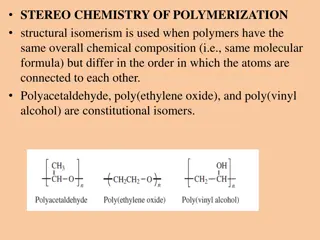
Polymers: Classification and Properties
Polymers are large molecules formed by joining many monomers together. The process, known as polymerization, creates long chains with unique structures. This article explores different classifications of polymers based on origin, monomers, thermal response, formation mode, structure, application, physical properties, and tacticity. Natural polymers sourced from materials like silk and wool are contrasted with semisynthetic polymers derived from chemical treatments of natural polymers. Dive into the world of polymers to grasp their significance in various industries.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Minia University Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering Department Classifications of Polymers By Prof. Wael Abdelmoez Professor of Environment & Energy
Polymers are very large molecules made when hundredsof monomers join together to form longchains. The word polymer comes from the Greek words poly (meaning many ) and meros (meaning parts ). Example: POL YETHYLENE = (ETHYLENE+ ETHYLENE+......)n Where n = 4,000
The small individual repeatingunits/molecules are known as monomers(means singlepart). Imagine that a monomer can be representedby the letter A. Then a polymer made of that monomer would have thestructure: -A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-
The process by which the monomermolecules are linked to form a big polymer molecule is called polymerization . Polymerization is a process of bonding monomer, or single units together through a variety of reaction mechanisms to form longer chains named Polymer Asimportant as polymers are, they exist with monomers, which are small, single molecules such as hydrocarbons and aminoacids.
1. ByOrigin 2. ByMonomer 3. By ThermalResponse 4. By Mode OfFormation 5. ByStructure 6. By Application & PhysicalProperties 7. ByTacticity
Natural Polymers Polymers which are isolated fromnatural materials are called as natural polymers. E.g. Silk, Wool, Natural rubber, Cellulose, Starch, Proteins etc.
NaturalRubber HeveaBrasiilensis
Semisynthetic Polymers The polymers obtained by simple chemical treatment of natural polymers to improve their physical properties like lustrous nature, tensile strength are called semisynthetic polymers E.g. Cellulose acetate, Cellulose nitrate
Synthetic Polymers Polymers synthesized in laboratory fromlow molecular weight compounds, are called as, synthetic polymers. E.g. Nylon, Terylene, Polyethylene, Polystyrene, Synthetic rubber, Nylon, PVC, Bakelite, Teflonetc.
Homo Polymers A polymer consistof identical called homo polymer. E.g. Polyethylene, PVC, Polypropylene, Nylon6 monomers is Co Polymers A polymer consist of monomers of different chemical structure are calledcopolymers. E.g. Nylon 6,6
Thermoplastic Polymers They are easily moulded in desired shapes by heating and subsequent cooling at roomtemperature. They are soft in hot and hard oncoding. They my be linear or branched chain polymers. E.g. PE, PVC, PS,PP
Thermosetting Polymers This polymer is hard and infusible on heating. These are not soft on heating under pressure and they are not remolded. These are cross linked polymers and are not reused. E.g. Bakelite