural structural components components of of cartilage, cartilage, tendons tendons and and bones bones. .
Cont.... Cont.... Lignin Lignin is is not not a a carbohydrate carbohydrate but but is is closely closely associated associated with with this this group group of of compounds compounds. . Provides Provides biological biological resistance resistance to to the the cell cell wall wall & & mechanical mechanical strength strength to to the the plant plant. . Polymer Polymer that that originates originates from from three three derivatives derivatives of of phenylpropane phenylpropane ( (coumaryl coumaryl alcohol, alcohol, coniferyl coniferyl alcohol alcohol and and sinapyl sinapyl alcohol) alcohol) & & are are made made up up of of many many phenylpropanoid phenylpropanoid units units associated associated in in a a complex complex cross cross- -linked linked structure structure. . Wood Wood product, product, mature mature hays hays and and straws straws are are rich rich in in lignin lignin. . Poorly Poorly digested digested unless unless treated treated chemically chemically to to break break the the bonds bonds between between lignin lignin and and other other carbohydrates carbohydrates. .
Discussion.......... Questions, if any? THANKS