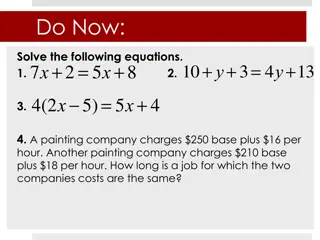Solving Equations in One Variable: Core Objectives
In this educational material, you will delve into solving equations in one variable, ranging from one-step to multi-step equations, and equations with variables on both sides. Each chapter focuses on specific objectives, providing detailed notes and guidance on isolating variables, combining terms, and identifying solutions. From equivalent equations to rearranging formulas, enhance your mathematical skills through a structured learning approach.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 2.1 Common Core A.CED.1 & A.REI.3 Create equations in one variable and use them to solve problems. Objectives To solve one-step equations in one variable.
Ch 2.1 Notes Equivalent Equations are equations that have the same solutions. To solve equations you must isolate the variable by either adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing the same number to both sides of the equation.
Chapter 2.2 Common Core A.REI.3, A.CED.1, & A.REI.1 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Objectives To solve two-step equations in one variable.
Ch 2.2 Notes To solve two-step equations you must get the variable all by itself and the get rid of any coefficients in front of the variable.
Chapter 2.3 Common Core A.CED.1 Create equations in one variable and use them to solve problems. Objectives To solve multi-step equations in one variable.
Ch 2.3 Notes To solve multi-step equations you must first combine like terms and then solve them like you did with two-step equations.
Chapter 2.4 Common Core A.CED.1, A.REI.1, & A.REI.3 Create equations in one variable and use them to solve problems. Objectives To solve equations with variables on both sides. To identify equations that are identities of have no solution.
Ch 2.4 Notes To solve equations with variables on both sides of the equal sign First get the variables on one side of the equation and the numbers of the other side of the equation. Second combine like terms Third solve for the variable
Chapter 2.5 Common Core A.CED.4, N.Q.1, A.ED.1, A.REI.1, & A.REI.3 Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations. Objectives To rewrite and use literal equations and formulas.
Ch 2.5 Notes Literal Equations is an equation that involves two or more variables. Formula is an equation that states a relationship among quantities. Formulas are special types of literal equations.
Perimeter of a Rectangle Area of a Rectangle Circumference of a Circle Area of a Circle Area of a Triangle Distance Traveled *Temperature Formula -
Chapter 2.6 Common Core N.Q.1 & N.Q.2 Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas. Objectives To find ratios and rates. To convert units and rates.
Ch 2.6 Notes Ratio compare two numbers by division ? ? Rate a ratio that compares quantities measured in different units 1ft 12in Unit Rate is a rate with a denominator of 1 $20 1 shirt Conversion Factor is a ratio of two equivalent measures in different units. 5 miles = ______ft unit
Chapter 2.7 Common Core A.REI.3, N.Q.1, & A.CED.1 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Objectives To solve and apply proportions.
Ch 2.7 Notes Propotion is an equation that states two ratios are equal. ? ?= ? ? To Solve a proportion you cross multiply - a*d = b * c
Chapter 2.8 Common Core A.CED.1 & A.REI.3 Create equations in one variable and use them to solve problems. Objectives To find missing lengths in similar figures. To use similar figures when measuring indirectly.
Ch 2.8 Notes Similar Figures have the same shape but not necessarily the same size (scale model). Scale Drawing is a drawing that is similar to an actual object or place (like a map). Scale is the ratio of the drawing (the key on a map)
Chapter 2.9 Common Core N.Q.3 Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities. Objectives To solve percent problems using proportions. To solve percent problems using the percent equations.
Ch 2.9 Notes To Solve Percent Problems of means ______ is means ______ to change a percent to a decimal you must move the decimal 2 places to the _______ Simple Interest Formula I = Prt where the I = interest, P= Principle, r = rate, and t = time
Chapter 2.10 Common Core N.Q.3 Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities. Objectives To find percent change. To find the relative error in linear and nonlinear measurements.
Ch 2.10 Percent Change is the ratio of the amount of change to the original amount. Percent change, p% =?????? ?? ???????? ?? ???????? ???????? ?????? *amount of increase = new amount original amount * Amount of decrease = original amount new amount
Relative Error is the ratio of the absolute value of the difference of a measured value and an actual value compared to the actual value. Relative error = |????????? ????? ?????? ?????| ?????? ????? When relative error is expressed as a percent, it is called percent error.