Substituent Effects on Benzene Reactivity and Orientation
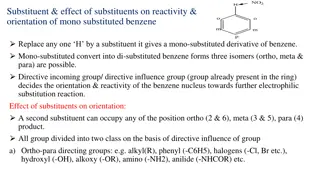
Substituents in benzene derivatives influence reactivity and orientation in electrophilic substitution reactions. They can be classified as ortho-para directing or meta directing based on their effect. Ortho-para directing groups increase electron density and activate the ring, while meta directing
7 views • 14 slides
Understanding Effects of Substituents on Benzene Reactivity
Substituents on an aromatic ring impact reactivity and substitution orientation. Activating groups make benzene more reactive, while deactivating groups reduce reactivity. Ortho-para and meta directors guide future substitutions to specific positions. Examples of activating and deactivating groups a
1 views • 10 slides
Understanding the Hammett Equation in Chemical Reactions
The Hammett equation explores how substituents influence the dissociation of benzoic acid, affecting its acidity. By quantifying this influence through a linear free energy relationship, the equation helps predict the impact of substituents on different processes. Through parameter definitions and m
0 views • 9 slides
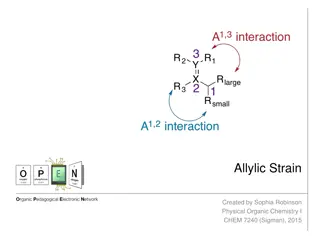
Understanding Allylic Strain in Organic Chemistry
Allylic strain refers to the unfavorable nonbonding repulsion caused by certain substituents in the allylic position of a molecule. This strain can impact reaction outcomes and diastereoselectivity, as seen in examples like Diels-Alder and hydroboration oxidation reactions. Proper understanding and
1 views • 9 slides
Understanding Hammett Parameters in Organic Chemistry
The Hammett Parameters analysis, particularly the Hammett Plot, is a valuable tool in studying the electronic effects of substituents on aromatic systems. This linear free-energy relationship approach aids in optimizing reaction conditions and probing reaction mechanisms. Applications of Hammett Par
0 views • 8 slides
Benzidine Rearrangement: Mechanism and Substituent Effects
Benzidine rearrangement involves the conversion of hydrazobenzenes into a mixture of benzidine and diphenylene under acidic conditions. Various substituents influence the product formation, with o-/m- positions favoring benzidines, and p- positions leading to different products based on the nature o
0 views • 15 slides
Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation: Mechanism and Migration Aptitude
The Baeyer-Villiger oxidation is a key organic reaction that transforms ketones into esters or cyclic ketones into lactones using peroxyacids. The mechanism involves protonation of the carbonyl group and migration of substituents. Migration aptitude in this reaction determines the regioselectivity,
0 views • 10 slides
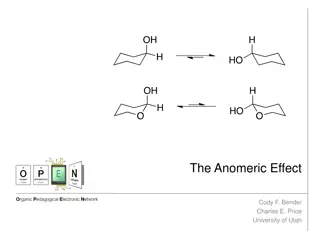
Unraveling the Anomeric Effect: Origins and Mechanisms
The anomeric effect, discovered in 1955, reveals the preference of certain substituents in cyclohexyl systems to occupy the axial position. This phenomenon was first observed by J.T. Edward, N.-J. Chu, and R.U. Lemieux, challenging existing conceptions. The effect is attributed to hyperconjugation a
0 views • 10 slides
Introduction to Aromatic Compounds and Benzene Nomenclature
Learn about aromatic compounds, their resonance in benzene, orbital structure, nomenclature for benzenes, and different types of substituents like monosubstituted and disubstituted benzenes. Explore the stability of aromatic compounds compared to aliphatic ones and understand the nomenclature for va
0 views • 19 slides