Principles of Government Systems and Types Explained
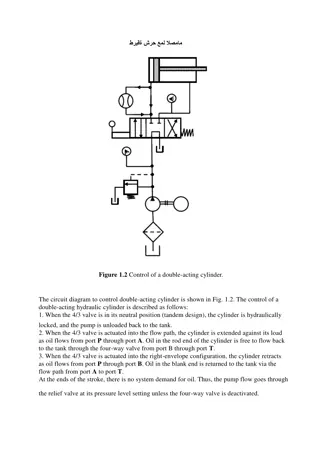
Explore the fundamental features of different government systems such as unitary, confederal, federal, autocratic, oligarchic, democratic, presidential, and parliamentary. Learn about the various forms of government, theories on the origin of states, and key characteristics of democratic government in this comprehensive overview.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Principles of Government Systems, Forms, and Types
Standard: SSCG 19 : Compare and contrast governments that are unitary, confederal, federal, autocratic, oligarchic, democratic, presidential and parliamentary. Essential Question What are the similarities and differences between the many forms of government including; unitary, confederal, federal, autocratic, oligarchic, democratic, parliamentary and presidential?
Objectives Learn the four essential features of a state (not a State ). Learn the four theories about the origination of states Understand the difference between unitary, confederal and federal systems of government Learn about the three major forms of government Identify key characteristics of democratic government
State or state? State (capitalized) refers to a political subdivision of the United States, such as the State of Montana state (lower case) refers to a nation-state or country, such as France or the United States
Theories on Origin of states Divine right (God given right to rule) Social contract (Society s need for order) Force theory (organize to resist enemies) Evolutionary theory (extended family rule became government)
Systems and Types of Government In order to study government, we first need to look at the following: Systems: How is the Power distributed Types: Who rules and who participates
Systems of government are based on one question How is the power distributed? There are three ways governments distribute power: Unitary Confederation Federal
Unitary One central government controls everything Power is NOT shared between states, counties, or provinces. Examples: The United Kingdom, France, the Netherlands, and Spain
Confederal A voluntary association of independent states that agrees to follow a central government. States can choose to follow or not follow the lead of the central government Examples: CSA, Russian Federation
Federal Power is shared by a central government States or Provinces are given considerable self-rule, usually through their own legislatures. Examples, the United States and Germany
Types of government are based on one question Who governs and what is the citizenship participation? There are three types of government: Autocracy Oligarchy Democracy
Autocracy Government in which the power to govern is held by one person Generally the power to rule is inherited or by military force There are three types of autocracy Example: Iraq, and Great Britain Dictatorship- absolute rule generally by force Absolute Monarchy- absolute rule inherited through family ties Constitutional Monarchy-share power with elected officials, seen for as figurehead with limited to no power
Oligarchy A government in which a few people such as a dominate clan or clique hold all the power The group gets their power through either military, wealth, or social status Elections may be held but offer only one candidate Examples: Greek-City states, Russian Federation.
Democracy Ruled by the people Individual freedom and equality is valued Free elections are held Decisions are based on majority rule Citizens vote by secret ballot Example: the United States Two forms of democracy Direct Democracy- People vote on all issues Representative Democracy (Republic)- citizens elect representatives and give them the power to vote on the issues
Two Major Types of Democratic Governments Parliamentary Voters elect members to Parliament House of Commons-the Political Party with the most votes in the House of Commons chooses the Prime Minister, the government s leader with no set length of term House of Lords: little power with most members being nobles having inherited their titles Presidential Voters elect legislatures Voter elect (indirectly) the president Therefore, in the presidential system voters have a more direct say about those who serve in two branches of the government Legislative Executive

 undefined
undefined