Modeling Natural Convection Cooling of a Vacuum Flask in COMSOL
This example demonstrates the modeling of natural convection cooling in a vacuum flask holding hot coffee using COMSOL. It compares two approaches to describe thermal dissipation, focusing on calculating the flask's cooling power over time. Results include temperature analysis, heat transfer coefficients, and fluid flow simulations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Natural Convection Cooling of a Vacuum Flask COMSOL
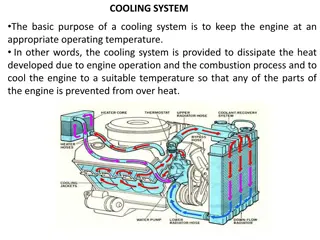
Introduction This example solves a pure conduction problem and a free-convection problem in which a vacuum flask holding hot coffee dissipates thermal energy The main interest is to calculate the flask s cooling power; that is, how much heat it loses per unit time The coffee has an initial temperature of 90 C and cools down over time The observation period is 10 h This tutorial compares two different approaches to model natural convection cooling: Using heat transfer coefficients to describe the thermal dissipation Modeling the convective flow of air outside the flask to describe the thermal dissipation
Model Definition Geometry 1
Model Definition Heat Transfer in Solids
Model Definition Geometry 2
Model Definition Heat Transfer in Solids and Fluids 2
Model Definition Laminar Flow
Results Temperature results for the model including the fluid flow
Results Isothermal domain temperature over time for both approaches
Results Heat transfer coefficient along the vertical flask walls. Blue line: modeling approach using the heat transfer coefficient library, green line: modeling approach including the fluid flow
Results Fluid velocity for air around the flask