Tools for Centrality Measurements at MPD
This study examines centrality measurements at the MPD using tools like TPC/TOF in the participant region and FHCal in the spectator region. It explores two approaches for measurements and their combination, along with simulations for TPC and FHCal. Ambiguities in centrality measurements are addressed, highlighting the need for multiple approaches. Different distributions of spectator spots for various centralities are analyzed, aiding in the resolution of ambiguities through an asymmetry approach. The construction of observables in FHCal for centrality measurement, such as transverse and longitudinal energies and the cone of spectators, is also discussed. Moreover, the study presents centrality measurements using transverse and longitudinal energies, providing insights for better separation of central and peripheral events.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Centrality at MPD: fast look at problem. A.Ivashkin Institute for Nuclear Research RAS, Moscow on behalf of the FHCal group (INR, MEPhI, JINR ) Tools for the centrality measurements. MC results Approaches for the experimental data 1
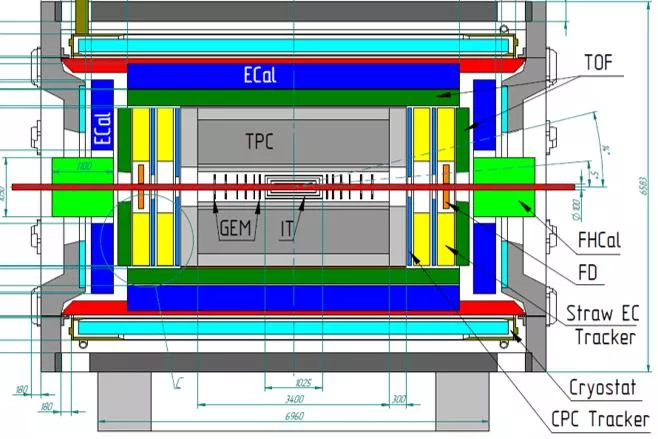
Tools for centrality measurements. Two types of measurements: Participant region (TPC/TOF) Spectator region (FHCal) Two approaches for centrality measurements. Combination of two approaches.
Centrality with TPC (MC simulation). FHCal TDR Use of TPC track multiplicity can estimate the impact parameter with accuracy <10% for mid-central events. 3
Centrality with FHCal (MC simulation). FHCal TDR Ambiguity in the centrality measuremens (Beam hole). To resolve the ambiguity other approaches are needed! 4
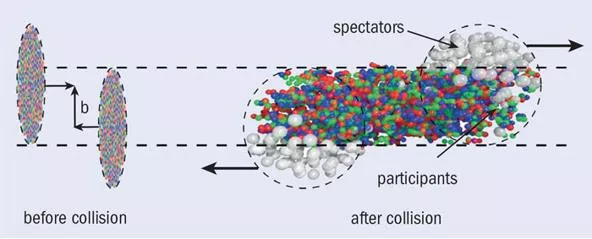
Spectators spots in FHCal have different distributions for different centralities. 11 = NN S GeV b<6 fm b<6 fm b>6 fm b>6 fm R, cm Cone for central events The energy deposition in inner and outer parts of calorimeter must be different for different centralities. Eout Ein Cone for peripheral events Let s introduce energy asymmetry: 5
Centrality with FHCal (asymmetry approach). FHCal TDR Ambiguity is resolved with some accuracy! 6
Construction of other observables in FHCal for the centrality measurement. ?? Transverse energy: ??= ??????? and Longitudinal energy: ??= ??????? ? Cone of spectators ?? = GeV 11 S = GeV 5 S NN NN A bagel structure in ET, ELcorrelations. 7
Centrality measurements with ETand EL. = = GeV 5 S GeV 11 S NN NN Each color bin is 10% of centrality. Each color bin is 10% of centrality. = GeV 5 S = GeV 11 S NN NN One can construct other observables for better separation of central/peripheral events! 8
Experimental situation. The above results were obtained from MC simulation, where the impact parameter is precisely known. How to proceed in experimental data? TPC case. MC Glauber model fit of the experimental multiplicity would provide the correspondence between the geometry of collision and track multiplicity. Other approach with only experimental data (without Glauber model) is suggested: Sruthy Jyothi Das, Giuliano Giacalone, Pierre- Amaury Monard, and Jean-Yves Ollitrault Relating centrality to impact parameter in nucleus-nucleus collisions PHYSICAL REVIEW C 97, 014905 (2018) 9
Experimental situation (FHCal case). Is it possible to apply MC Glauber model fit to FHCal? PHENIX did it for ZDC and BBC! PHENIX One can apply the TPC multiplicity correlation with the FHCal energy. Use of TPC multiplicity centrality classes would provide the centrality classes for FHCal energy. (ALICE like solution). ALICE In MPD the situation must be understood. The corresponding techniques are to be developed! New FHCal observables can be found! 10
Experimental situation (Combined case). If there are a few independent methods of centrality estimation, one can combine them statistically in iteration procedure: ALICE like Can the Machine Learning (ML) be applied? Such approach is under development at ALICE: EPJ Web of Conferences 137, DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/201713711001 At MPD we should have at least two methods: TPC and FHCal. Can FD contribute to centrality? BBC counters? 11
Outlook The measurement of centrality is a necessary task at MPD. TPC and FHCal are dedicated detectors here. What is about other detectors? The situation with TPC is straightforward but the methods must be developed. The situation with FHCal is more complicated and a few approaches can be considered: MC Glauber model fit, correlation between TPC multiplicity and FHCal observables, ... Combination of TPC and FHCal measurements can be done in a few ways: statistical combination or ML- technique. A dedicated physics group must be arranged. Who will do it? 12
Thank you! 13