National Approaches to Safeguards in REDD+ Implementation
This content discusses core elements of a national approach to safeguards in the context of REDD+ implementation, highlighting key features, development processes, and tools to support safeguard initiatives. It emphasizes the importance of safeguard policies, laws, and regulations, along with the establishment of safeguard information systems and governance structures to oversee safeguard implementation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
National Approaches to Safeguards Kimberly Todd, UNDP/UN-REDD REDD+ Beyond Carbon: Safeguards and Multiple Benefits 13 November, 2012
Outline Core elements of a national approach to safeguards Key features of national approaches to safeguards Development of a national approach to safeguards UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards
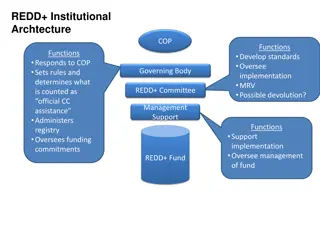
Core Elements of a National Approach to Safeguards Institutions 2. Safeguard Information System (SIS): Existing or new indicators, methodologies for collecting information, and framework for provision of information 1.Identification and development of relevant safeguards: Policies, laws and regulations, either existing or those created for REDD+ Processes and Procedures
Safeguard Policies, Laws, Regulations (PLRs) Addressing and respecting the safeguards through the implementation of PLRs Considering the specific potential REDD+ risks and benefits in the country May already exist or need to be created Depends on the country-defined objectives Legal framework may not be required E.g., national-level guidelines to promote/support a safeguard as opposed to a policy/law
Safeguard Information Systems (SIS) approach for collecting and providing information on how REDD+ safeguards are being addressed and respected throughout REDD+ implementation Likely components: Indicators Methodologies for collection of information (e.g., household surveys, participatory monitoring of biodiversity) Framework for provision of information Should build on existing systems to the extent possible
Key features of national approaches to safeguards Developing standards, policies, etc. for promoting and supporting safeguards Conducting preliminary assessments of: the potential social and environmental risks of REDD+ existing safeguards in order to understand what additional safeguards are needed in responding to Cancun Holding multi-stakeholder consultations to assess the risks of REDD+ and to develop safeguards Defining the overall approach to implementing safeguards in a strategic plan or draft policy Establishing a governance system (e.g. a working group) to oversee work on safeguards
Development of a National approach to safeguards Not a fixed, linear path for design Will depend on what s in place and the objectives defined by that country Throughout the process, effective participation will be essential
Determining the Objectives Clearly define what the safeguards approach is supposed to do: interpreting what is contained in the UNFCCC decisions from the country perspective consideration of the specific social and environmental risks as well as benefits that might be associated with REDD+ in the country Responding to any other objectives identified by the country
Developing Safeguard PLRs Gap analysis of existing country PLRs consider what, if any, PLRs need to be in place to achieve the objectives Determine the effectiveness of existing systems Existing tools can be helpful to assess gaps Safeguard policy framework Provides the basis for the country s response to UNFCCC and other requirements
Developing the SIS Ideally follows the objective setting and PLR gap analysis National assessment of existing information sources and systems for information-sharing Development of indicators Information/data methodologies and approaches that address: What data is to be collected (e.g. income data) Methodologies to be used (e.g. household surveys; participatory approaches, such as participatory biodiversity monitoring) Who collects the data Frequency of data collection The scale at which data is collected (e.g. at the country, local or project level)
UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards (1) Step UN-REDD tools Explanation of how the tools can contribute to the activity Detailed activities Objective setting Defining goals of the country safeguards approach SEPC Provides more detailed criteria that can be used to unpack the Cancun safeguards UN-REDD/FCPF Stakeholder Engagement Guidelines Provides guidance on how participation of stakeholders can be ensured in UN- REDD activities, including how to apply the principle of FPIC; could be used by countries in the development of REDD+ PLRs and adapted to national context if necessary UN-REDD FPIC Guidelines Provides a framework for applying the principle of FPIC at community and national levels; primarily designed for UN-REDD activities but could be adopted in REDD+ PLRs and adapted to national context
UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards (2) Step UN-REDD tools Explanation of how the tools contribute to the activity Provides a list of questions across a broad range of issues in order to assess existing PLRs Detailed activities BeRT Defining or developing safeguard policies, laws and regulations Gap analysis of existing PLRs PGA Provides governance data based on extensive stakeholder contributions, which serves as a basis for improvements in governance; can be used by governments in their planning and policy-making Provides a more detailed framework (compared to BeRT) for assessing corruption risks in REDD+ Draft Guidance on Conducting REDD+ Corruption Risk Assessment FPIC Guidelines Development of new PLRs (if necessary) Provides a framework for applying the principle of FPIC at community and national levels; primarily designed for UN-REDD activities but could be adopted in REDD+ PLRs and adapted to national context Provides guidance on how to assess and strengthen existing PLRs and institutional capacity to address REDD+ related grievances Guidelines on Strengthening/ Establishing National- Level Grievance Mechanisms Participatory Law Development (LEG- REDD+) Provides a participatory approach for formulating legal and policy reforms and drafting new PLRs in response to REDD+
UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards (3) Step UN-REDD tools Explanation of how the tools contribute to the activity Detailed activities PGAs SIS Indicators Provides an overall approach for developing governance indicators for REDD+ schemes through a participatory approach Provides a tool for designing robust and comprehensive sets of governance indicators Framework for assessing and monitoring forest governance Draft Guidelines for monitoring the impacts of REDD+ on biodiversity and ecosystem services Methodologies for collection of information Provides draft guidelines that could be used by government in establishing aspects of the SIS that are relevant to biodiversity Draft manual on the collection of forest governance data Provides a range of practical considerations, methods and available resources for collecting governance data