Introduction to Aromatic Compounds and Benzene Nomenclature
Learn about aromatic compounds, their resonance in benzene, orbital structure, nomenclature for benzenes, and different types of substituents like monosubstituted and disubstituted benzenes. Explore the stability of aromatic compounds compared to aliphatic ones and understand the nomenclature for various aromatic hydrocarbons.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GPAT_Organic chemistry Dr. Zamir G Khan Assistant Professor H R Patel Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research Shirpur, Dist. Dhule, (M.S) 425405
Introduction to aromatic compounds Mr. Zamir G Khan Assistant Professor H R Patel Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research Shirpur, Dist. Dhule, (M.S) 425405
Learning Outcomes After completion of this topic student shall be able to Describe meaning of aromatic compounds Differentiate between aliphatic and aromatic compounds Describe resonance in benzene Explain orbital structure of benzene 09-10-2024 3
Aromaticity hydrocarbons aliphatic aromatic alkanes alkenes alkynes 09-10-2024 4
Aliphatic compounds: open-chain compounds and ring compounds that are chemically similar to open-chain compounds. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, dienes, alicyclics, etc. Aromatic compounds: unsaturated ring compounds that are far more stable than they should be and resist the addition reactions typical of unsaturated aliphatic compounds. Benzene and related compounds. 09-10-2024 5
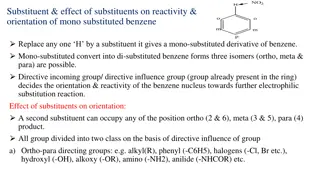
Nomenclature for benzene: monosubstituted benzenes: Special names: CH3 NH2 OH aniline toluene phenol SO3H CO2H benzoic acid benzenesulfonic acid 09-10-2024 6
others as substituted benzenes Cl NO2 Br bromobenzene nitrobenzene chlorobenzene Mercedes Benzene 09-10-2024 7
Disubsituted benzenes: ortho- meta- para- 1,2- 1,3- 1,4- 09-10-2024 8
NO2 CH3 Br Br Cl Br o-dibromobenzene m-chloronitrobenzene 3-chloro-1-nitrobenzene p-bromotoluene 1,2-dibromobenzene 4-bromotoluene If more than two groups on the ring, use numbers! NH2 Br Br Br Br Br Br 1,2,4-tribromobenzene 09-10-2024 2,4,6-tribromoaniline 9
Some other aromatic hydrocarbons: napthalene anthracene phenanthrene 09-10-2024 10
Resonance We can draw more than one classic structure that differ only in where the electrons are. The two structures are of the same energy, so resonance is important. I II The adequately represented by classic structures but must be thought of as a hybrid of the contributing structures. molecule cannot be Hybrid Additionally, the hybrid is more stable than any of the contributing structures (resonance stabilization energy). 11 09-10-2024
Resonance Can you draw resonating structure of acetate ion and carbonate ion? 09-10-2024 12
Orbital picture of benzene Structure of benzene is planar All carbon-carbon bond length similar Bond length is in between C-C single bond and C=C double bond Six carbons in benzene are SP2 So each carbon has three hybrid orbitals Two of which are used in formation of C-C sigma bond One in formation of C-H sigma bond 09-10-2024 13
Orbital picture of benzene 09-10-2024 14
Orbital picture of benzene Every carbon has p orbital with unpaired electron In all six p orbital overlap sideway Overlap sideways to form pi electron cloud above and below the plane of the ring Due to this overlap six electrons are shared equally and this is known as delocalization of electrons 09-10-2024 15
Orbital picture of benzene It is evident that double bonds are not localized between any two carbons There is continuous delocalization of pi electrons This delocalization causes all six Carbon-Carbon bond lengths to be same (1.39Ao) This value lies in between pure C-C bond length (1.54Ao) and C=C double bond (1.33Ao) 09-10-2024 16
Orbital picture of benzene C C single bonds 1.54 C = C double bonds 1.33 The bonds in benzene are all equal and 1.39 Bond angle 120o Bond length 1.39 SP2- SP2 overlap Bond angle 120o Bond length 1.08 09-10-2024 17
Outcomes achieved Summary Student has gained knowledge and shall be able to Describe meaning of aromatic compounds Differentiate between aliphatic and aromatic compounds Describe resonance in benzene Explain orbital structure of benzene 09-10-2024 18
Thank you Mr. Z. G. Khan, Assist. Professor, H R Patel Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research Shirpur, Dist Dhule (M.S) 425 405 Email: khanzamir.5588@gmail.com Webpage: https://khanzamir5588.wixsite.com/zamir YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCsQae74- x4t5iYK02iPRTxA?view_as=subscriber Whatsapp: +91 9890 044 661 09-10-2024 19