Solving Triangles with Law of Sines
Learn how to solve oblique triangles using the Law of Sines, including the ambiguous case. Practice finding missing sides and angles in triangles without right angles. Explore examples and applications to enhance your trigonometry skills.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm Up Solve the following triangles for the missing side or angle: 1) 2) 3) 9 10 32 48 14 27 8 x x
Law of Sines Section 6.1
Objectives Students will be able to Solve oblique triangles using the Law of Sines (including the ambiguous case) Solve application problems for all triangles using trigonometry
Homework Law of Sines Worksheet - EVENS
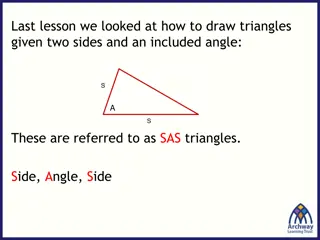
Oblique Triangles Triangles without a right angle Four Cases: C 1. Two angles and any side (AAS or ASA) a b 2. Two sides and an angle opposite one of them (SSA) (ambiguous case) A B c 3. Three sides (SSS) 4. Two sides and their included angle (SAS) First 2 cases can be solved using the Law of Sines
Law Of Sines If ABC is a triangle with sides a, b, and c, then ? ????= ? ? ????= ???? C C a b a b 0 0 A c B B c A *Can be written as ???? =???? =???? ? ? ?
Example - AAS Given C = 102.3 , B = 28.7 and b = 27.4 feet, find the remaining angles and sides C a b A B c
Example - ASA A pole tilts toward the sun at an 8 angle from the vertical and it casts a 22 foot shadow. The angle of elevation from the tip of the shadow to the top of the pole is 43 . How tall is the pole? 0
Ambiguous Case - SSA In a triangle where you are given a, b and h (h = b sinA) If angle A is acute And a < h no triangle is possible And a = h one triangle is possible (right triangle) And a b one triangle is possible And h < a < b two triangles are possible If angle A is obtuse And a b no triangle is possible And a > b one triangle is possible
Example Given a = 15, b = 25, and A = 85 , solve the triangle.
Example Given a = 22 in, b = 12 in, and A = 42 , find the remaining side and angles.
Example Solve the triangle, given a = 12 m, b = 31 m, and A = 20.5 .
Example A bridge is to be built across a small lake from a gazebo to the dock is S 41 W. From a tree 100m from the gazebo, the bearings to the gazebo and the dock are S 74 E and S 28 E respectively. Find the distance from the gazebo to the dock. T G D
Practice Law of Sines Worksheet
Closure Given A = 102.4 , C = 16.7 , and a = 21.6, solve for the remaining angle and sides